Chapter 3 and 4
Chapter 3
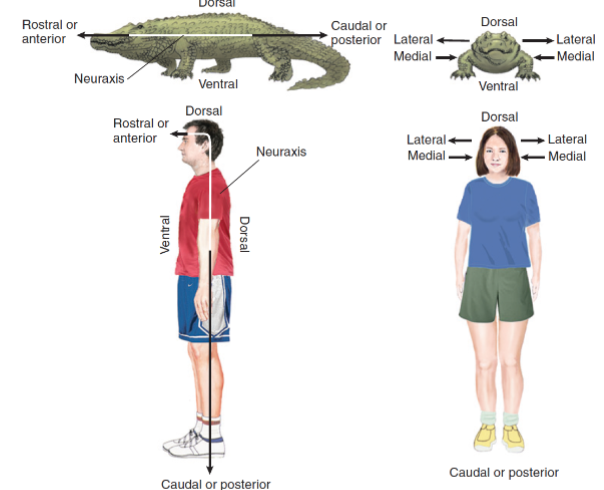
Directional Terms
Rostral/Anterior (same)
Located near or towards the head in central nervous system
toward the beak; with respect to the central nervous system in a direction along neuraxins towards the front of the face; toward side of body away from middle
Caudal/Posterior (same)
Located near or toward the tail in CNS
toward the tail; with respect to the CNS, in a direction along neuraxins away from front face
Dorsal
Toward the back; with respect to the CNS, in a direction perpendicular to neuraxins toward top of head or back
Ventral
relating to or situated on or close to the abdomen
relating to or situated on or close to the anterior aspect of the human body or the lower surface of the body of an animal
Medial
Toward middle of the body, away from side
Lateral
Of, relating to, or situated at or on the side
Ipsilateral
refers to structures on same side of body
(ipsi means same)
Contralateral
refers to structures on opposite sides of body
Protections of the CNS
Skull and vertebral column
vertebrae —> Spinal Cord is protected by Segmented Vertebra
cervical
Cervical Vertebra —> back of the neck
thoracic
Thoracic Vertebra —> chest region
lumbar
Lumbar —> lower back
sacral
coccyx —> tailbone
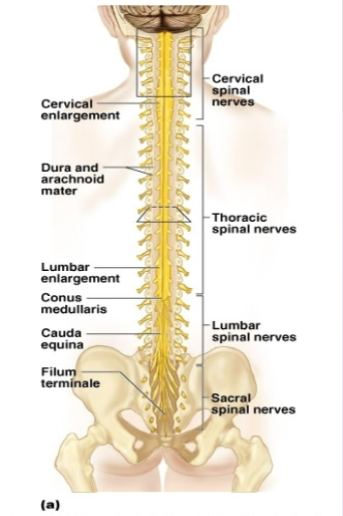
Spinal Cord —> the cord of nervous tissue that extends from the brain lengthwise along the back in the spinal canal, giving off pairs of spinal nerves, carrying impulse to and from the brain, and serving as a center for initiating and coordinating many reflex acts.
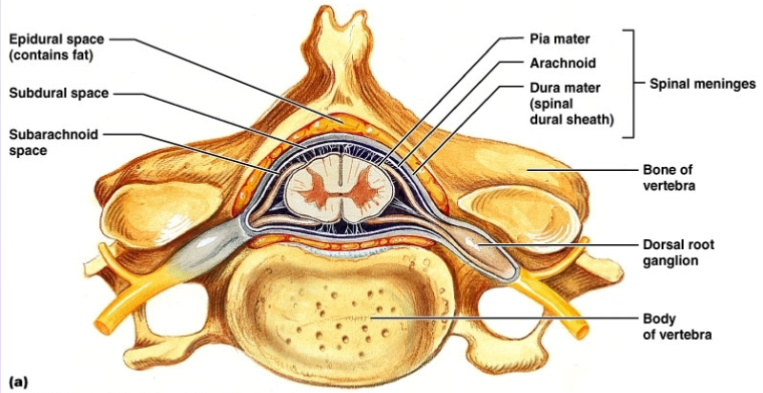
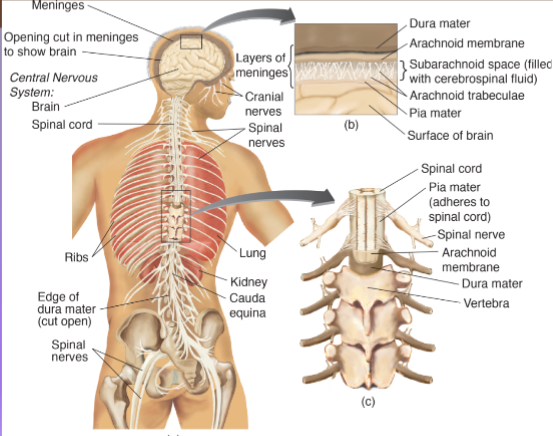
Meninges (FYI) —→ three layers of tissue that encase the CNS
Pia matter —> inner most layer of the meninges that clings to surface of brain; thin and delicate
Arachnoid Membrane —> middle layer, in between pia matter and dura matter
Dura Matter —> outermost of the meninges; tough and flexible exterior
Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF)
cushions against a blow
brain floating in water, so weighs less
Clear Fluid, similar to blood plasma, that fills ventricular system of brain and subarachnoid space surrounding brain and spinal cord
Division of Brain
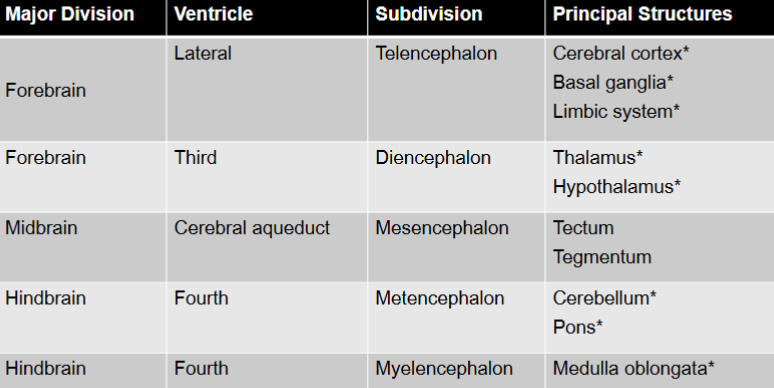
Forebrain
cerebral cortex —> outermost layer of gray matter of cerebral hemispheres
Primary visual cortex
region of posterior occipital lobe
primary input from visual system
Primary auditory cortex
region of superior temporal lobe
