1.7 - CompTIA A+ Core 2
1.7a - Windows Network Technologies: Professor Messer
Domain joined vs. workgroup
Windows workgroup: Peer-to-peer network where all devices are standalone, with separate authentication (username/password).
Windows domain: Business network with centralized authentication and device access - can support thousands of devices over multiple networks.
Domain information can be viewed from “About” in Windows settings by clicking on “Domain or workgroup.”
User accounts are managed centrally via Active Directory Domain Services.
Shared resources

Makes a folder or printer available across a network - the resource is “shared” with others, and they can view it in File Explorer.
Shares can be mapped to drive partitions (drive letters) via the Computer Management utility (Control Panel → Windows Tools → Computer Management) or the
net usecommand.Shares ending with a dollar sign ($) are “hidden” Administratively - they won’t appear in a dropdown menu, but users can find them if they know their name.
Printers
Similar to sharing a folder, but the printer is being shared.
Access Print share settings via Printer Properties: Printers & scanners → [printer name] → Printer Properties
File servers
Mapped drives
1.7b - Configuring Windows Firewall: Professor Messer
Local OS firewall settings
Separate settings for Private, Public and Domain networks.
Application restrictions and exceptions
Applications/Windows features can be allowed via Windows Firewall.
Port numbers can be specified as blocked or allowed for all applications to receive incoming connections on.
Configurations
Block all incoming connections: Ignores your exception list and prevents all incoming connections - needed for when you are concerned about any connections to your machine
Allow specific applications: This option enables you to create rules that permit certain applications to receive incoming connections, ensuring that essential services remain accessible while still maintaining security.
Predefined exceptions: Provide a list of system/preinstalled applications for a user to enable or disable.
Custom rule: Allows users to build thier own configuration options for using Windows Defender Firewall.
1.7c - Windows IP Address Configuration: Professor Messer
Client network configuration
IP addresses are automatically configured via DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - default protocol for cnofiguring IP addresses on a network.
IP addresses may be configured via APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing) - this occurs when there is no manual/static IP or DHCP server.
APIPA allows for only local/link-local communication and assigns IPs from 169.254.1.0 to 169.254.254.255, and provides no Internet connectivity (no default gateway for external network connections).
Internet Protocol (IP) addressing scheme
Domain Name System (DNS) settings
Domain Name System (DNS): Converts human-readable domain names into IP addresses.
IP address
IP address: Unique identifier of a device on a network.
Subnet mask
Subnet mask: Specific IP used to find what subnet or private network an IP address belongs to.
Gateway
Default gateway: IP address of a router that forwards traffic from the internal network/subnet to other networks (other internal networks or external networks i.e., the Internet).
Loopback address
Loopback address (127.0.0.1): IP tha defines the internal IP address of your machine. Check connectivity to confirm the IP protocol stack is working.
Static vs. dynamic
Static addressing: Manual IP assignment - used for devices that need to have a consistent IP address (e.g., servers, printers).
Requires very specific details to ensure proper configuration.
Static addressing (in Windows) is done via the Alternate Configuration (for Network and Sharing Center):
Control Panel → Network and Sharing Center
Click on your active connection type (Ethernet or Wi-Fi)
Click on the “Properties” button
Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) to manually configure your IP addresses
Click the radio button to enable 'Obtain an IP automatically' and navigate to the “Alternate Configuration” tab
Enter your preferred IP address along with the subnet mask and default gateway settings.
Dynamic IP addressing: IP addressing via DHCP.
1.7d - Windows Network Connections: Professor Messer
Establish network connections
Via Control Panel: Network and Sharing Center → “Set Up a Connection or Network”
Via Windows Settings: Settings → Network and Internet
Both options include a step-by-step setup wizard with confirmations during the process, and many different connections are available for each (direct, dial-up, VPN, etc.)
