Biology 1.2.4 - Cell Transport
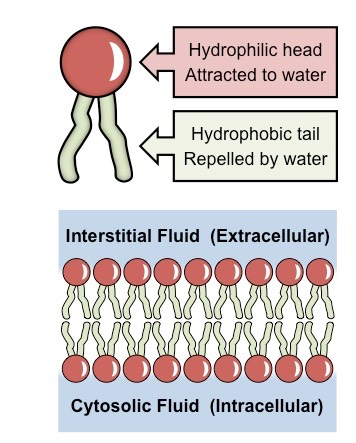
Membrane
made up of a bilayer of phospholipids
mostly phospholipids, then proteins, cholesterol, and sugars
Phospholipids are selectively permeable based on their rotation:
creates an entrance with heads on the outside and tails on the inside
 Proteins in the membrane
Proteins in the membraneact as doors for material exchange
provides a passage through the membrane
Cholesterol in the membrane
cholesterol keeps the balance of liquid and solid in the membrane
Carbohydrates in the membrane
referred to as “membrane sugars” even though they are polysaccharides
Membrane sugars identify things in the cell
called glycoprotein when on a protein, called glycolipid when on a lipid
passive transport
if a molecule passes through the membrane it is called passive transport
they will pass through transport proteins called channel proteins
water will try to dilute an area with more molecules inside it - called osmosis
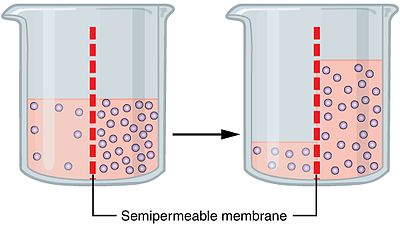
Goes from hypotonic solution - fewer molecules within it to hypertonic solution - more molecules within it. once this process is complete the solutions are called isotonic meaning they have equal ratios of molecules.
When a plant cell is within a hypertonic solution during osmosis it collapses - called plasmolysis, also known as wilting
In a hypotonic solution, an animal cell will burst in lysis, but a plant cell will be saved from the cell wall, but will still have water in it. This state of a cell is called turgid and it is very beneficial for a plant.
Active Transport
- molecules move through cells using energy or ATP
- molecules move through diffusion using active transport, sometimes they need carrier proteins or protein pumps
- The most important carrier protein is the sodium-potassium pump
- endocytosis - brings large substances into the cell
- phagocytosis - larger substances are pulled in for digestion
- pinocytosis - drops of liquid are pulled in for osmoregulation
- exocytosis - takes large substances out of the cell