Humanities Exam Checklist
%%Unit 1: Biomes and Food Security%%
%%Textbook Chapters 2 and 3%%
- ^^8 Terrestrial biomes and their characteristics (plant and animal species, climate)^^
- Polar Biomes
- even cooler than tundra biomes
- includes the continent of Antarctica
- virtually no native species
- only 2 flowering species of plants exist
- the largest land animal is the wingless midge
- too cold, too dry, and too windy for flora and fauna to flourish
- Tundra Biomes
- circles north pole
- low temps, short growing seasons, little plant diversity
- tundra means treeless plain
- animals: arctic hare, polar bear
- plants: arctic moss, artic poppy
- Boreal Forest Biomes
- major life zone of vegetation
- covers 11% of the land mass
- cold climate
- animals: wood bison, moose
- plants: fir, pine
- Mountain Vegetation Biomes
- steep, sloping sides
- animal: big horn sheep, brown bear
- plants: pines, conifers
- tough, cold, windy, lots of sunlight
- Temperate Forest Biomes
- wet climate, fertile soil
- plants: maple trees, walnut trees
- animals: slugs, spiders
- Desert Biomes
- very little rainfall, clear skies, slow-growing plants
- animals: coyote, Gila monster
- plants: prickly pear, agaves
- Grassland Biomes
- large terrains of rolling grass, flowers, herbs, open and continuous fairly flat areas
- animals: bison, pronghorn
- plants: wild oats, foxtail
- have dry wet seasons, mostly warm, the air is dry
- Tropical forest Biomes
- hot, moist, rains all year long
- animals: capybara, jaguar
- plants: ferns, bamboo
^^Distribution of world biomes – use the PQE method to describe biome distribution^^ ^^IN WORKBOOK^^
^^Indigenous Land Management practices^^
Firestick farming
- aids in the creation of a landscape that sustains life
- controlled burns of low intensity that manage flora and fauna within a biome
- majority of lands are rotated through in patches to allow plants and animals to survive in those not being burned
- the timing of the fire was adjusted throughout the year according to the type of country being burned and the condition it was already in
- weather conditions = strictly considered
- neighbouring clans communicated and advised each other of fire activity
- burns were not to occur during the growing season of plants
Cultivation of grains
- The cultivation of yam daisies was widespread in Australia’s southeastern regions
- Aboriginal Australian soil management techniques such as aeration could sustain or increase the food supply
- The practice was disturbed by the arrival of white colonists
- Hard-hooved livestock being let out into pastures and grasslands where the yams led them to become hard to find because the livestock hardened the soil
- crops raised or grown under controlled settings
^^Food security definition and factors that are required to achieve food security^^
Food security:
- when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life
Factors include
- Availability, the supply of food within a community affecting the food security of individuals, households or entire populations
- Access, is a food that is retrieve able and ready to eat or in a location where it is easy for a child to reach. Has to be safe food as in the food has to be healthy and poison free
^^Global Patterns of food security^^ ^^ASK IF IT IS ENOUGH^^
