5A

Photosynthesis is a reaction in which light energy is used to split apart the strong bonds in water molecules (photolysis), to combine hydrogen with carbon dioxide to produce a fuel in the form of glucose. Oxygen is a biproduct.
Rate of photosynthesis: carbon dioxide concentration, light intensity, and temperature

ATP
Made of a ribose sugar, three phosphate groups and adenine

When energy is needed, third phosphate bond can be broken through a hydrolysis reaction which is catalysed by the enzyme ATPase. The product of this is ADP (free inorganic phosphate group - Pi and energy)
Reversible reaction: ATP can be synthesised from ADP and a phosphate group through a condensation reaction, catalysed by the enzyme ATPase

Light Dependent Stage (occurs in the thylakoid membrane)
Light energy excites electrons in the chlorophyll in the thylakoid membrane, causing them to leave the chlorophyll and pass to an electron acceptor at the start of the electron transport chain (photoionisation).
Excites: causes a pair of electrons in chlorophyll a to move to a higher energy level
Electrons pass down the chain from one electron carrier to the next through a series of redox reactions. The energy released as the electrons pass down generates ATP from ADP and a phosphate group in a process called photophosphorylation. (cyclic)
Light splits water into protons (H+ ions), electrons and oxygen, known as photolysis of water. Electrons replace those lost in the first stage, protons are pumped across the membrane using the ATP produced through a process known as chemiosmosis, creating a potential gradient. (non-cyclic)
Reduced NADP is generated as the electrons in the electron transport chain are transferred to NADP along with hydrogen.
Protons pass back through the membrane through an ATP synthase enzyme. ATP and Reduced NADP are used for the light independent stage.
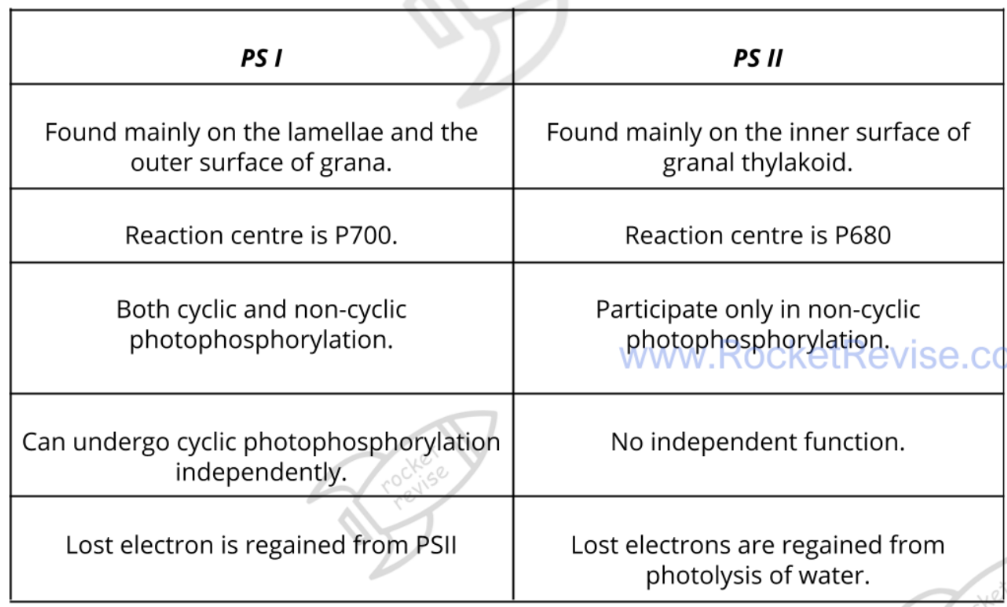
Photosystems (PSI and PSII)
Photosystems are involved in absorbing light required for photosynthesis and converting it into chemical energy
Chlorophyll:
Chlorophyll a = (absorb red and blue light, green light is reflected)
Chlorophyll a = primary pigment
Other = chlorophyll b, carotenoids, xanthophyll, phaeophytin
Primary pigment + other proteins = reaction center
Accessory pigments+ other proteins = light harvesting system
Together the light harvesting systems and are known as photosystems
Different accessory pigments absorb different wavelengths of light so as much light energy is harvested as possible
Thylakoid membranes contain different photosystems (I or II)
Chemiosmosis
Energy is used to pump protons from the stroma into the thylakoid interior (thylakoid interior is impermeable to protons so cannot diffuse back) - concentration of protons is greater in the interior than the stroma (electrochemical potential gradient)
Chemiosmosis activates ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP to form ATP
Cyclic photophosphorylation occurs when chloroplasts require an increased amount of ATP

Light Independent Stage (Calvin Cycle) - occurs in stroma
RuBP is combined with carbon dioxide in a reaction called carbon fixation catalysed by the enzyme RUBISCO
RuBP is converted into two glycerate 3-phosphate molecules (GP)
Reduced NADP and ATP are used to reduce GP to form glyceraldehyde 3-phospate (GALP/ TP). Reduced NADP becomes oxidised
1/6 GALP molecules are used to make simple sugars such as glucose, fructose and galactose, which are then converted into polysaccharides, amino acids, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids
The remaining 5/6 molecules are used to regenerate RuBP with the help of ATP
RuBP - ribulose bisphosphate (5 carbons)
GP - glycerate 3-phosphate (3 carbons)
GALP - glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (3 carbons)
RUBISCO - ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/ oxygenase
Carbohydrates (simple sugars) are made by joining two GALP molecules, polysaccharides are made by joining hexose sugars in different ways.
Lipids are made using glycerol (synthesised by GALP) and fatty acids (synthesised by GP)
Amino acids are made from GP
Nucleic acids are made using GALP


Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis:
Contains stacks of thylakoid membrane called grana which contain photosynthetic pigments
Contain stroma (fluid surrounding the grana) which contains all the enzymes required for the light independent stage of photosynthesis
Grana are connected by lamella which maximises efficiency of chloroplasts

Absorption spectrum: graph showing the amount of light absorbed by a pigment against the wavelength of light
Action spectrum: a graph demonstrating the rate of photosynthesis against the wavelength of light
Reflected light = colour presented
Absorbed light = used for photosynthesis

Chromatography can be used to separate chloroplast pigments
Extract pigments from a plant by grinding up leaves with propanone and then filtering it
The pigment travels up at different speeds separating the pigments as they have different solubilities in the solvent
Calculate Rf value = distance travelled by solute/ distance travelled by solvent