Data Sources
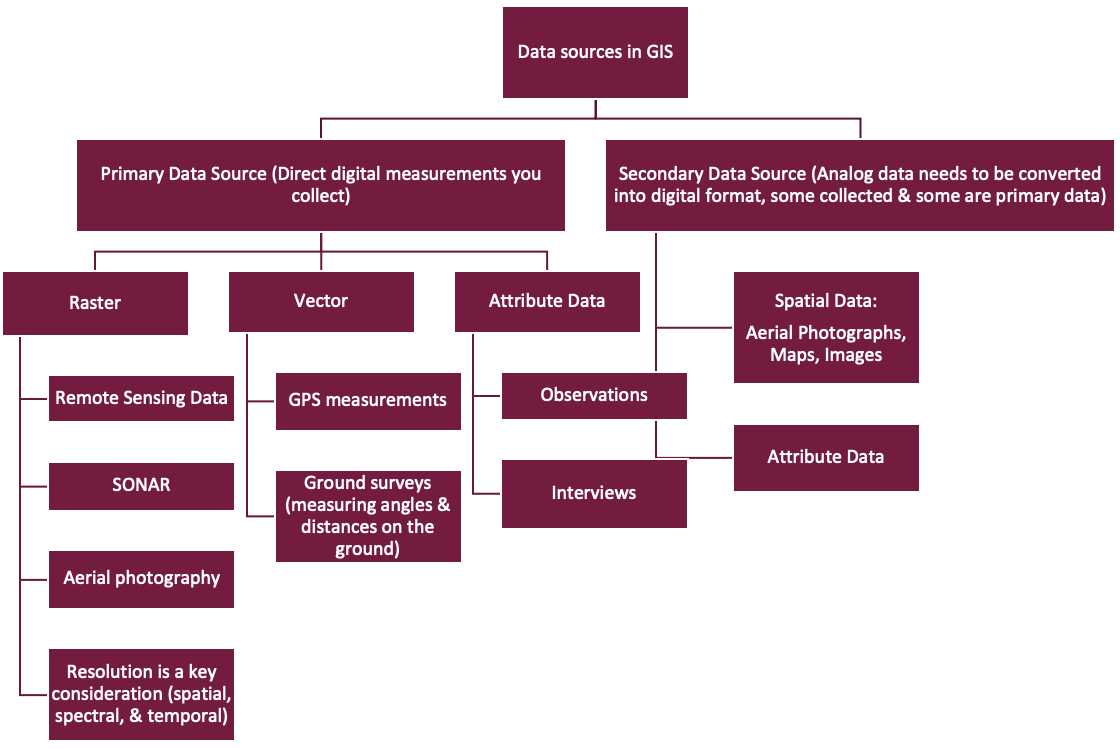
Types of resolution:
- Spatial Resolution: refers to the size of the object that can be resolved and the most usual measure is a pixel size
- Spectral Resolution: refers to the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum that is measured
- Temporal Resolution: describes the frequency with which images are collected in the same area
The GPS system is composed of 3 segments:
The space segment
Consist of the GPS satellites that collect the following information:
- Precise time segment
Normally 24 satellites – enough for accurate positioning
The control segment
a. Consists of a system of tracking stations located around the world, that monitor the information sent by satellites and send corrections to orbital and time information periodicallyThe user segment
a. Consist of the GPS receivers and the user communities
i. GPS receivers convert satellite signals into position in latitude and longitude, altitude from sea level, and time in Universal Time Coordinates (UTC).
ii. Typically 4 satellites are required to compute a location (X,Y, Z)
Trilateration is the process of determining absolute or relative locations of points by measurement of distances, using the geometry of circles, spheres, or triangles. It has a practical application in surveying and navigation, including GPS.
Other types of global navigation satellite system (GNSS):
- BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), owned by China
- Galileo, owned by the EU
- GLONASS, owned by Russia
- Navigation Indian Constellation (NavIC), owned by India
- Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), owned by Japan