Biology II - 2022 Midterm - Font
Unit 1 - Evolution
Describe first life on earth. What was the atmosphere like?
- details
- Earth’s age is approx. 4.6 billion years
- mass of gas and dust was pulled together by gravity → sun
- more debris was pulled into the Earth during development of the sun
- atmosphere: no ozone = UV radiation, electricity in atoms, lipids and hydrates
- theory about atmosphere: little no oxygen existed
- first life: anaerobic, heterotrophic, prokaryotes
- elements: all found in organic compounds when Earth first formed
What was Lamarck’s theory about evolution? Why was he wrong?
- theory: inheritance of acquired characteristics
- i.e. you lose an arm during your life so your offspring get one arm
What does the most “fit” mean in a population?
- defined by individual’s heredity contribution to the next generation
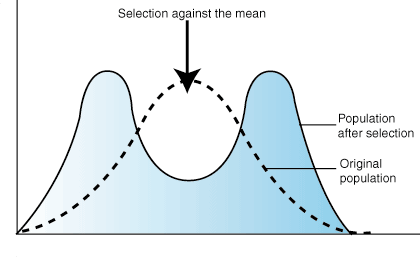
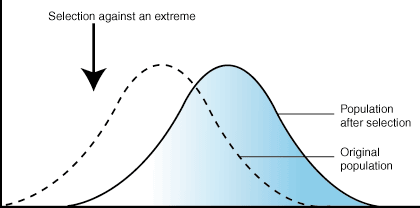
Recognize and be able to explain the graphs of types of natural selection.
three types of graphs of types of natural selection
stabilizing selection: individuals with the AVERAGE form of a trait have the greatest fitness
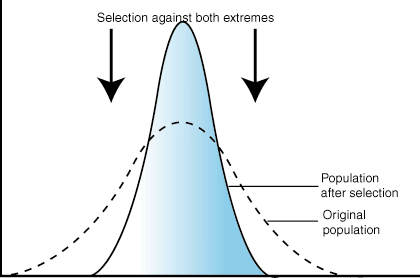
disruptive selection: individuals with EITHER EXTREME form of a trait have the greatest fitness
directional selection: individuals with ONE EXTREME form of a trait have the greatest fitness
Unit 2 - Taxonomy
Know the order of taxonomic classification.
- domain → kingdom → phylum → class → order → family → genus → species
Be able to read a cladogram.
- \
Know basic characteristics for Kingdom Bacteria, Protista, Fungi, and Plantae.
- bacteria/eubacteria
- domain bacteria
- “true bacteria”
- lack nucleus, organelles
- pepticlogylian cell wall
- multicellular
- heterotrophic, autotrophic
- either chemosynthetic or photosynthetic
- overlapping traits (domain eukarya, eukaryotic, complex nucleus and organelles, and cell walls):
- protista
- not a plant, animal, or fungi
- cell wall (usually of cellulose)
- mostly unicellular, multicellular = lack tissue organization
- autotrophic by photosynthesis, heterotrophic by phagocytosis, or both
- fungi
- 70,000 species
- cell wall of chitin
- unicellular and multicellular
- heterotrophic by secreting digestive enzymes into the environment
- plantae
- mosses, ferns, conifers, and flowering plants
- cell wall of cellulose
- multicellular, develop from embryos
- autotrophic by photosynthesis
Unit 3 Part 1 - Bacteria and Viruses
What are the “extreme” bacteria? What are the groups? Where would you find each?
- domain archaea
- methanogens
- convert hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide into methane
- swamps, hot springs, salt lakes
- halophiles
- salt-loving
- great salt lakes and the dead sea
- thermoacidophiles
- acidic environments with high temperatures
- hot springs of yellow stone, volcanic vents, hypothermal vents
- serve as producers for communities living at great depths
Know the arrangements for all bacterial groups.
Know how bacteria and viruses are treated (medically) differently.
- viruses are sometimes used as biotechnology tools
- vaccines
Describe cell walls of bacteria and how they can be used to classify by gram staining.
- gram-negative
- complex cell wall, small amounts of peptidoglycan
- stain pink or red
- gram-positive
- simple
- have more peptidoglycan
- stain purple
Know your basic viral shapes.
What are prions?
- infectious protein particles with no genome
Unit 3 Part 2 - Protists and Fungi
What characteristics are used to divide protists into 3 classes?
- characterized based on how they move
- animal-like
- all heterotrophs
- 4 phyla determined by the movement
- some are decomposers
- some are the base of some food chains
- some cause disease
- plant-like
- based on single celled or multicellular + color they are
- fungi-like
- heterotrophs
- decomposers
- have centrioles
- plant diseases (i.e. potato famine)
- two groups
- slime molds - free living cells in soil on surface
- water molds - thrive on dead or decaying organic material in water or plant, are parasitic on land
What is the function of the contractile vacuole in Paramecium?
- contractile vacuole - collect water, maintain hemostasis
How does each of the “animal-like” protists move?
- zooflagellates - flagella (tail-like)
- sarcodines - cytoplasmic extensions (finger-like dragging)
- ciliates - cilia (hair-like)
- sporozoan - parasite and don’t move on their own (rely on a host to move)
What part of the fungi would you find buried in the ground?
- mycelium - the roots of fungi and where food is absorbed
Describe what an absorptive heterotroph is.
- digest food outside their body and absorb it
Unit 4 - Botany
Recognize different arrangements of vascular tissue in dicots and monocots.
- monocots - have distinct epidermis, enclosing vascular bundles of xylem and phloem
- dicots - vascular bundles arranged in a ring-like pattern called a pith
What is vascular tissue made of?
- xylem - conducts water from roots to rest of plant
- phylum - conducts materials throughout the plant
Recognize 3 types of roots (fibrous, adventitious, tap).
- taproots - dominant root develops from the stem and then leads to other roots coming from it
- fibrous - thin roots developing from the stem
- adventitious - form from non-root tissue
What group did the first plants evolve from?
- plant-like protists
What is the advantage of producing seeds?
- embryos are protected in seeds
What parts make up the male part of the flower? Female?
- male - anther (top) and filament (stem-like)
- female - stigma (top), pollen tube (stem-like), and ovary (inside flowering part, sphere-like)
Differentiate between 3 types of plant tropisms.
- phototropism - response to light
- gravitropism - response to gravity, causes roots to grow downward
- thigmotropism - response to touch
Unit 5 - Intro to Animal Kingdom
Basic characteristics of all chordates.
- dorsal, hollow nerve cord
- notochord
- tail that extends beyond the anus
- pharyngeal pouches
Identify different types of symmetry.
- radial - extend outward from the center
- bilateral - identical left and right sides
- asymmetry - no symmetry
Describe the 3 germ layers and what they differentiate into.
- endoderm - digestive and respiratory systems
- mesoderm - muscular, reproductive, circulatory, and excretory systems
- ectoderm - nervous and integumentary systems
Review vocab and animal chart for this unit!