Sociological Perspective on Education
- Why study the institution of Education?
- Today there are no clear pathways to adulthood that begin without education, and obtaining a basic education is considered a universal right
- We require every child in the country to get exposed to education
- There are inequities between the school, but public education is available regardless
- Public education system was initially started to get children together and keep them from causing trouble when parents aren’t home
- What are the major functions of schooling?
- From the structural functionalist perspective, all institutions in the country provide specific purposes
- When you do something to the purposes, the institutions will have trouble
- Socialization
- We get an understanding of time management, learn about delayed gratification, learn about social skills that are applicable in later life
- Schools in low SES areas, children are taught more routine/rote behaviors
- Higher SES areas have more seminar classes
- As a result children from lower SES will get jobs where the follow what theory are told, whereas children from higher SES get management positions
- Social Integration/Value Transmission
- You learn to get along with people who don’t already love you
- You have to learn how to do things in ways that would get people to like you
- Cultural Innovation & Dissemination
- Meet people who are different from us
- Have been a center of racial and ethnic integration
- Research done at colleges have been disseminated through society
- Access to resources and who gets resources
- Credentialization
- Schools are responsible for saying who is able to do things in the real world
- What are the latent functions of schools?
- Activities for young people
- Marriage markets?
- Research demonstrates that by spending the years between 18-22 in a particular environment, you are more likely to meet someone who is like you, and hence marry them
- As you pursue higher education, you have a higher chance of meeting someone you will marry
- Hidden Curriculum
- Thinking about our discussions of social location, what else do schools teach?
- Schools teach differently to students in different SES
- They teach us how to be obedient and competent
- Schools share remarkable similarity to work situations
- Boss = teacher who pays you with grades
- Work hours, and consequences if not on time
- Performance evaluations = parent teacher conferences
- School boards hold vast majority of power, but are run by people who have political desires and not necessarily degrees in education
- Control what's written in the textbooks and which books can be distributed in the school
- Politically driven
- The Great Equalizer?
- As long as we provide someone with education ,they can solve everything
- CAP
- What inequalities exist in school funding?
- Not all schools are funded equally
- Arlington spent $18K per student per year, Utah spent $5K per student per year
- It doesn’t necessarily matter if you’re spending the same money on students (eg: Youngstown)
- Funding based on property taxes
- People living in better neighborhoods receive better education
- If we equalize funding for schools, will we equalize chances?
- Youngstown, OH (not great schools) spent $15K per student, and was 40% above national average and only half the students graduated
- Kids living in unsafe environments can’t just go to school and learn
- Parents don’t have time to help with homework
- Need to look at whole picture
- Resources provided within school had negligible impact on the student when compared to home situations
- The 1966 Coleman Report showed differences in achievement among schools were explained by two primary factors, family background and peers—NOT RESOURCES
- Inequality in the Classroom
- Tracking: splits students into groups based on ability
- Higher class white students are overrepresented in the highest tracks
- Regardless of score on the test, white, higher SES parents don’t accept lower placement, but lower SES parents do
- Higher SES parents call the school and move the child up
- Tracking
- Is widespread, but often subtle, in the U.S.
- Creates instructional, social, and institutional differences in learning experiences
- Influences student self-esteem and expectations about academic performance
- Because you're spending your whole day with people who are actually smart
- Limits teachers’ perceptions of what grades are appropriate for students in different tracks
- Gap between what the teachers think the child is capable of and how they actually perform, hence affecting grade
- The Pygmalion effect, or self-fulfilling prophecy, is the process that occurs when behavior is modified to meet pre-existing expectations.
- People in the higher level class are pressured to meet their peers’ results so they work harder
- People in the lower level class have no motivation to try as hard
- If teacher thinks you’re a great student and you can get it, they’ll keep working with you till you understand
- Young’s study put a group of low achieving students in a class with high achieving students
- The low achieving students did better, because peer influence matters
- Labeling
- Lareau (2003) suggests that higher income parents are more likely to defend their children from negative labels, while lower income parents are more likely to accept the negative labels put upon their children by teachers and administrators
- Idea of labeling theory
- We are aware of the labels placed on us
- Affects how we see ourselves and how we behave
- You know the rich kids, the smart kids
- Label people and act accordingly
- Struggling to meet standards
- More than 1/3 of all students and 1/2 of students in urban school districts fail to master the basic in reading, math, and science on the National Assessment of Educational Progress exam
- Makes them reduce what it takes to graduate from high school
- Dropout Zones
- 2009 Graduation Rates by City:
- Minneapolis 45%
- Atlanta 44%
- Los Angeles 44%
- Baltimore 42%
- Milwaukee 41%
- Detroit 48%
- Higher Education
- Still– Education levels are rising
- In 1910, less than 3 percent of men and women over age 25 had a college degree.
- In 2016, 31 percent of men and women over age 25 had a college degree.
