Electricity Study guide
Name Snap Date: Post Date:__
Static Electricity
All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Atoms contain even tinier particles called electrons. An electron is a particle with a negative charge. Electrons can move from atom to atom and from one object to another. The number of electrons on the surface of an object can make the object have a negative or positive charge. If the surface has more than the usual number of electrons, the object has a negative charge (-). If the surface has fewer than the usual number of electrons, the object has a positive charge (+). A negative charge can build up on an object when electrons move to it from another object. An object can get a positive charge if electrons move from it to another object.
Static electricity is the buildup of electric charge on an object. Unlike the electricity used in your home, static electricity does not flow through wires. The word static means “not moving”. But if the charge is strong enough, static electricity may “jump” from one object to another.
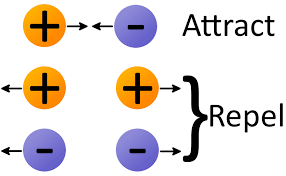
Charges Repel and Attract
Charged objects can push apart or pull toward each other. Objects that have like charges repel, or push away from each other. Objects that have unlike charges attract, or pull toward each other.
Charging an Object
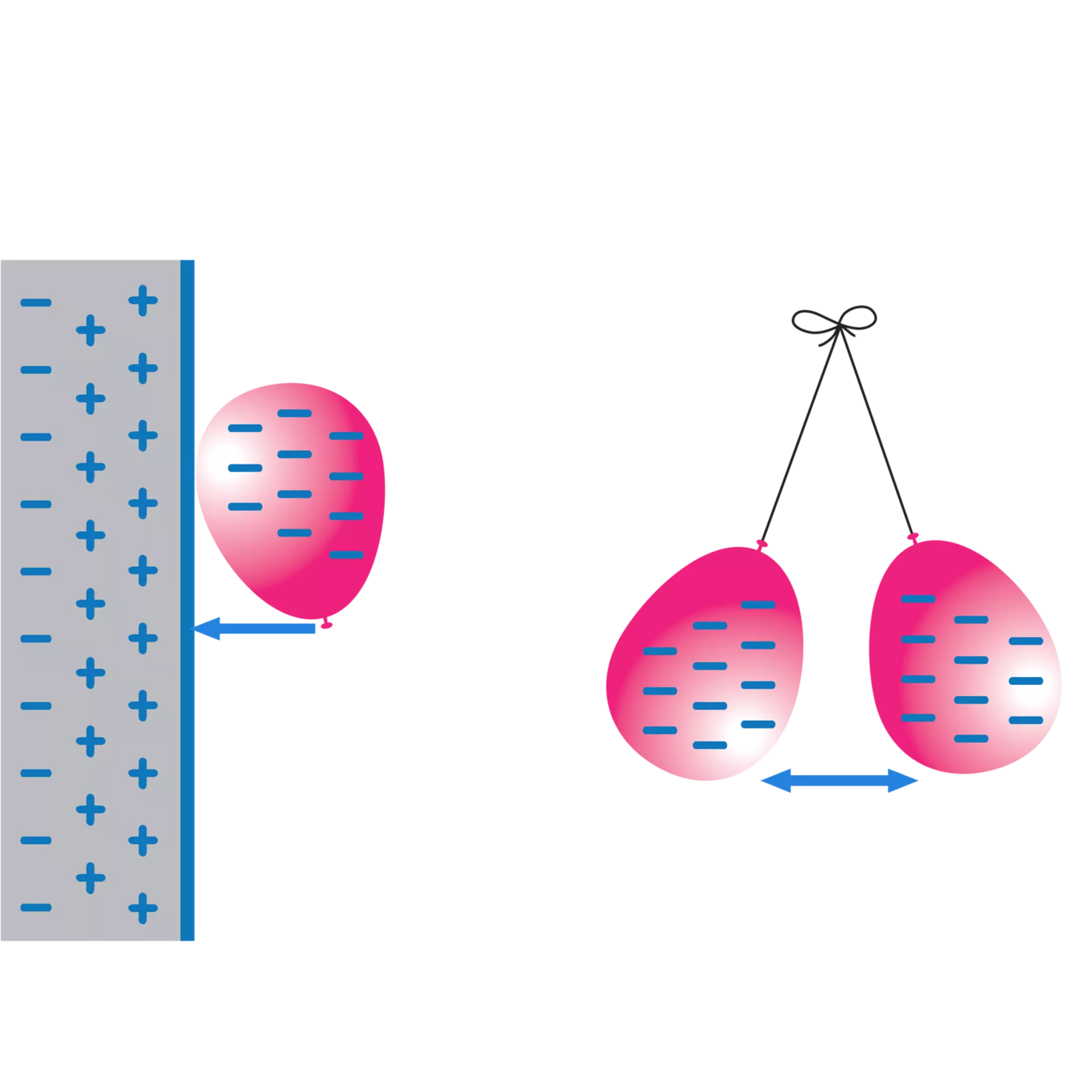
When two objects rub against each other, electrons will move. The object that loses electrons will then have a positive charge. If you rub a balloon on a wool sweater, electrons move from the wool to the balloon, giving the balloon a negative charge and the wool a positive charge. Objects can also become charged without touching each other. If you move the negatively charged balloon toward a wall that has no charge, the balloon’s electrons repel the electrons on the wall’s surface causing them to move toward the other side of the wall. Then the wall’s surface has a positive charge.The balloon will stick to the wall because the two surfaces have opposite charges and opposites attract. If you walk across the carpet on a dry day, a negative charge may build up on your body. If you were to grab a metal doorknob, electrons will jump from you to the doorknob, leaving the doorknob with a positive charge. You might feel a mild shock, and see a spark of light. When electrons quickly move from one object to another it is called an electric discharge.