- Ukraine used to be food secure but when the war started they became insecure because their farms were bombed or taken over by soldiers
- Ethiopia is food insecure because they rely heavily on rain for crops and food, since there is drought there right now, food security is at risk
- Ireland is food secure because they have a high-quality marine environment, has the highest proportion of grassland and they produce a lot of agricultural commodities
^^Threats to food security^^
Water Scarcity
- rainfall patterns are changing, diff amounts of water supply
- melting glaciers have acted as reservoirs and sources of water for millions
- high demand for water, population + economic growth
- agriculture uses 70% of freshwater from rivers, used for irrigation
Climate Change
0-1 degrees
- increased chance of extreme weather events
- flooding farmland
- small mountain glaciers melt, evaporation
- impacts on water supply
1-2 degrees
- lesser crop yields in developing regions
- decrease in cereal-growing productivity
2-4 degrees
- significant decrease in water availability (Mediterranean and South Africa)
- more extreme weather increased casualties
4 degrees
- failing crop yields
- global malnutrition
Threats from non-native plants, animals and insects
- desert locusts cause damage when conditions are right, cause frustration
- locusts cause crop loss + damage if not fully eaten
- increases poverty
- threatens development through impact
Competition for land
- converted into houses, gold mines, golf courses, etc for tourism and recreational purposes
- food security = threatened by corporate
- countries choosing tourist attractions over farmland as a reliable income
- cities growing = less farmland
- population increase, urban areas = 2% of land
farmers are pushed further out but the land is not suitable there, risk of food security
Use of land for fuel instead of food
- the greater production of biofuel needs more than just waste, needs crops
- crops being used for fuel makes food less accessible
Armed conflict
- developing countries are at the highest risk of food insecurity
- 75% of Africa’s countries are at a high or extreme risk of food insecurity
- brings extra threat to already critical
- government can deliberately keep food away from opposition fighters and locals who support the
- food security can cause more deaths than the conflict
- food + water = poisoned or damaged
- food shortages are common because they have an addition of other threats
- land mines are planted causing lasting danger
- disruption of food markets + food aid
- land for agriculture = destroyed
^^Use the PQE method to describe the spatial distribution of food insecurity^^ \n
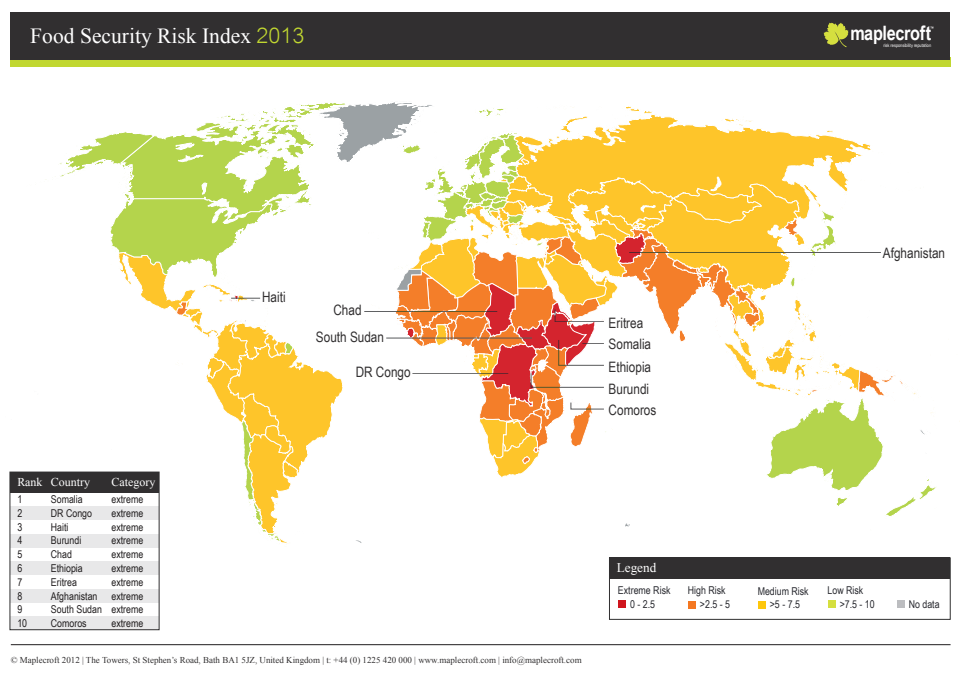
In the east of Africa, extreme risks of food security are noticeable but in Asia and South America, there is a medium risk of food security. The severity of food security circulates around the middle of the map and the risks lower as it gets farther away from the centre of the map. In the east of Africa, food security is at 2.5 or lower, in Asia and South America, the food security is at 5-7.5 and In Australia and North America have a low risk of food insecurity and it is about 7.5-10. The exception to this pattern is in the north and west of South America, which have a low risk of food insecurity at a 7.5-10.
