KKDP: 6 means by which aus constitution acts as a check on parliament
Role of the high court in protecting the principle of a rep gov
facts of the Roach Case
cmwlth passed a law (electoral & refferendum amendment act 2006)
changed the law that allowed prisoners serving 3 years and under to vote,
new law dissallowed all prisoners the right to vote
sec 7 & 24 of the constitution
Section 7
is the senate should be composed of senators for each state, & chosen directly before by the people
Section 24
is the house of reps should be composed of members chosen directly by the ppl
Abilty of the high court to protect the principle of a rep gov
Strengths
judges are independant of the gov
judges are appointed, not elected
judges are experienced & experts in constitutional law
Weaknesses
high court cannot change the actual words of the constitution
The decision of the high court may depend on the composition of teh justice
judges are reactive & have to wait until a case is brought to them
judges can only rule on teh facts of teh case before them
Sep of legislative, executive and judicial powers
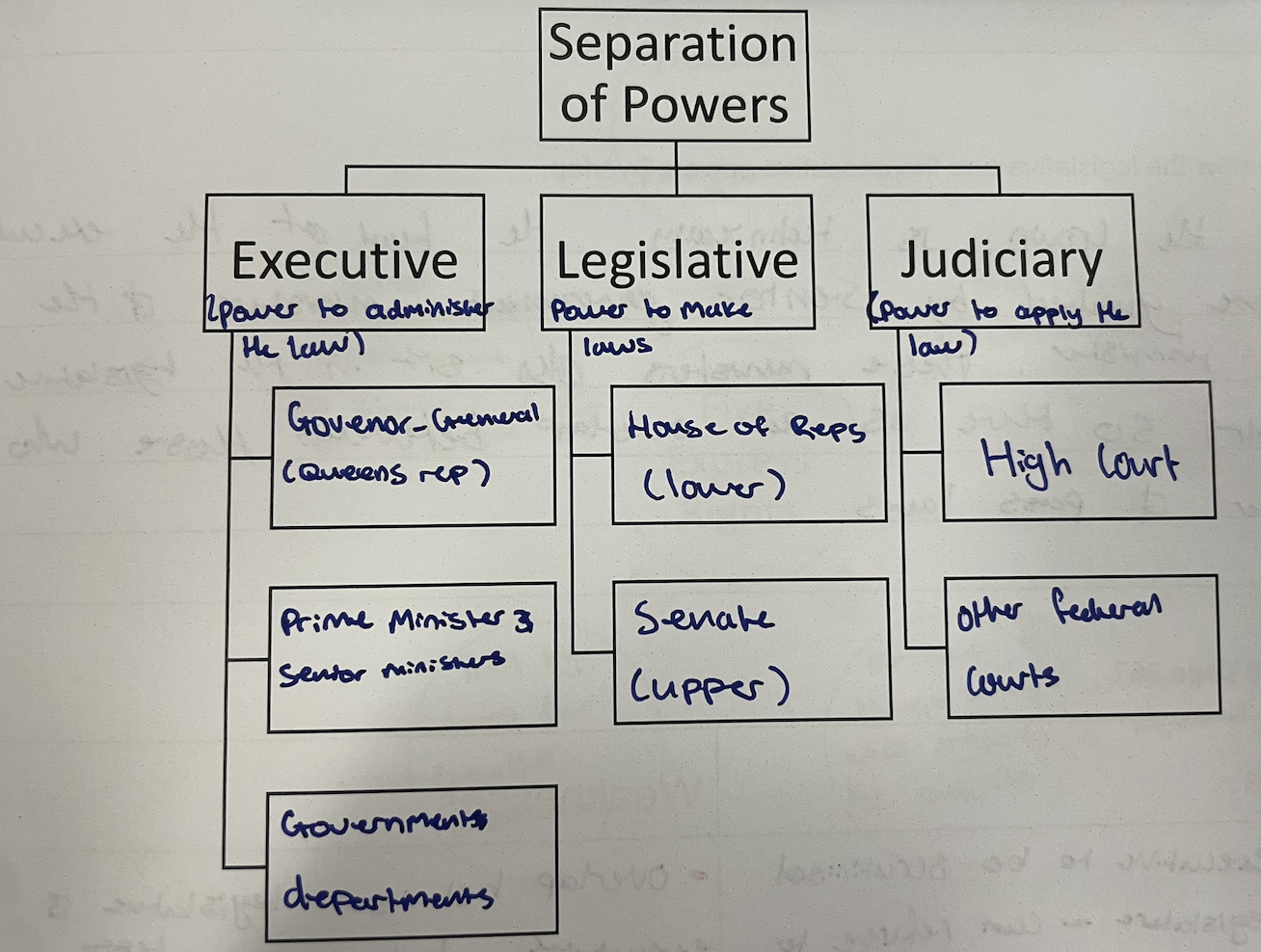
types of powers
Executive
power to administer the law & manage the business of government. (put laws into action)
Legislative
power to make law (parliament)
Judicary
Power to enforce law, settle disputes & interpret the law
Reasons for the sep of powers
no single arm of gov has complete control
decisions made by one arm will be checked & reviewed which reduces corruption
sections 61 & 67 of the constitution
Section 61
states that the executivepower of the cmwlth is vested in teh queen and can be excersised by the gov gen, extends to teh execution of teh constitution
Section 67
The Governor-General can hire and fire public servants (like government department staff), but must follow the rules set by the Parliament.