Virtual private network (VPN)
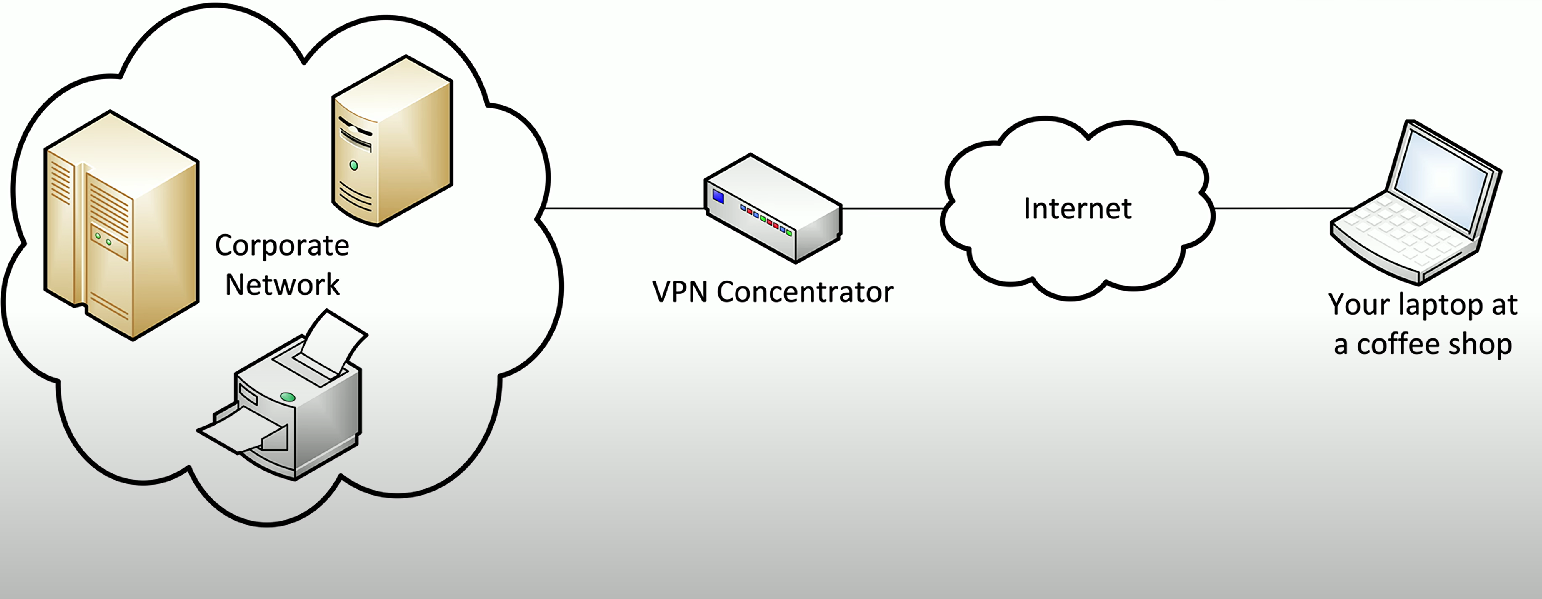
Virtual private network (VPN): Network architecture that allows your machine to communicate over public networks securely by encrypting data communications.
Functions by encrypting data from a VPN client (i.e., the VPN software on your machine), decrypting the information (via a VPN concentrator), to be read by a corporate network.
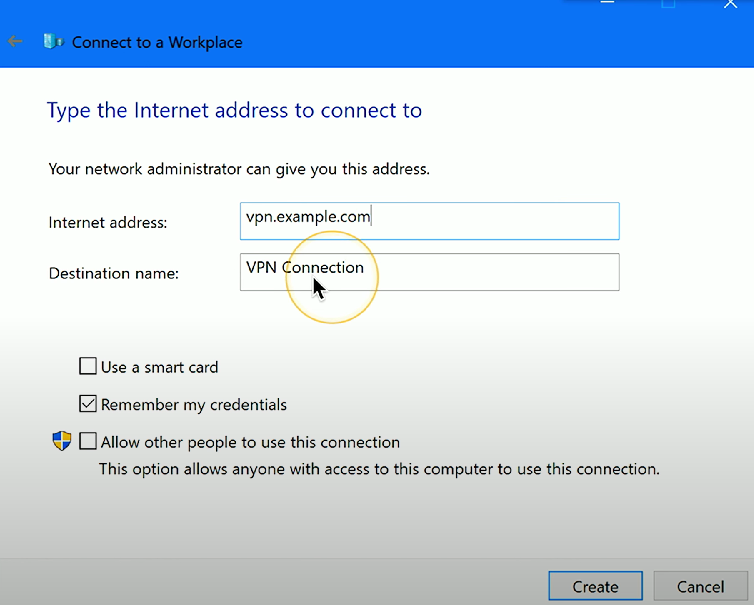
Windows includes a built-in VPN client:
Windows Control Panel → Network and Sharing Center → Connect to a workplace
Select “Use my Internet connection (VPN)” if the dialog presents both a VPN and dial-up option.
Enter the IP address of the VPN server, and configure additional options for smart cards, biometrics, or credentials.
Wireless
Windows Control Panel → Network and Sharing Center → Set Up a Connection or Network
Select “Manually connect to a wireless network”
Enter the Set the Network name (SSID), the security type (e.g., WPA2), the encryption type (TKIP, AES), and the security key (i.e., the password).
WPA2/3-Personal: Common security type for personal wireless networks - use a pre-shared key (PSK) for authentication.
WPA2/3-Enterprise: Common security type for enterprise wireless networks - use 802.1x authentication by connecting to a centralized authentication server.
Wired
Wired connection: Networking via direct Ethernet connection. Typically the fastest, and is therefore the default connection for Windows networking.
Setting up a Wired network connection:
Control Panel → Network and Sharing Center
Click on your active connection type (Ethernet)
Click on the “Properties” button
Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) to manually configure your IP addresses
Click the radio button to enable 'Obtain an IP automatically' and navigate to the “Alternate Configuration” tab
Enter your preferred IP address along with the subnet mask and default gateway settings.
