Microeconomics 1
The basic economic problem
-Scarcity is the basic economic problem, finite resources but infinite wants
So how to allocate scarce resources given unlimited wants?
There are factors of production
1) Capital - man made aids to production (machinery, tractors and vehicles)
2) Enterprise - entrepreneurship, people, risk takers that innovate goods & services to make profit
3) Land - farmland like where goods can be produced
4) Labour - workers to produce
All of these things are finite resources, which forces choices to be made: what to produce,how to produce, and for whom to produce
Opportunity cost - the cost of the next best alternative when a choice is made
Production possibility frontiers
PPF curve shows:
1) maximum possible production of 2 goods/services with given factors of production
2)various combination of 2 goods/services that can be produced with given factors of production
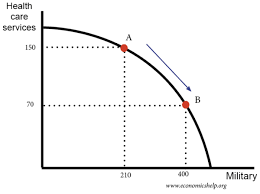
linear line - constant opportunity cost
concave line - increasing opportunity cost
Demand in economics
Demand - the quantity of a good/service consumers are willing & able to buy at a given price in a given time period
An increase in price is a contraction of demand, which makes the price go up, a movement left along the demand curve
A decrease in price is an extension of demand, as there is more quantity demanded, movement right along the demand curve
This is for price related factors
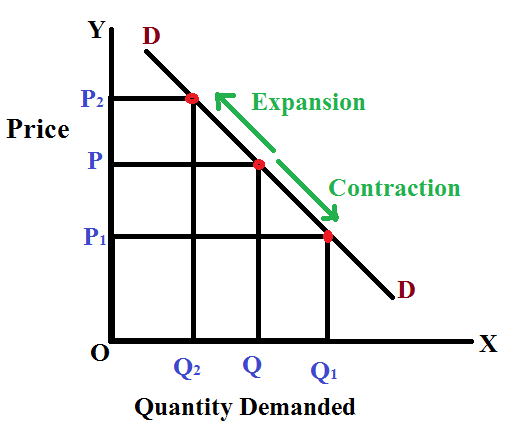
Law of demand - theres an inverse relationship between price and quanitity demanded. As price increases, demand decreases and vice versa. ASSUMING CETERIS PARIBUS - all other factors stay the same.
Non price related factors SHIFT the curve, rather than a movement along the curve.
Non price related factors:
Population
Advertising
Substitutes price
Income
Fashion/tastes
Interest rates
Complements price
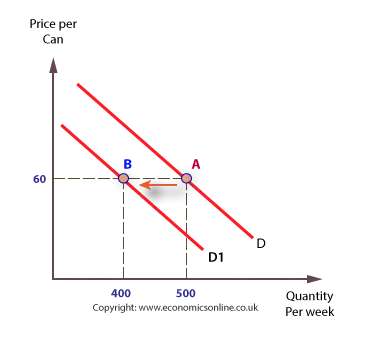
Non price related increase in demand: right shift
Decrease in demand: left shift
Supply in economics
Supply - the quantity of a good or service producers are willing and able to produce at a given price in a given time period
Law of supply - theres a direct relationship between price & quantity supplied. When price increases, quantity supply increases (assuming ceteris paribus)
There is a direct relationship because of profit motive - if a goes up, theres an opportunity for more profit to be be made
An extension of supply happens when the price goes up, so supply will move right along the curve.
A contraction of supply happens when price decreases, so supply will move left along the curve.
