AP HUG VOCAB
UNIT 1
1.1 Key Terms
Terms | Definition | Example |
Physical Geography | the study of the physical appearance of the many environments on the Earth | the study of landforms, bodies of water, the climate, ect |
Human Geography | the study of human activities | the study of population, cultures, economics, ect |
Models | representations about reality, that focus specific factors of something to make it more understandable | a globe |
Spatial Models | a visual of an area that illustrate spatial distributions | |
Non-spatial Models | something that uses words, graphs, and/or tables to show changes over a period of time; more accurate than spatial models | |
Time-distance decay | things that are physically closer to each other are more closely related to each other |
|
Spatial Patterns | refer to the general set-up of things in different locations/distributions; the distribution of a phenomena in a general area. | density, dispersion, clustered scattered, linked, ect |
Networks | interconnected systems/units; nodes | roads that connect to other states |
Topographic Maps | points of equal elevation are connected, creating shapes that show surface features | a map of the elevation of a mountain |
Direction | used to indicate where something is in comparison to something else | NESW, NE, NW, ect |
Scales of analysis | understanding topics from different scale levels; local, regional, country, or global | the United States at night VS the city of Atlanta at night |
Small-scale maps | show a larger amount of area with less detail | a global scale of the Earth at nigh |
Elevation | the distance of something above the sea (sea level); usually measured in feet or meters; usually shown on maps with contours (isolines) |
|
Physical Maps | display physical features | mountains, rivers, deserts, ect |
Road Maps | display roads/paths | roads, highways, alleys, ect |
Plat Maps | display representations of ownership of land | land/building ownership |
Thematic Maps | visual ways of displaying the relationship of locations and their features, and the phenomenon that happen in those areas |
|
Chloropleth Maps | use colors to display patterns of locations |
|
Dot Distribution Maps | used to show the specific location and distribution of a something on a map; each dot represents one specified quantity |
|
Graduated Symbol Maps | use symbols to indicate size of something; larger size = more; smaller size = less |
|
Isoline Maps | use lines that connect to points to represent change; the closer the lines, the more rapid change; the further the lines, the more relatively similar it is; isometric maps |
|
Accessibility | how quickly and easily people can interact with others in a different location | |
Qualitative Sources | data that is not statistically based | interviews, photos, satellite images, descriptions, cartoons, ect |
Cartographic Scale | the way a map shows the ratio of its size to what it is representing | words: “1 inch equals 10 miles”, ratios: “1:20”; lines: a line that shows how big an area really is |
Relative Distance | indicates how close something is based on time, money, and/or mode of travel | “LHS is about a 10 minute car ride from my house” |
Absolute Location | the precise location of a place | an address, coordinates, ect |
Latitude | horizontal distance; latitude is fat-itude |
|
Equator | imaginary horizontal line; designated as 0 degrees and the poles as 90 degrees north and 90 degrees south |
|
