17.2 ATP synthesis
Synoptic links
plasma membranes chapter 5
ATP 3.11
ATP production
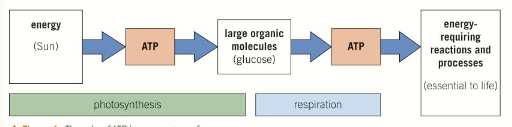
In photosynthesis, light provides the energy needed to build organic molecules like glucose. This energy is used to form chemical bonds in ATP, which are then broken to release energy needed to make bonds as glucose is formed.
In respiration, organic molecules such as glucose are broke down and the energy released in used to synthesis ATP. This ATP is then used to supply the energy needed to break bonds in the metabolic reactions of the cell.
 Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis
The ATP is synthesised primarily by a process called chemiosmosis. This involves the diffusion (facilitated) of protons from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a particularly permeable membrane (electrochemical gradient) The movement of the protons are they flow down their electrochemical gradient releases energy that is used in the attachment of an inorganic phosphate to ADP, forming ATP.
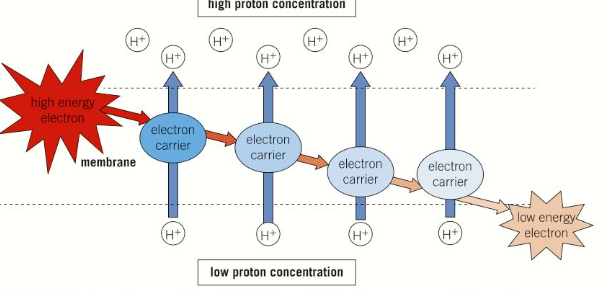
Chemiosmosis depends on the creation of a proton concentration gradient, the energy to do comes from high-energy electrons (excited electrons)
Excited electrons - when they are raised to higher energy levels
electrons present in pigment molecules are excited by absorbing light from the Sun
high energy electrons are released when chemical bonds are broken in respiratory substrate molecules.
The excited electrons pass into an electron transport chain and are used to generate a proton gradient.
Electron transport chain
As electron transport chain is made up of a series of electron carriers, each with a progressively lower energy levels. As high energy electrons move from one carrier to another, energy is released, This is used to pump protons across a membrane, creating a concentration difference across the membrane and therefore a proton gradient. The proton gradient is maintained as a result of the impermeability of the membrane to hydrogen ions.
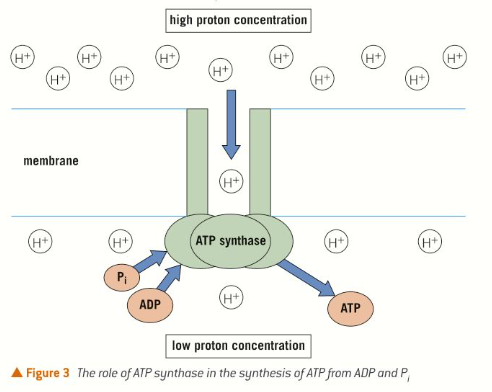
 The only way that protons can move back through the membrane down their concentration gradient is through hydrophilic membrane channels linked to enzyme ATP synthase which catalyses the formation of ATP. The flow of protons through these channels provides the energy used to synthesis ATP (from ADP and Pi)
The only way that protons can move back through the membrane down their concentration gradient is through hydrophilic membrane channels linked to enzyme ATP synthase which catalyses the formation of ATP. The flow of protons through these channels provides the energy used to synthesis ATP (from ADP and Pi)
 In photosynthesis, ATP is used to synthesis glucose and other organic molecules. The ATP produced in respiration provides the energy needed by metabolic processes and reactions essential to life.
In photosynthesis, ATP is used to synthesis glucose and other organic molecules. The ATP produced in respiration provides the energy needed by metabolic processes and reactions essential to life.
The process of oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation are also vital in chemiosmosis.