U1L3 Intramolecular Bonds
Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are formed between atoms by interaction of their respective electrons
Three types of intermolecular bonds (bond that hold atoms in a molecule together
Ionic bonds
Covalent bonds
Polar covalent bonds
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bond: occurs when there is a transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another
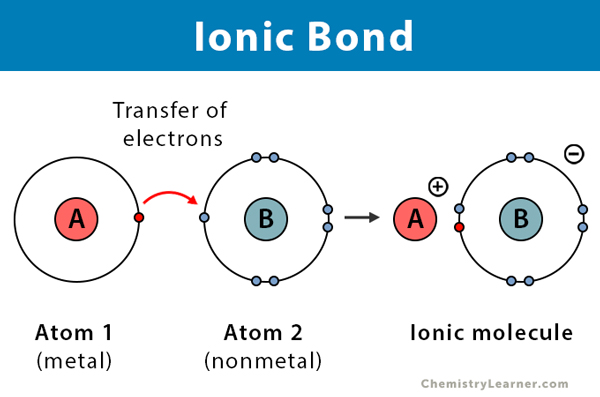
Transfer leads to the formation of a cation and anion
Resulting electrostatic attraction between these two oppositely charged ions is an ionic bond
Losing=positive, gaining=negative
Opposite charges attract
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bond: involves sharing of electrons between atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration (stable octet)
Ex. 2 hydrogen atoms combine to form a molecule of hydrogen gas
Electrons always attempt to move as far away from one another as possible creating different molecular shapes (VSEPR Theory)
Like charges repel
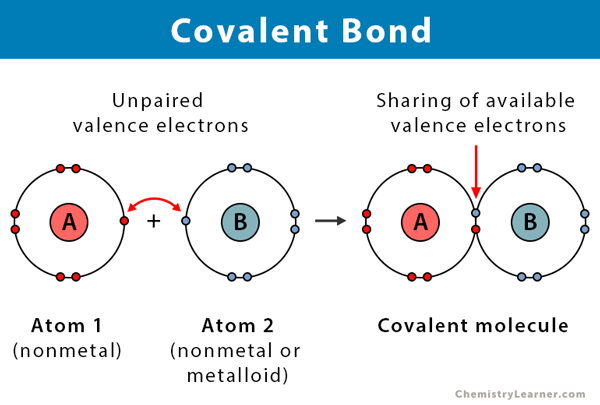
When there is an equal sharing of electrons, the bond is purely covalent
Same electronegativity and electron affinity, so same strength
Polar Covalent Bonds
Polar covalent bond - occurs when there is an unequal sharing of electrons within a molecule
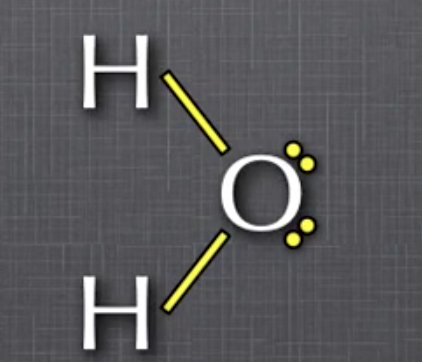
Ex. in water, polar bonds are formed because O has a greater attraction for shared electrons (electronegative) than H
EN O = 3.5, EN H = 2.1
ΔEN = 3.5 - 2.1 = 1.4
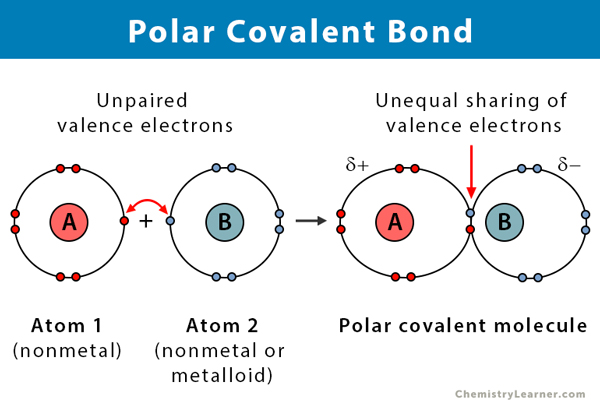
Polar bonds doesn’t always mean polar molecules
Determining Bond Type
Type of bond that forms is determined by the difference in electronegativity of the 2 atoms involved
Bond | EN Difference | Example |
Covalent | < 0.5 | H-H (ΔEN = 2.1 - 2.1 =0) |
Polar Covalent | 0.5 - 1.7 | O-H (ΔEN = 3.5 - 2.1 = 1.4) |
Ionic | > 1.7 | Na-Cl (ΔEN = 3.0 - 0.9 = 2.1) |
Determining Molecular Polarity
Draw a Lewis Dot Diagram for each atom

Determine structural formula of molecule
Does molecule have a positive end and a negative end?

Symmetrical = non-polar
Asymmetrical = polar
Polar molecules are good solvents because they can disrupt ionic bonds
Polar Molecules are Good Solvents
When salt and water are mixed, the negative end of water molecules are attracted to Na+, while the positive end of water molecules are attracted to Cl-
Water molecules form “spheres of hydration” around ions, causing the salt to dissolve