Cell Organelles
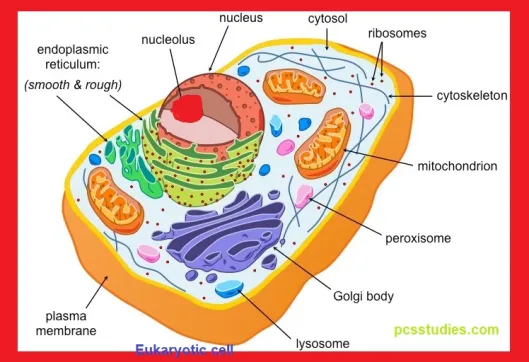
Cell Organelles and other structures
Organelle: Cell Wall
Type of Cell: Plant, Fungi, Bacteria
Description: Rigid, outermost layer; allows H2O, O2, CO2 to pass
Function: Support, protection
Organelle: Cell Membrane
Type of cell: All
Description: Selectively permeable; Primary components phospholipids; Also contains cholesterol for stability and proteins for transport
Function: Determines what enters and exits the cell; provides a barrier between the cell and environment
Organelle: Nucleus
Type of cell: Eukaryote
Description: Control center of the cell
Function: Stores the cells’ DNA, membrane-bound
Organelle: Nucleolis
Type of cell: Eukaryote
Description: Inside of the nucleus; Disappears during cell division
Function: Makes ribosomes
Organelle: Nuclear membrane
Type of cell: Eukaryote
Description: Surrounds the nucleus; selectively permeable
Function: Determines what enters and exists the nucleus
Organelle: Nucleoplasm
Type of cell: Eukaryote
Description: The liquid found inside the nucleus
Function: Supports contents, provides location for DNA and RNA synthesis
Organelle: Ribosomes
Type of cell: All
Description: Made of RNA and protein; very small; many in each cell; may be floating in cytoplasm or attached to the Endoplasmic Reticulum
Function: Makes proteins, free-floating: to stay in the cell; Attached for outside the cell
Organelle: Rough ER
Type of cell: Eukaryote
Description: Network of membrane-bound tubes with ribosomes attached
Function: Ribosomes synthesize proteins for export or the cell membrane
Organelle: Smooth ER
Type of cell: Eukaryote
Description: Network of membrane-bound tubes
Function: Lipid synthesis; detoxification of meds, alcohol, and waste
Organelle: Lysosome
Type of cell: Animal, Fungi
Description: Rarely found in plants; contains hydrolytic enzymes; small, round with membrane
Function: Breaks down cellular food and old cell parts
Organelle: Golgi bodies/apparatus
Type of cell: Eukaryote
Description: Stacked flattened sacs; Often found close to the cell membrane
Function: Modifies and packages proteins for export
Organelle: Small vacuole
Type of cell: Animal
Description: Small, membrane-bound, fluid-filled, round
Function: Helps to move proteins from Golgi to membrane for export, may store water
Organelle: Large central vacuole
Type of cell: Plants
Description: Large membrane-bound pouch
Function: Stores water, carbs, nutrients, and waste; contains hydrolytic enzymes
Organelle: Contractile vacuole
Type of cell: Protists
Description: Found in some protists such as the paramecium; membrane-bound sac
Function: Pushes water out when full to regulate water in the cell and avoid bursting
Organelle: Chloroplast
Type of cell: Plants
Description: Usually appear as green, oval-shaped disks, contain pigments including chlorophyll; membrane-bound
Function: Absorbs energy from the sun (light) to produce carbohydrates (food) for the plant
Organelle: Centrioles
Type of cell: Animals
Description: Paired structures near the nucleus; Made of microtubules, a type of protein
Function: Spindle fibers elongate from here during cell division, helps to separate chromosomes
Organelle: Cytoplasm
Type of cell: All
Description: Clear thick jelly-like substance in which the organelles are floating; Cytosol is the name of just the liquid
Function: Supports organelles; site of metabolism
Organelle: Mitochondria
Type of cell: Eukaryote
Description: Bean-shaped; double membrane inner membrane convoluted to increase surface area
Function: Breaks down sugar molecules to produce usable energy (ATP) for the cell
Organelle: Cilia
Type of cell: Some Animal, Protist
Description: Short numerous projections on the outer surface; made of microtubules
Function: Moves water around the cell; may result in movement of the cell
Organelle: Pili
Type of cell: Some bacteria
Description: Short numerous projections on the outer surface; Made of microtubules
Function: Helps cell to stick to other surfaces
Organelle: Flagella
Type of cell: Some Animals, protists, Bacteria
Description: Long tail-like or string-like structure; may have more than one
Function: Allows for locomotion of the cell
Organelle: Cytoskeleton
Type of cell: All
Description: Most numerous in those without a cell wall; Scaffolding within the cytoplasm
Function: Provides structure and support
Organelle: Plasmodesma
Type of cell: Plant
Description: Gap between two adjoining cells in the cell wall
Function: Allows material to be transported through the cell
Organelle: Chromoplast
Type of cell: Plant
Description: Storage molecules that contain pigments; not green
Function: Can perform photosynthesis
Organelle: Amlyplast
Type of cell: Plant
Description: Storage organelle
Function: Stores starch in plants
Organelle: Tight and gap junctions
Type of cell: Animal
Description:
Function: Communication and connection between neighboring cells