primary input from auditory system
Lateral Fissure
Fissure that separates temporal lobe from overlying frontal and parietal lobes
Central Sulcus
Sulcus that separates frontal lobe from parietal lobe
sulci —> small grooves
Fissures —> large grooves
gyri (fyi) —> bulges
Gray Matter —> consist of neuronal cells bodies, neutrophil, glial cells, synapses, and capillaries.
primarily responsible for processing and interpreting information int he brain.
White Matter —> composed of myelinated axons which are extensions of nerve cells.
located deeper in the tissues of the brain, spinal cod, and beneath the grey matter.
Crucial for coordinating communication between parts of the brain
Lobes and Association Areas:
Frontal
prefrontal cortex —> planning, strategies, critical thinking
impulse control, especially for regulating emotions
personality; sense of self
motor cortex —> intentional, voluntary movement
anterior portion of cerebral cortex, rostral to parietal lobe and dorsal to temporal lobe;
Parietal
process touch, temperature, pressures
region of cerebral cortex caudal to frontal lobe and dorsal to temporal
Occipital
processes visual input
region of cerebral cortex caudal to parietal and temporal lobes
Temporal
processes auditory input
processes visual memories
region of cerebral cortex rostral to occipital lobe and ventral to parietal and frontal lobes
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
pituitary gland
basal ganglia
Limbic System
amygdala
Hippocampus
septum
formix
mammillary bodies
Midbrain
Superior Colliculi
Inferior Colliculi
Reticular Formation
Hindbrain:
Pons
Cerebellum
Medulla Oblongata
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain
spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Somatic
Autonomic
parasympathetic
sympathetic
Chapter 4
Principles of Psychopharmacology
drug effect
site of action
routes of administration
IV
IP
SC
Oral
Sublingual
Intrarectal
Inhalation
Topical
Intracerebral
IVC
Inactivation and Excretion
Inactivation:
Excretion:
Drug Effectiveness
Dose-response curve
therapeutic index
margin of safety
Effects of Repeated Administration
tolerance
sensitization
withdrawal
placebo effects
Sites of Drug Action
antagonists
Agonists
Neurotransmitters and Neuromodulators
Acetylcholine
dopamine
epinephrine/Norepinephrine
Serotonin
GABA
Endocannabinoids
Chapter 16
Terms
Addiction
Positive reinforcement
negative reinforcement
tolerance
withdrawal
Simulant drugs
cocaine
amphetamine
nicotine
Depressant drugs
alcohol
Cannabis THC