The Truth: Scientific Method
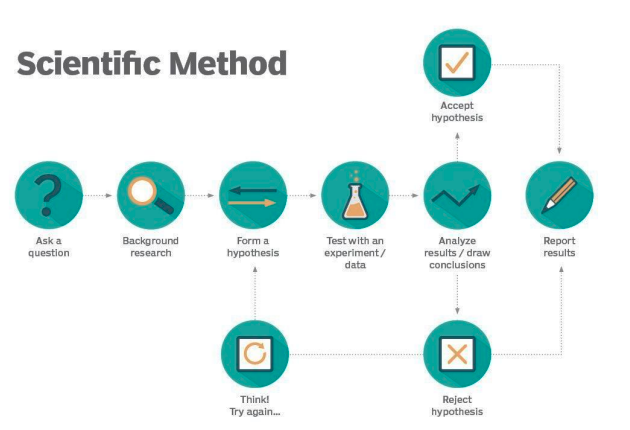
The scientific method is a systematic approach to investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge, typically involving observation, forming a hypothesis, experimentation, and analysis to draw conclusions. The three fundamental tenets of the Scientific method are falsifiability, testability, and replicability, which together represent the verification process.
Initial Question:
The scientific process begins with a question based on observations. This question should be specific and testable. For example, "Does exposure to sunlight improve plant growth?"Background Research:
Before conducting an experiment, scientists review existing literature, studies, and theories related to the question. This helps refine the hypothesis and ensures the research is built upon prior knowledge. For example, one might research how photosynthesis works and how different wavelengths of light affect plants.Hypothesis:
A hypothesis is a testable statement that predicts the outcome of an experiment.Testing:
The experiment is designed to test the hypothesis. It involves the following components:Participants:
In human research, this refers to the individuals involved. In a plant study, participants would be different plant species or groups of plants.Data Collection:
Scientists collect data by measuring relevant variables. In our plant example, this might include measuring plant height, leaf size, or the number of leaves over time.
Analysis:
The collected data is analyzed using statistical methods to determine patterns or significant differences. Graphs, charts, and statistical tests help interpret the results. If plants in more sunlight grew taller on average than those in the shade, this would support the hypothesis.Conclusion:
Scientists summarize their findings and determine whether they confirm or revise the hypothesis. If the data supports the hypothesis, the conclusion states that increased sunlight positively affects plant growth. If not, the hypothesis may need revision.Communication:
The final step is presenting the results to others through scientific journals, presentations, or reports. This allows for peer review, replication of experiments, and further advancements in the field.