Module 29: Internal Political Boundaries
Module 29: Internal Political Boundaries
Introduction to Internal Political Boundaries
This section provides foundational insights into how geography and internal political boundaries influence electoral outcomes.
The content is designed strictly for use by educators in classroom settings.
Learning Goals
29-1: Influence of Geography and Political Boundaries on Voting
Understand the ways geography and internal political boundaries help shape voting outcomes.
29-2: Reflection of Regional Differences in Voting Outcomes
Explore how voting outcomes can reflect differing regional characteristics.
Electoral Geography
Definition
Electoral Geography: A subfield of political geography focusing on the examination of political preferences based on geography and how these spatial factors impact voting behaviors.
Voting District Definition
Voting District: A defined territorial division designated for public elections, whereby only residents of that district are eligible to cast votes.
The Electoral College
Structure and Function
Electoral College: Comprising a total of 538 electors in the United States, it requires a majority of 270 electoral votes to successfully elect a president. Each state has a number of electors equivalent to its total congressional delegation: one for each member in the House of Representatives, plus two for the U.S. Senators.
Example of Disparity in Delegates
Inquiry: Explain why New Jersey, with 14 delegates, has more than Wisconsin, which is larger in terms of population and has only 10 delegates.
Historical Voting Patterns
Election of 2016 Data Overview
Donald Trump (Republican): 304 electoral votes, 62,984,828 popular votes.
Hillary Clinton (Democrat): 227 electoral votes, 65,853,514 popular votes.
Other notable candidates included Gary Johnson (Libertarian) and Jill Stein (Green), with significantly fewer votes (4,489,341 and 1,457,218 respectively).
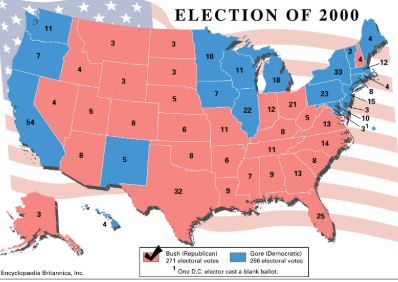
Electoral Battleground States
Case Study: Florida in the 2000 presidential election, where the result hinged on just 500 votes, illustrating critical irregularities which led to a Supreme Court ruling in favor of Bush’s victory.
Legislative Processes Impacting Voting
Reapportionment
Reapportionment: The process that redistributes the 435 seats in the U.S. House of Representatives proportionally based on state population figures following every U.S. census.
Redistricting
Redistricting: Involves redrawing the boundaries of congressional districts to account for population changes identified in the U.S. census.
Gerrymandering
Definition
Gerrymandering: The strategic manipulation of electoral district boundaries to favor a particular political party or outcome.
Techniques of Gerrymandering
Packing: Concentrating opposition voters into a single district, creating a large majority for one party while diminishing the opposition’s influence in other districts.
Cracking: Splitting opposition voters across multiple districts to dilute their voting power and inhibit the formation of a majority within any district.
Implications of Gerrymandering
Analysis of Maryland’s third congressional district as an example of gerrymandering.
Case Study: Wisconsin's Gerrymandering
The state has seen different congressional district plans over the years, specifically comparing plans from 2008, 2012, to 2024, focusing on the implications and motivations behind the changes.
The Wisconsin Democracy Campaign has developed toolkits in 2019 and updated in 2023, aimed at combating gerrymandering and promoting fair redistricting advocacy.
Regional Voting Patterns
Observational Study
Each student is to track the voting patterns of specific states from the 1980-2024 presidential elections to understand regional voting tendencies (red, blue, or purple states).
Breakdown by Political Party Characteristics
Republican Party Ideology
Generally conservative beliefs, advocating for:
Increased military spending.
Opposing gun control laws.
Anti-abortion stances.
Resistance to gay marriage.
Lower taxes for the wealthy and less support for immigration.
Skepticism regarding climate change.
Democratic Party Ideology
Liberal stance, supporting:
Lower military spending increases.
Greater gun control measures.
Pro-choice policies concerning abortion.
Advocacy for gay marriage.
Higher taxes for affluent individuals.
Expanded support for immigration.
Recognition and action regarding climate change.
Electoral Map Insights
Impact of Color-Coded Maps
Analyze state-level results from the 2020 presidential election to determine cultural conservatism vs. liberalism in the U.S. and assess the limitations of viewing voter mapping through color coding alone.
Cartograms vs. Traditional Maps
Understand how cartograms represent true voting behavior by illustrating results per capita, contrasting with conventional maps to better reflect electoral nuances.
County-Level Analysis
Detailed analysis indicating substantial differences at the county level, highlighting the limitations of a statewide lens on electoral results and demonstrating regional variations.
Three-Dimensional Cartography
Use of three-dimensional maps to represent voting densities and geographic variances between urban (Democratic-leaning) and rural (Republican-leaning) areas.
Review Notes
Key Definitions and Comparisons
Electoral Geography: Analysis of geographical influences on political preferences.
Voting District: Defined area for public voting eligibility.
Electoral College: Comprised of electors allocated based on each state's congressional representation.
Reapportionment vs. Redistricting: Reapportionment redistributes House seats post-census, while redistricting redraws their boundaries based on population changes.
Gerrymandering: Defined as the manipulation of voting district boundaries for political advantage, executed through packing and cracking methods.
Understanding the significance of scale in electoral maps, contrasting macro views (state-level) with micro views (county-level) to evaluate regional political landscapes.