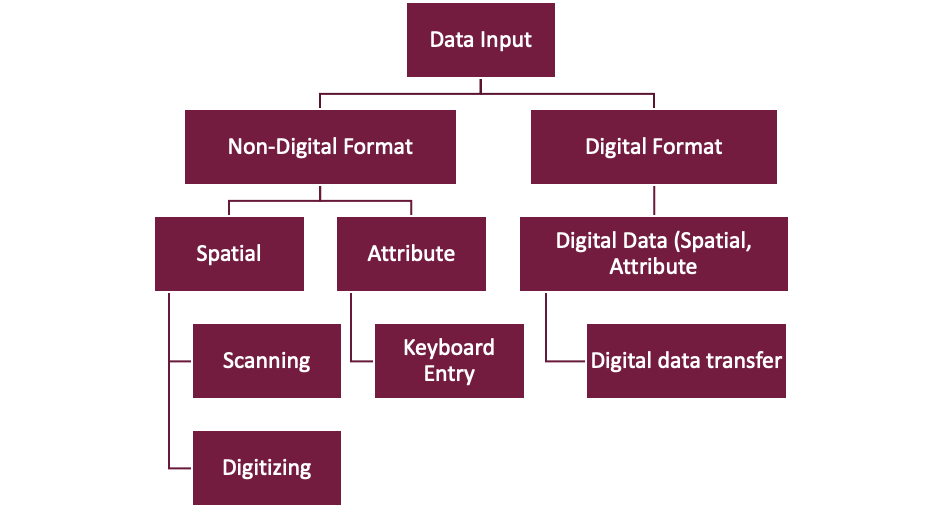
Data Input
Before inputting data, we have to ask ourselves some questions:
- Does this data contain the information that I need to answer my question?
- Is the data well documented, so that I understand what I am looking at?
- Is the data in a usable format, if not can I convert it?
- Can I link it to GIS?
- If multiple versions or similar dataset exist, which should I use?
A metadata record is an information file that captures the basic characteristics of geographic data or information resources, representing the who, what, when, where, why, and how of the geodata resource. Geospatial metadata records includes:
- Core library catalog elements such as title, abstract, and publication data
- Elements such as Geographic Extent and Projection Information
- Database elements such as attribute label definitions and attribute domain values
- Metadata standards are defined in USGS Standards or in Federal Geographic Data Committee (FDGC) Standard.
Data integration is the linking of information that you plan to used has been digitized to produce a geospatial database. When integrating data from different sources, we have to pay attention to the following:
Projections (all data should be in the same projected/coordinate system)
Georeference (satellite images, aerial photographs)
Generalization (method to reduce detail in GIS data to simplify it and reduce its storage – i.e. resampling, rescaling of vectors and raster)
Data conversion (raster to vector, vector to raster)