3. Viral Infection & Immunomodulation [HIV & AIDS]
Learning Objectives
Define acquired immunodeficiency
Discuss the effect of HIV on the immune system
Explain possible diagnostic tests and relate to HIV Structure
Discuss treatment of HIV infection, including mode of action and relate to the life cycle of HIV
What is acquired deficiency?
Full or partial impairment of the immune system
What is AIDS?
applies to the most advanced stages of an HIV infection
What is HIV?
The virus that targets cells of the immune
Retrovirus
envelopes RNA viruses
uses reverse transcriptase in the conversion of viral RNA to DNA which is then incorporated into the host genome
2 types
HIV-1 more aggressive global epidemic
HIV-2 (West Afrca)
What is HIV Structure
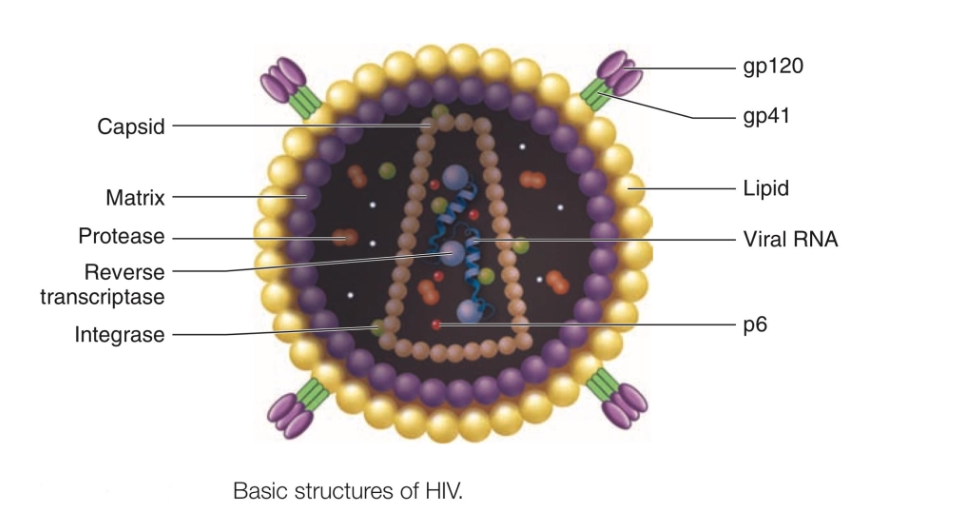
Capsid | Protein shell Made up of capsid proteins, p . Contains 2 strands of RNA (viral genome) |
Envelope | Outer surface (phospholipid bilayer derived from the membrane of the host cell.) |
Enzymes | Proteins that carry out steps in the HIV life cycle |
Glycoproteins | Protein “spikes” embedded in envelope. G are anchored to the virus via interactions with the transmembrane protein g |
Matrix Shell | A matrix shell comprising approximately 2000 copies of the matrix protein (MA, p ) lines the inner surface of the viral membrane |
Protease | cuts up precursor proteins into proteins |
Reverse transcriptase | Converts RNA into DNA |
Integrase | inserts viral DNA into the host chromosomal DNA |
P6 | Multiple roles. Important for the formation of infectious viruses |
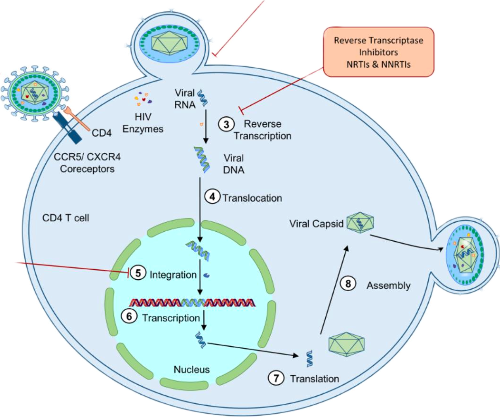
What are 7 stages of HIV lifecycle
All Frogs Ride In Rainy Autumn Breezes.