Wireless wide area network (WWAN)/cellular network

Wireless wide area networks (WWAN): Provide wireless connectivity using cellular network connections (used in mobile devices), instead of traditional 802.11 wireless networks. Can use a physical expansion card or a USB hardware adapter (pictured), tethering two devices together, or using a mobile hotspot.
Proxy settings
Proxy settings: Proxies act as intermediaries between client and server. Proxies intercept and send requests for clients, receive the server response for the client’s behalf, check the server response, and then send the response to the client.
Accessible via:
Windows Settings: Network & internet → Proxy
Within these settings, you can configure the proxy to start automatically, authentication for the proxy server, and proxy exceptions.
Control Panel: Internet Options → Connections → LAN settings
Public network vs. private network
Public network: Network with less security - common in public areas like restaurants, coffee shops, and airports. File sharing and device connections are disabled, and firewalls are typically enabled in Windows for these connections.
Private network: Network with higher security - firewalls are typically in place, and used for home/enterprise networks. Device connections and file sharing are typically enabled to allow easy access to shared resources among trusted devices.
Settings can be customized for each network profile.
File Explorer navigation
Network paths
Network paths: Refers to network paths being visible in File Explorer - also called "Mapping a network drive”
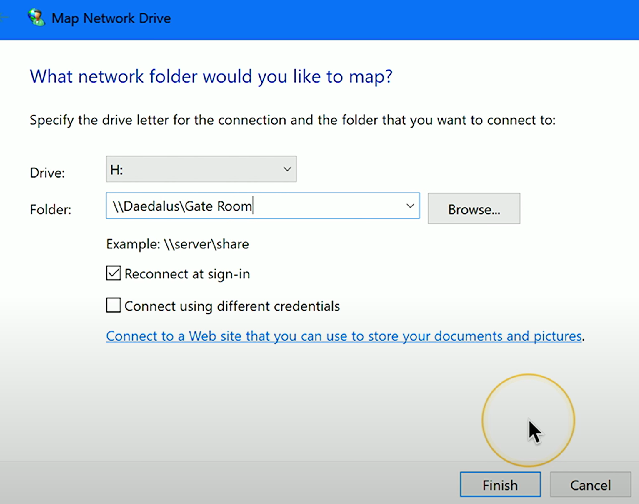
Network drive mapping involves linking a storage drive partition to a specific network location - saves time specifying the server and drive location every time the user needs to access the network share.
Can also use the command line:
net use [drive letter]: \\server\share
To disconnect - the mapped network drive, users can right-click on the drive in File Explorer and select 'Disconnect' from the context menu.
Metered connections and limitations
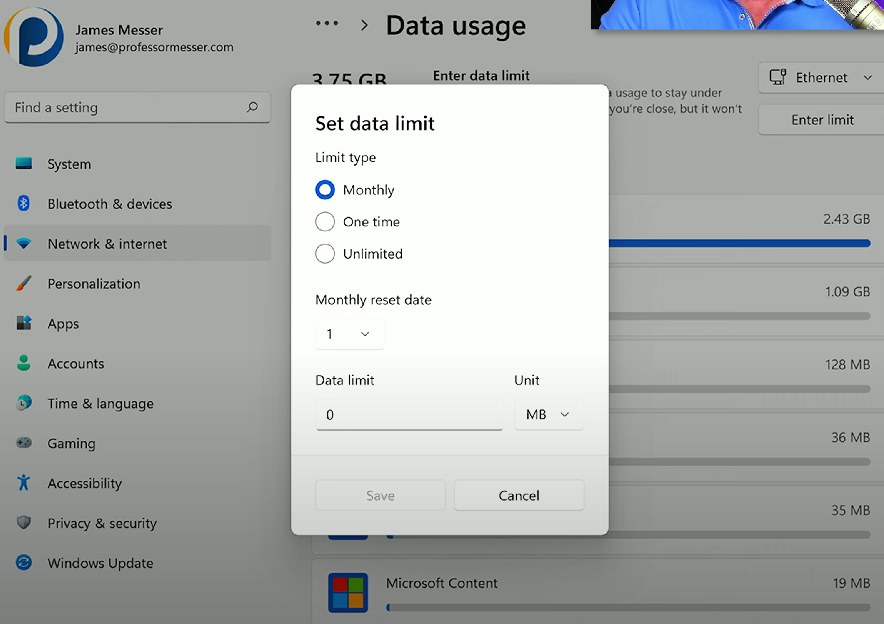
Metered connections: Internet connections where you pay for the quantity of data you use - limit the transfer of data, and can incur additional charges or reduced speeds if the limit is exceeded.
Metered connections Windows configuration:
Settings → Network & internet → Advanced network settings
Click on the “Enter limit” button
Configure options t o set monthly, one time, or unlimted data limits, with reset times, and data caps.