Electrical Energy
Electrical Energy also involves the movement of electrons. When you turn on a TV, electrons flow through wires to the TV. This flow of electrons through a wire is called an electric current, but most people just call it electricity. To be useful, electrical energy must change into other forms of energy. Electrical energy can change into light, heat, sound, and motion. When you switch on a light, the current flows through wires to the light bulb which causes a wire or gas inside the bulb to give off light and heat. Toasters and hair dryers use electric current to produce heat, and when an electric current passes through wires made of certain metals, the wires get very hot and glow. In a hair dryer, electric current also runs a small fan that blows air over the hot coils. When the fan spins, electrical energy changes into the energy of motion.
Electrical Circuits
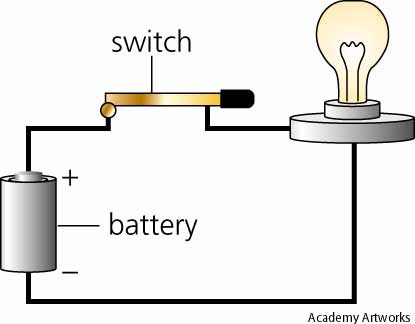
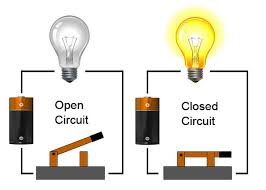
An electrical circuit is the path that an electric current takes. A simple one has four main parts - an electrical source, a load, a connector, and a switch. The source can be anything that supplies current like a battery or a socket. The source supplies the electrons that move through the wires. A load is any device that uses current, like a lamp or computer. Usually wire made of metal (like copper) is the connector between a source and a load, and a switch opens and closes a circuit. In the circuit shown, a battery is the electrical source. One end of the battery is negative (-) and the other is positive (+). Current flows from the negative end toward the positive end. The load is a light bulb. Wires and a metal switch connect the battery and the bulb. This is a closed circuit, which forms a complete path for the flow of electric current. Current can only move in a closed circuit. An open circuit is an incomplete path for the flow of electric current because it has one or more breaks in it. If the switch were open, it would break the circuit and current could not move through it.
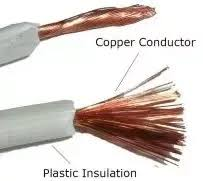
Insulators and Conductors
Some materials allow electric current to flow through easily, and some materials block the flow. Both kinds of materials are useful. Conductors let electric current pass through easily. Most conductors are metals, like copper, iron, and aluminum. They conduct current, which means they let current flow through them. Electrical wires in the home are usually made out of copper, and the power lines along the road are aluminum. Of all the metals, silver is the best conductor, but it’s very expensive. Materials that block the flow of electric currents are called insulators. Most non-metal solid materials are insulators (rubber, glass, wood, plastic). Copper wires in electrical cords are usually coated with plastic or rubber which makes them safe to touch. Current flows through the copper, but not through the plastic/rubber coating to shock your hand. The plug is also insulated for safety. Most power lines don’t have insulation around them so they are dangerous to touch. (Never touch them!) People who repair the lines use insulated tools.
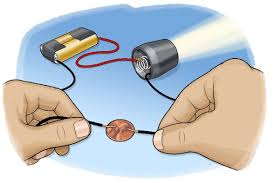
Investigating Conductors and Insulators
You can use an electrical circuit to test whether a material is a conductor or an insulator. Since current can only flow in a closed circuit, all materials must be conductors for the pathway to stay closed. In the diagram, a piece of aluminum foil connects two pieces of wire. Aluminum is a good conductor, so the circuit is closed and electric current can move through it to light the bulb. If you replace the foil with a rubber eraser, the bulb will not light up because the eraser blocks the flow of current and the circuit is broken. This lets you know that rubber is an insulator. You can test other materials in this same way to find out if they are conductors or insulators.
| Conductors | Insulators |
|---|---|
| copper | Most plastics |
| aluminum | rubber |
| iron | glass |
| steel | wood |
| gold | Cloth |