- Rise in Educational Attainment
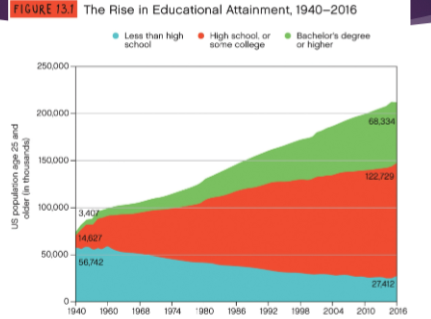
- Increase in bachelors decrease and decrease in people that have less than a high school degree
- Higher Education Issues
- Faculty research is emphasized
- But, Faculty teaching is not rewarded
- Bayh Dole act made it so that the university can make money off of patents
- Makes research more financially driven
- If u get a million dollar grant to conduct research, the researcher gets about 450K, and the rest goes to the university
- Infrastructure of the university is supported by researcher
- Hence the researchers are more supported than the teachers
- Told that teacher evaluations were positive, meaning that she wasn’t spending enough time on research
- Teaching faculty paid less salary than researchers
- Students aren’t learning much
- Because all they have to do is show up
- Study looked at CLA test which measures skills in critical thinking, reading and writing
- There was no change in test score between beginning of freshman and junior year
- Students aren’t studying much
- Cheating is rampant
- Especially during COVID
- 1963-1993, cheating doubled
- 26% admitted to cheating in college compared to well over 50% in 1993
- Full time college students spent 27 hours a week studying in 2016
- Across all demographic groups
- Students aren’t Graduating
- Only 34% of students finish a Bachelor’s degree in 4 years
- Only 64% graduated in 6 years
- Students have excessive student loans and no hamsters degree to propel their learning further
- Interest adds up as they learn
- Students going into debt before they even get the degree
- Students aren’t doing much homework
- Homework is reduced
- Students regularly had to write papers 20 pages or longer
- Now 83% of freshman say they've never done this
- Because it takes long to grade and the teachers don’t get paid more to do this grading
- Because research>>>>>teaching
- But despite all this, grades are still higher than ever
- **
 **
**- Grade inflation
- Average GPA went from a 3.0 in 1983 to a 3.4 in 2013
- Get better grades for doing less
- Students have high expectations
- Despite less work
- When surveyed about dreams and hopes, a lot of kids have no clear plans as to how they're going to achieve their dream, but they have high dreams
- Kids don’t understand what goes into achieving high levels of success
- 46% of high school students thought that they could make dreams come true without working
- 81% of school students want to go to graduate school
- 39% want graduate or doctorate degree
- Only 66% graduate, so 89% will not get a doctorate
- College is Expensive
- Student Loans are extensive
- Students are Consumers of college
- Why do we get College Degrees?
- Job Prospects
- Pay ratio doubled between 1977 & 2007
- Impediments to Higher Education
- Cost
- Admissions Standards
- Course enrollment
- College Mismatch
- Average Estimated College Budgets
- Who’s going to college?
- In Fall, 2016 20.5 million students attended American colleges and universities
- 11.7 million females
- 8.8 million males
- Between 2000 & 2015:
- Total increase of about 5.2 million students
- percentage of Black college students 11.7 to 14.5 %
- percentage of Hispanic students 9.9 to 16.5 %
- About 30% of today’s young people will earn a Bachelor’s Degree
- In 2009, fewer than 10% of students in the bottom income quartile (less than $33,000) received a bachelor's degree

- Who’s going to college?
- Among high school students:
- 70% aspire to get a degree
- 50% start a degree
- 30% finish a degree
- Does your college selection matter?
- SATs as Meritocracy?
- SAT score accurately predicts:
- freshman year GPA
- likelihood of graduation
- Student’s chance of obtaining advanced degree
- BUT…
- So do high school records
- It only works for white kids
- SATs may not be the predictors after all, but rather are correlated with race and SES that are good predictors of Success
- Returning to Affirmative Action
- Affirmative action is a set of policies that grant preferential treatment to a number of particular subgroups
- Women
- Racial minorities
- Small probability Events
- Abolishing affirmative action would increase a white student’s chance of acceptance by .05%
- It would decrease black and Hispanic acceptance rates by ½ to 2/3
- Does affirmative action allow underprepared students admission?
- Affirmative action: Reverse Racism?
- "Assertions of reverse racism often fail to consider the historically specific ways in which racial hierarchies and inequalities were institutionalized.“--Miri Song
- 2007-08 data (population 62%white):
- White students were 40% more likely to win private scholarships than minority students.
- White students received more than 76 % of all institutional merit-based scholarships
- White students received 69.3 % of private scholarships recipients.
- The way we test is culturally biased in terms of both SATs and high school GPAs
- Take home message
- Schools often reproduce disadvantage that already exist
- While schools are powerful institutions, they may not be the silver bullet that we wish.
**