IB ITGS HL - 15. IT Systems in Organizations
Types of development
When an organization decides to investigate a new IT project, it can choose from two types of software:
Off-the-shelf software: software that is widely available for general purchase from software vendors.
Custom / bespoke software: software created specifically for a single organization. More tailored to their needs.
Development tools
Software developers use a variety of programs to create new software
Text editor to enter the program’s source code
A compiler translates the source code into machine code
Debugging tools to help find and fix errors in the program
These tools are packaged together in an Integrated Development Environment.
Legacy systems
Legacy system: a computer system that is no longer available for purchase or is no longer supported by the manufacturer.
Organizations may continue to use them because they are essential to their operations and there is no easily available replacement.
Emulation and virtual machines
One solution to using legacy systems in a modern environment is to employ a virtual machine, which creates a virtual computer running inside a window.
An emulator is a software recreation of an entire system’s hardware, allowing the user to run the emulated system in a window. This is used when the legacy system requires hardware that is different from the host computer.
System development life-cycle
System Development Life-Cycle: the stages involved in creating an IT system. There are 6 key stages.
Analysis: an investigation of the current system, the needs of the client, and the possibility of creating a solution.
Design: the planning of a solution to meet the needs of the client.
Development / Implementation: the creation of a system.
Testing: ensuring that the system function correctly.
Installation / Delivery: installing the software and any necessary hardware at the client’s organization. Removing the old system and transferring data may be required.
Maintenance: updates made to a system to fix bugs, improve performance or add new features.
Analysis
It must involve all key stakeholders, such as the client and the end users.
Project goals (aim) and its limitations (scope) must be carefully defined.
Data collection: to fully understand the current system, data about it must be collected from users, managers and administrators, and any existing documentation.
Questionnaires
Interviews
Observation of users
Organizational policies
Requirements specification: a technical document that describes the needs of an organization and the scope and aims of the project.
Functional requirements: features the system should have, such as input, output, storage, processing and UI.
Non-functional requirements: limitations on how the system should work.
Identification of possible IT solutions: many projects have several possible solutions.
Feasibility studies and justification of solution: a business case must be made, justifying the chosen solution in terms of time and cost of production versus the predicted benefits.
Project plan: a project manager and a project management methodology are chosen. Project milestones are defined.
Gantt charts provide a high level overview of a project schedule by showing tasks and the individuals that are responsible for it.
Program Evaluation and Review Technique charts represent scheduling information graphically and show the relationships between each task.
Critical Path is used to determine the longest route to determine the minimum time required.
Design
The user interface and the data flow of the system is designed.
Data Flow Diagrams
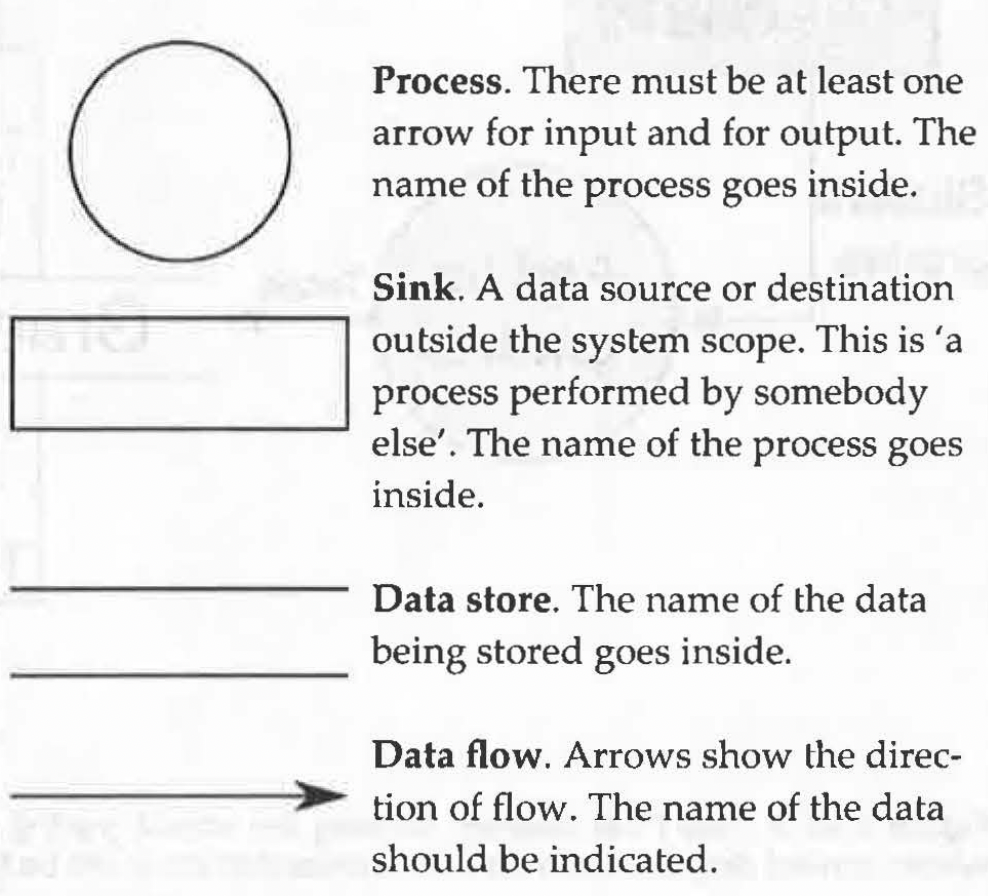
A data flow diagram shows the relationship between the data storage, in puts, outputs, and processes in a system.
