Honors Geometry chapter 8
geometric mean - x² = ab; x = √ab
geometric mean (altitude) theorem [def] - the altitude drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle separates the hypotenuse into two segments. The length of this altitude is the geometric mean between the lengths of these two segments
geometric mean (altitude) theorem [equation] - segment 1 / altitude = altitude / segment 2
geometric mean (leg) theorem [def] - the altitude drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle separates the hypotenuse into two segments. The length of a leg of this triangle is the geometric mean between the length of the hypotenuse and the segment of the hypotenuse adjacent to that leg.
geometric mean (leg) theorem [equation] - hypotenuse / leg = leg / corresponding segment
pythagorean theorem (def) - the sums of the squares of the lengths of the legs of a right triangle is equal to the square of the length of its hypotenuse
pythagorean theorem (equation) - a² + b² = c²
pythagorean triple - three integers that follow the pattern of the pythagorean theorem
converse of the pythagorean theorem [def] - if the longest side squared is equal to the sum of the other sides squared in a triangle, then it is a right triangle
converse of the pythagorean theorem [equation] - c² = a² + b² = right triangle
pythagorean inequality theorem (acute) [def] - if the square of the length of the longest side of a triangle is less than the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other 2 sides, then the triangle is acute
pythagorean inequality theorem (acute) [equation] - c² < a² + b² = acute
pythagorean inequality theorem (obtuse) [def] - if the square of the length of the longest side of a triangle is greater than the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides, then the triangle is obtuse
pythagorean inequality theorem (obtuse) [equation] - c² > a² + b² = obtuse
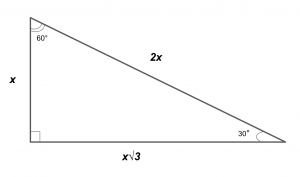
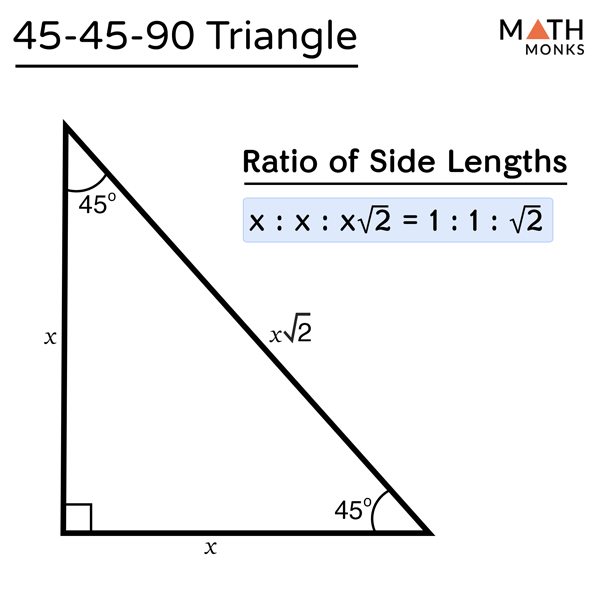
SOH-CAH-TOA - Sine: opposite/hypotenuse; Cosine: adjacent/hypotenuse; Tangent: opposite/adjacent
angle of elevation - angle made when you look up from the horizontal to the line of sight
angle of depression - angle made when you look down from the horizontal to the line of sight