%%Unit 2: Sustainable tourism & interconnections%%
%%Textbook chapter 4%%
^^Ways humans connect to place^^
Socially - religion, language, culture
Historically - war, family origin, colonialism
Economically - boom or crash, class systems
Environmentally - weather, climate growth, human impact
Politically - political climate
Technologically - infrastructure and access to it
^^Positive and negative impacts of tourism on places^^
Positive
- builds the local economy, creates jobs, boosts income
- interest in other cultures
Negative
- the commodification of local culture
- devalues important traditions
- tourists want to see local traditions and festivals
- the line between sacred traditions and other events can blur
^^Positive and negative impacts of global trade^^
Positive
- industries & economics expand
- employments increases
- global trade beings benefit
- consumers able to purchase products
- manufacturing industry (employment) contributes to alleviating poverty in LEDCs less (economically developed countries)
- Fairtrade foundations also help marginalised and rural communities (especially Pacific islands) to earn sustainable income & move out of the poverty cycle
Negative
- negative effects of social and environmental conditions
- for e.g in 2005, 59% of the world’s resources were bought and owned y 10% of the population
- creates huge disparities between the haves and have nots
- 2007 richest 1% owned more than 50% of the world’s wealth
- manufacturing LEDCs can have people working in unsafe conditions
- do not earn enough to come out of poverty
- cheap labour people in LEDCs earn below minimum wage
- child labour is common
^^Sustainable tourism – what it is and an example of it^^
Sustainable tourism - experiencing the natural world with the sole aim to learn how to protect, sustain and conserve the environment for future generations; ecotourism destinations need to prove they are protecting the environment, educating tourists and supporting local communities
Example
Kakadu National Park
- consists of different protected ecosystems that are all protected
- which includes wetlands, rock formations, indigenous rock art and a staggering array of birdlife and aquatic life
- activities include bushwalking, bird watching, swimming under waterfalls and many other nature-based activities
- the park is filled with wildlife and aboriginal culture
^^The concept of Interconnection with examples^^
Interconnection is what links two (or more) things together. Examples include the connections between countries. Australia and Indonesia are connected since Australians usually travel to Indonesia for tourism.
^^Impact of consumerism^^
The desire to own products that exceed our basic human needs.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| industries and economies expand, employment increases, operating phones does not use a lot of energy | negative effects on social + environmental conditions |
| global trade brings benefit | by 2040 it is predicted that tech will contribute to more than 14% of the world’s total carbon footprint |
| consumers are able to purchase products they want | replace tech too often |
| manufacturing industry (employment) contributes to alleviating poverty LEDCs | many people work in unsafe conditions and don’t even earn enough to lift out of poverty |
| working for big corporations = less wage |
==SHEEPT, geographers’ reasons for spatial pattern occurrence==
Socially - religion, language, culture
Historically - war, family origin, colonialism
Economically - boom or crash, class systems
Environmentally - weather, climate growth, human impact
Politically - political climate
Technologically - infrastructure and access to it
^^Flow Maps: how to read and interpret them^^
%%Unit 3: Economics%%
%%Textbook Chapter 17%%
==Types of resources==
Capital - man-made tools which assist in converting other resources into the final product
Natural - resources that occur naturally in the environment
Labour - human resources involved in producing goods and services who contribute physical and mental labour
- ^^Needs v wants^^
Needs are necessary for survival, wants are desires that are not entirely necessary. The wants will always exceed the needs. There are not enough resources to satisfy all wants.
- ^^Goods vs services^^
Goods are tangible, services are not. Services tend to not last for a very long time s it is typically someone doing something for the consumer.
- ^^Four participants in the economy and the role of each and their relationship^^
Consumers
- buy goods + services
- earn wages + salaries
- pays taxes
- receives government benefits
Producers
- produces goods + services
- aims to make a profit
- pays wages
- pays taxes
- imports + exports goods & services
Government
- charges taxes
- pays wages
- spends on goods + services
- provides benefits, payments and services to Aussies
- borrows money
Financial Institutions
- holds savings
- lends money
- aims to make a profit
- pays taxes
- ^^The decline of Australia's automotive industry^^
Building cars in the country is not sustainable because it is cheaper to do it overseas. Australia has pressure from imports, consumers now have 65 brands and 365 car models to choose from which makes it the most competitive automotive market in the world. The more cars are not produced, the cheaper they become and Aus did not produce an adequate amount. The high Aussie dollar made the exported cars more expensive overseas and imported cars cheaper in comparison.
- ^^Scarcity, opportunity cost^^
Scarcity - the state of being scarce or in short supply; shortage
Opportunity cost - opportunity cost is the value of the next-best alternative when a decision is made; it’s what is given up
- ==Australia’s trading partners, goods and services Australia’s imports and exports==
Trading partners
- China, 29.25%
- Japan, 11.9%
- USA 7.1%
- Korea, 5.7%
- India 3.4%
Top 10 exports
- coal
- iron ore
- natural gas
- education services
- travel
- gold
- aluminium ore
- beef
- crude petrol
- copper
Top 5 Imports
- personal travel
- refined petrol
- passenger vehicles
- telecom equipment
- crude petrol
- ^^Flow maps, how to read and interpret them^^
\n