Definition of the term ‘seperation of powers’ + the reasons for it
Definition
A division of powers of the government into 3 branches, to prevent the abuse of power and ensure checks and balances
Reasons for the sep of powers
no single arm of gov has complete control
decisions made by one arm will be checked & reviewed which reduces corruption
how legislative and executive powers overlap
although crown is technically the head of the executive they are guided by senior government ministers
these ministers also sit in the legislative parliament so there is an overlap between those who administer and those who pass laws
Strengths and weaknesses of the seperation of powers to act as a check on parliament
Strengths
allows exec to be scrutinised by the legislature, which can refuse to pass legislation sought by the executive
judicary is independant of the other two arms. important in cases where cmwlth is a party
power is entrenched in teh constitution (can only be changed via refferendum)
Weaknesses
overlap bet legislative and executive which means less scrutiny
judges are appointed by the executive
states are not bound by this seperation
The express protection rights
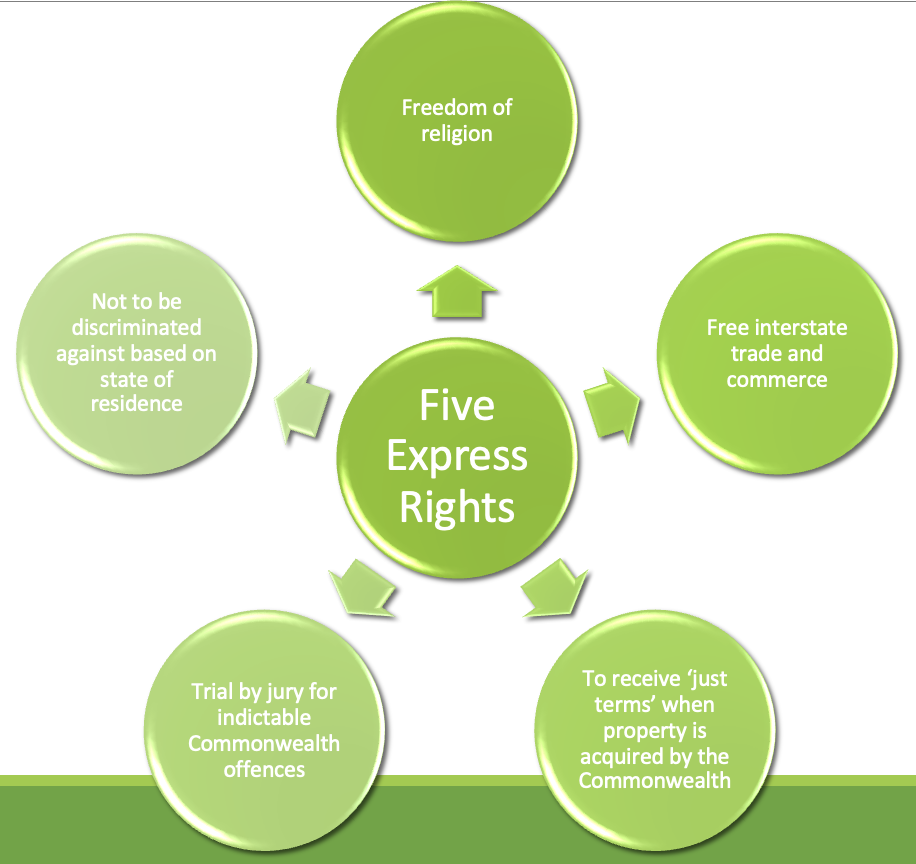
5 express rights/ def
Definition: Rights of the Australian ppl that are “specifically stated” in the constitution
freedom of religion
not to be discriminated against based on state of residence
trial by jury for indictable cmwlth offences
to recieve ‘just terms’ when property is acquired by the cmwlth
free intersate trade and commerce
Strengths and weaknesses of express rights to act as a check on parliament
Strengths
Acts as a check on parliament (cannot pass laws that conflict w express rights)
high court fully enforces these rights
fully protected & cannot be changed unless through a referendum
high court is ussually quick in declaring laws unconstutional
Weaknesses
referendum is teh only way to add new rights. they often fail
very expensive to go to high
there are only 5 & they protect rights may believe are outdated
cmwlth can pass laws that conflict w express rights & it will be valid until party challenges it