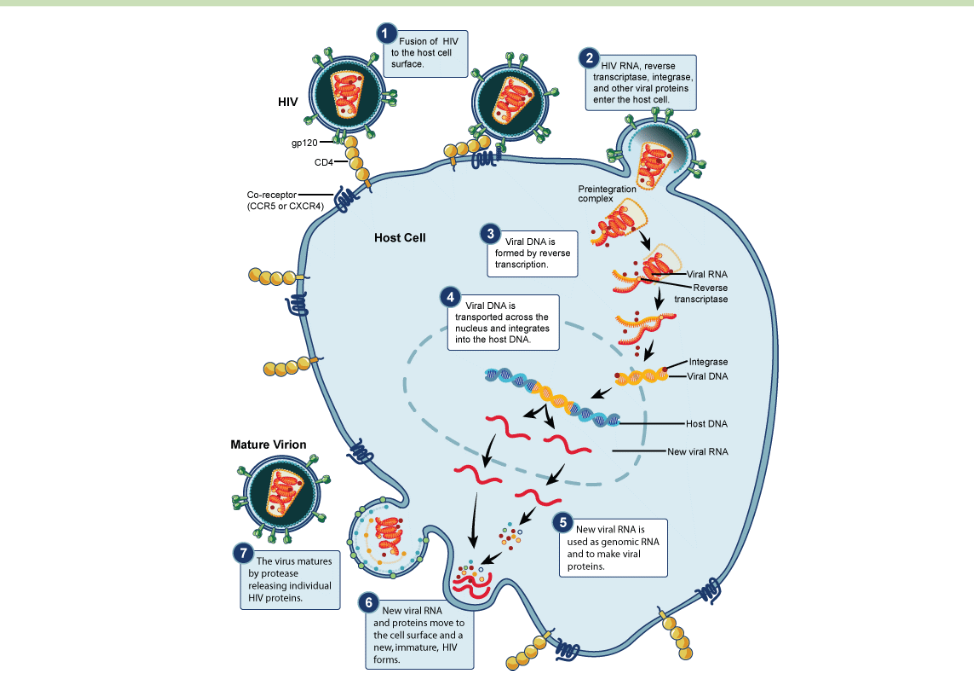
Attachment
HIV binds to CD4+ receptors on helper T cell lymphocyte
Co-receptor CXCR4 or CCR5 facilitates fusion
Fusion
Membrane fusion occurs as the hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions interact with each other
The core of the virion is released into the host cell cytoplasm and the two RNA strands are released
Reverse Transcription
Viral cDNA synthesis
Reverse transcriptase converts viral RNA to cDNA
Integration
cDNA is transported to the nucleus by integrase
Integration is probably a random event but relies upon transcriptionally active sites
Replication
Host cell produces new viral RNA
New viral RNA used as genomic DNA
New viral proteins synthesised
Assembly
New viral RNA and proteins move to the cell surface
Budding
Host cell membrane buds off releasing mature virion from cell
The new virus leaves the host cell to infect other cells
To help you memorize the sequence "A F R I R A B," we can create a mnemonic sentence where each word starts with the corresponding letter. Here’s a suggestion:
This sentence can help you recall the letters in the sequence:
All
Frogs
Ride
In
Rainy
Autumn
Breezes
What are the HIV effects on immune system
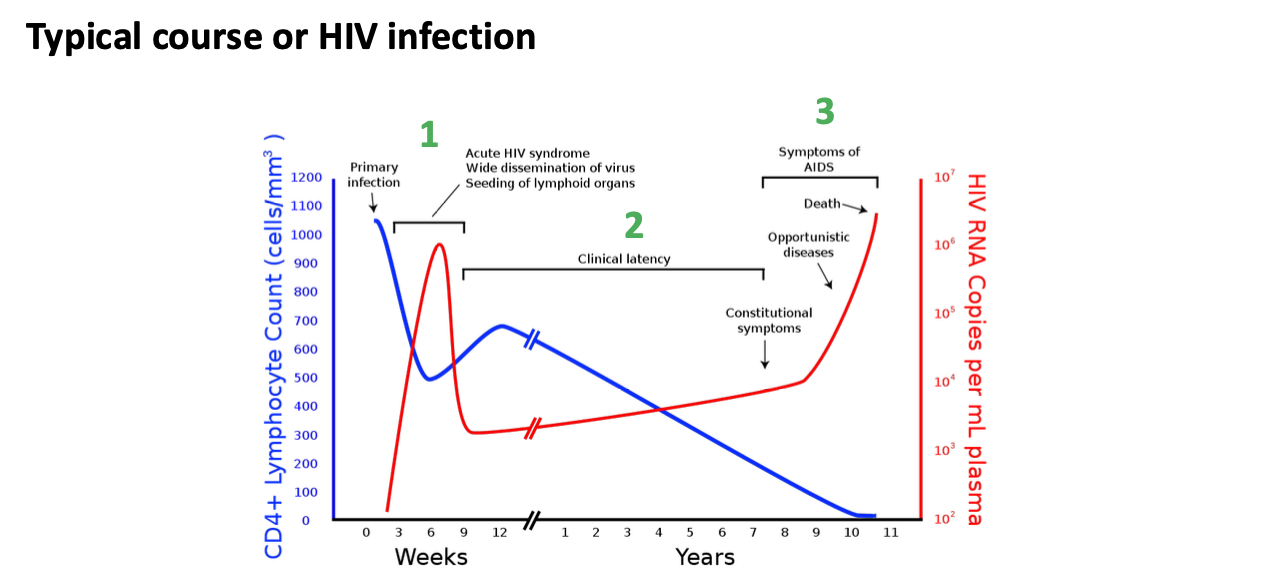
What are the HIV diagnostic factors
Sore throat
Fever
Enlarged lymph glands
Rash
Muscle aches
Sweating during the night
Twitching
Fatigue
Mouth ulcers
What tests are done to determine HIV diagnosis?
Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
4th generation = HIV Antigen/Antibody Combination Test
detects HIV in the blood by identifying either the:
HIV-1 p24 (coffin shaped capsid in virus) antigen or HIV antibodies.
Western Blot
Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
CD4+ Count - Flow cytometry
HIV Nucelic acid test - NATS
What are the current treatments for HIV now
Antiretroviral therapy (ART)
a combination of HIV medicines (a treatment regime) to be taken every day
ART recommended for all HIV infected patients
main goal is to reduce a person’s viral load to an undetectable level.
Shown to reduce disease progression
Decrease comorbid disease
Prevent transmission
how does it work?
blocking any part of the lifecycle will prevent stages of lifecycle to occur