Sink: external processes
System context diagram: shows a high level view of the system with only relations to external stakeholders.
Symbols:
Entity Relationship Diagrams
An ERD shows the groups of data stored, the attributes of each, and the relationships between the various data items.
Implementation
Implementation is also called development or construction.
During this stage, developers create the system, following the design documents previously created.
Alpha testing is performed to verify that the software works according to the requirements. This is done by a team of software testers.
Prototypes are created to show to the client and make sure that the project is meeting expectations.
Quality control processes are used to lessen the likelihood of serious problems.
Quality assurance methods are used to ensure the developers are following standardized practices.
Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI): is a type of quality assurance method that describes an organization in terms of five levels of maturity in order to improve performance.
Technical documentation is produced, targeted at system administrators and other developers who may change the system in the future.
User documentation explains how to use a system.
Testing
Beta testing is used to detect any small remaining bugs and to test the software’s usability under real world conditions.
User acceptance testing involves the client checking the system to ensure it meets their requirements.
Installation
Installation is also called delivery or deployment.
This stage concerns preparing the organization for the installation of the new system and the removal of the old one.
User training must be done so that employees can properly utilize the new system.
Changeover is the most crucial part because any small failures can have a big impact on the whole organization.
Direct changeover: all users start to use the new system immediately.
Phased changeover: switches gradually from the old to the new system, with some parts of the organization switching before others.
Parallel changeover: running the old system concurrently with the new system. Mostly used for safety critical systems.
Maintenance
Adaptive maintenance: updating the system to work with new hardware or software.
Perfective maintenance: adding new features as required by the changing organization.
Corrective maintenance: fixing bugs that weren’t found during testing.
Preventive maintenance: updating the software to prevent foreseeable problems.
Regression testing: the process of repeating old t estas to ensure they still work after alterations are made.
Development approach
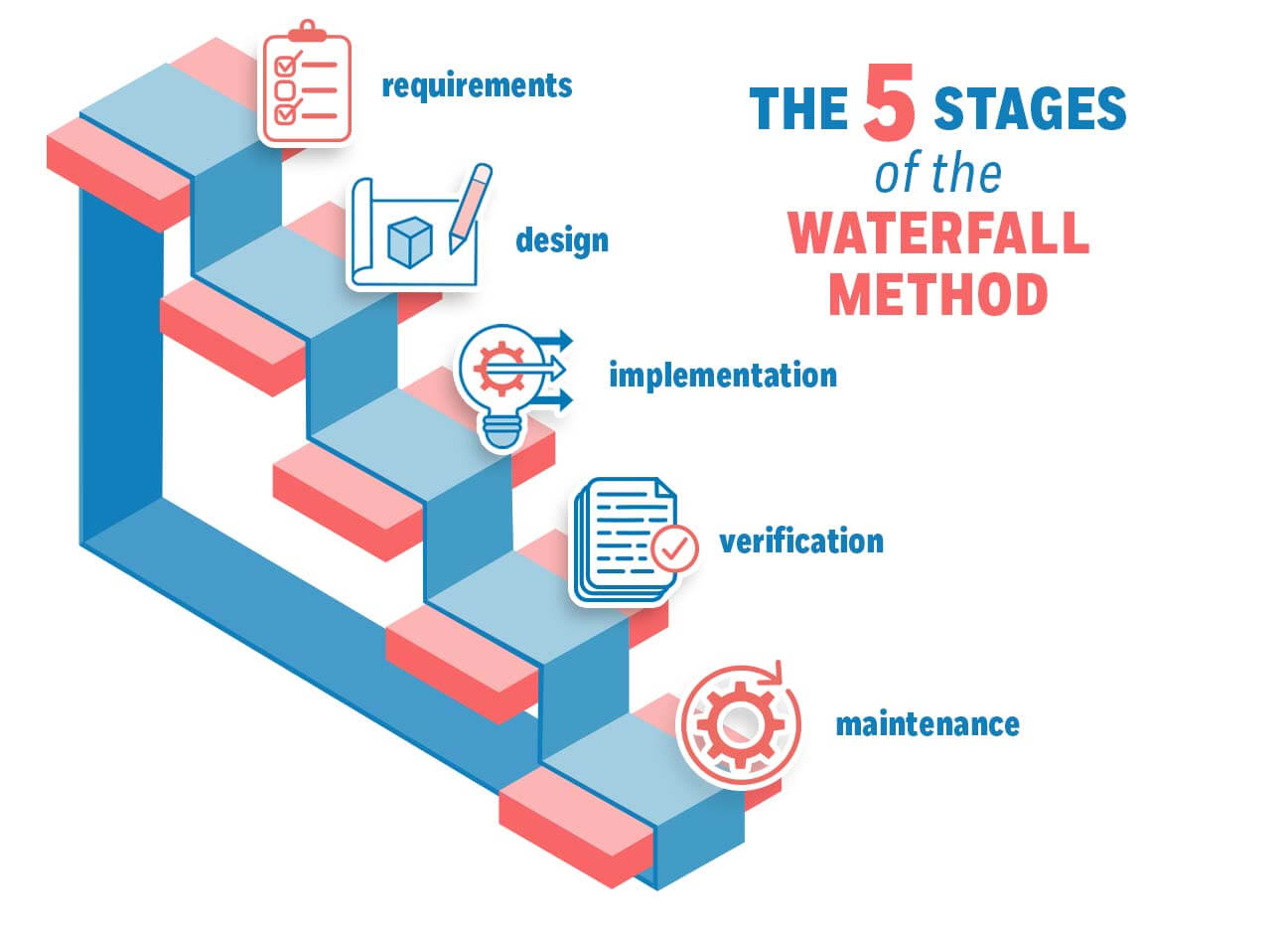
Waterfall model
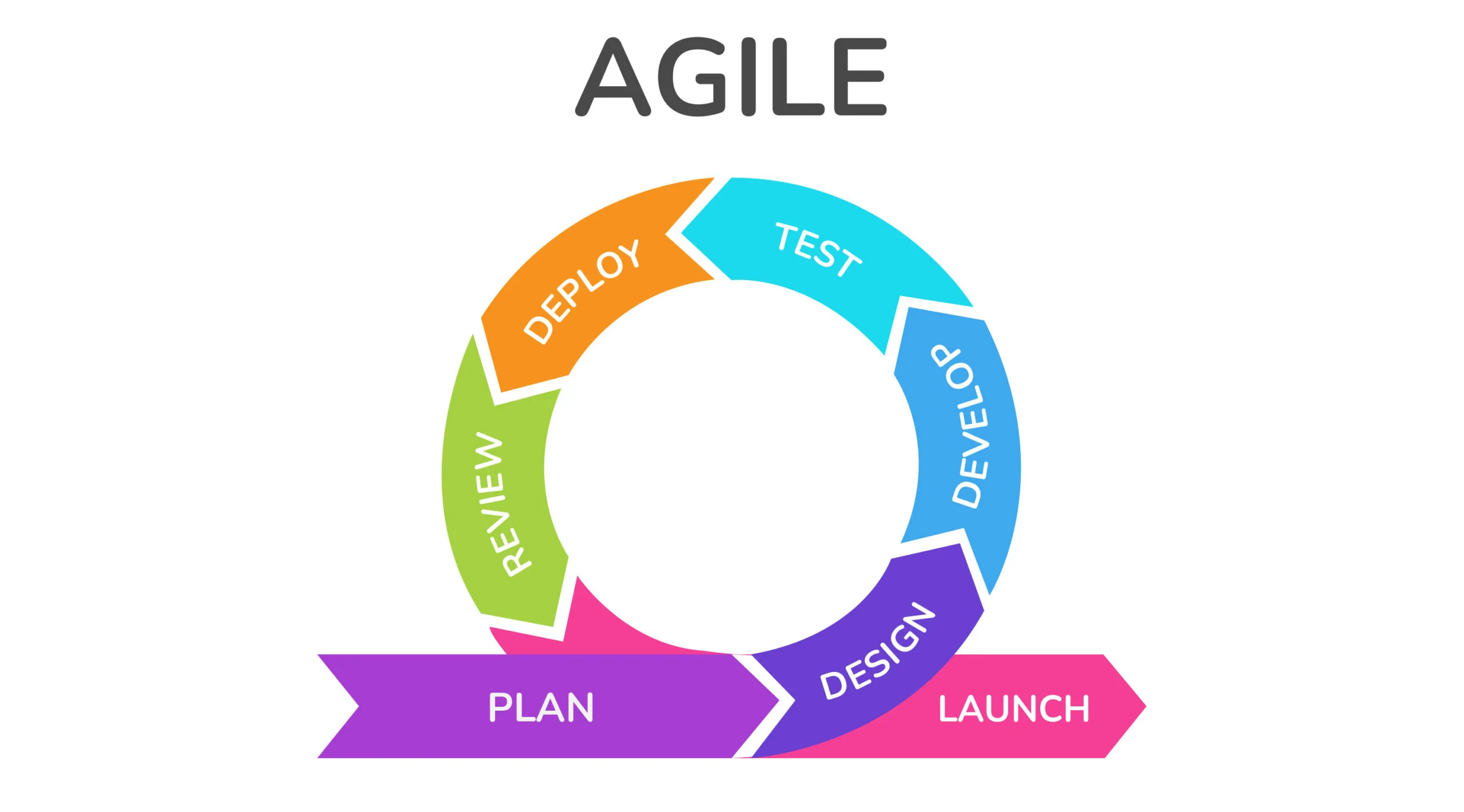
Agile development model
Project management methodologies
Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method (SSADM)
Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBoK)
PRojects IN Controlled Environments 2 (PRINCE2)