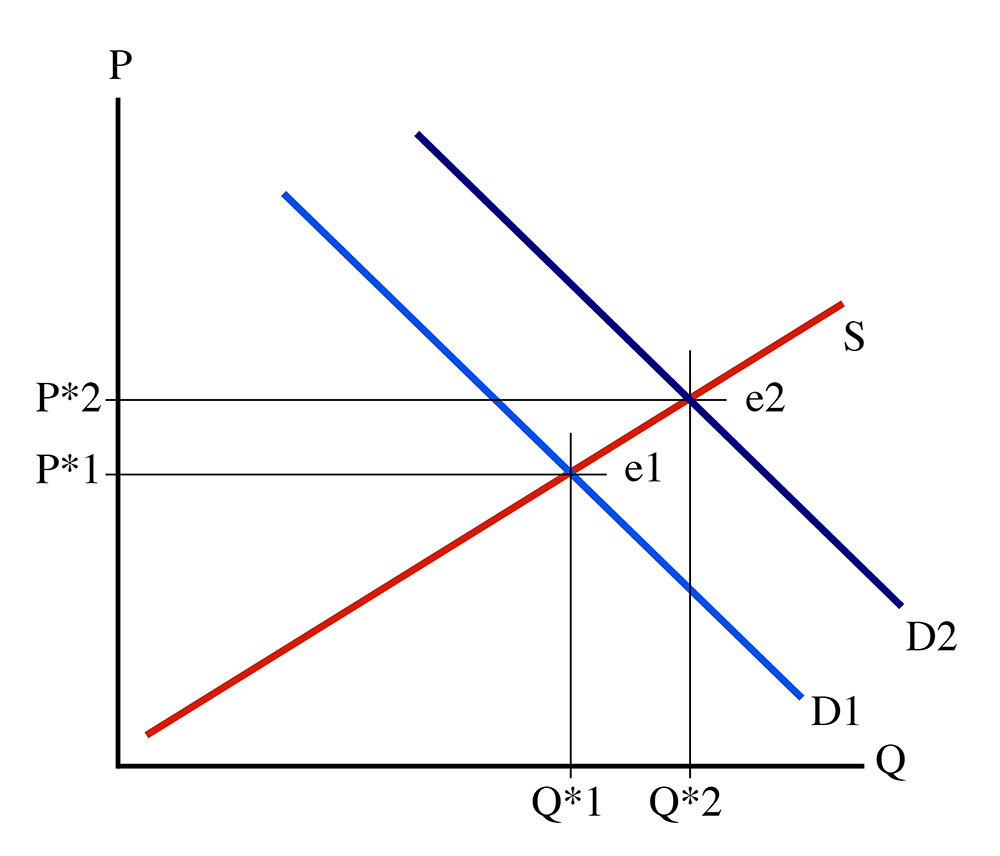
When a non price factor changes supply, the curve will shift.
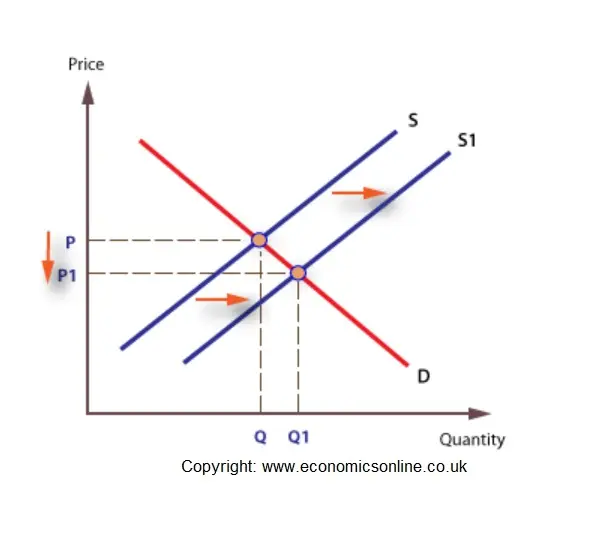
An increase in supply = shifts to the right
A decrease in supply = shifts to the left because producers are less willing and able to produce.
Costs of production:
Productivity
Indirect tax
Number of firms
Technology
Subsidy
Weather
Costs production (utilities, transport, regulation, labour, raw material, oil)
Market equilibrium
Free market - any place where buyers meet suppliers to exchange goods and services, free from market intervention, it can be physical or digital.
Equilibrium - where demand = supply (allocative efficiency)
Disequilibrium is the opposite
Excess demand - prices rise
Excess supply - prices fall