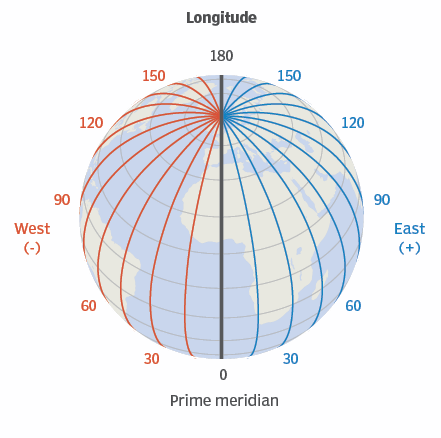
Longitude | vertical distance east + west of the Prime Meridian; longitude is long-itude |
|
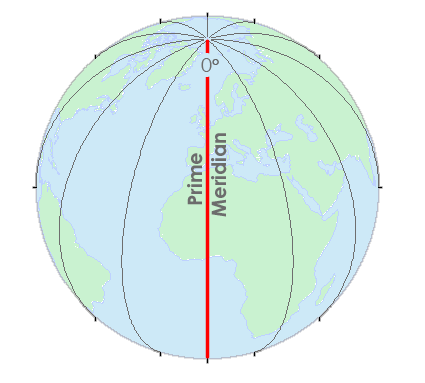
Prime Meridian | imaginary vertical line; designated as 0 degrees |
|
International Date Line | on the opposite side of the Prime Meridian; rough line that changes course to accommodate countries’ borders |
|
Relative Location | the location of something in relation to another; described in terms if connectivity and accessibility | “Georgia is north of Florida” |
Connectivity | how easy it is to get to one place from another with by roads or other links | |
Geospatial Data | data with some kind of location indicator as well as an analysis of something in that area | annual income by country |
Scale | the ratio between the size of something that has been made smaller to fit on a map, and the original size | |
Absolute Distance | measured in terms of feet, miles, meters, ect; quantitative units | “LHS is 4.7 miles away from my house” |
Political Maps | display man-made boundaries | state borders, countries, ect |
Distribution | the way a pattern of an event is spread over an area | |
Clustered (agglomerated) Distribution | arranged in a group/concentrated area | cities along the border of the United States and Mexico |
Linear Distribution | arranged in a straight line | towns along a railroad line |
Dispersed Distribution | spread out over a large area | distribution of malls around a city |
Circular Distribution | equally spaced from a certain place, making a circle | the homes of people who shop at a particular store |
Geometric Distribution | regular arrangement | squares/blocks formed by roads in the Midwest |
Random Distribution | no specific pattern or arrangement in their positions | pet owners in a city |
Quantitative Data | numerical data that can be measured | number of immigrants to a specific city |
Cartogram | the size of land according to a statistic |
|
Patterns | how things are arranged | |
Reference Maps | maps that are designed for people to use for general knowledge | |
Large-Scale Maps | show a smaller amount of area with more detail | the North American continent in the night |
1.2 Key Terms
Landscape Analysis | the description of an area of land | |
Field Observations | physically seeing and making observations about a place | |
Spatial Data | any information connected to a specific place | |
Remote Sensing | information about a place gathered by a satellite | |
Aerial Photography | professional pictures taken of a location within the atmosphere | |
Fieldwork | observing and recording data about a location |
1.3 Key Terms
Geovisual | 2D or 3D maps that help people zoom in and out to observe better | |
Community-Based Solutions | solutions to problems that are created so that the people of the area can accept it better | |
Geographic Information System (GIS) | a computer system for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on Earth's surface | |
Remote Sensing | pictures and videos taken and gathered by satellites | |
Global Positioning System (GPS) | the usage of multiple satellites to pin-point the exact location of someone/something |
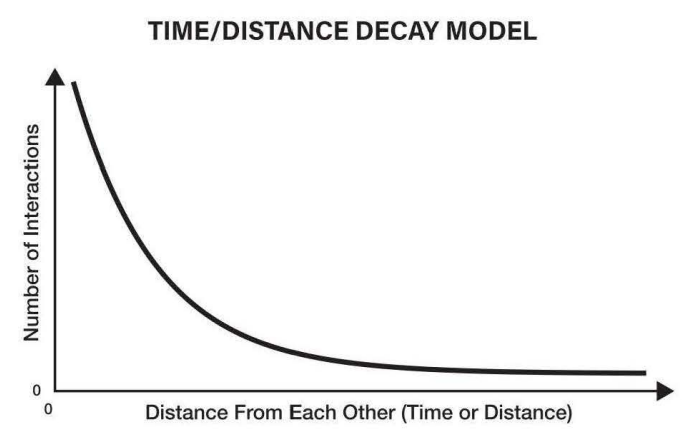 countries that are culturally and economically similar generally are physically closer to each other
countries that are culturally and economically similar generally are physically closer to each other Mount Everest is over 29,000 feet
Mount Everest is over 29,000 feet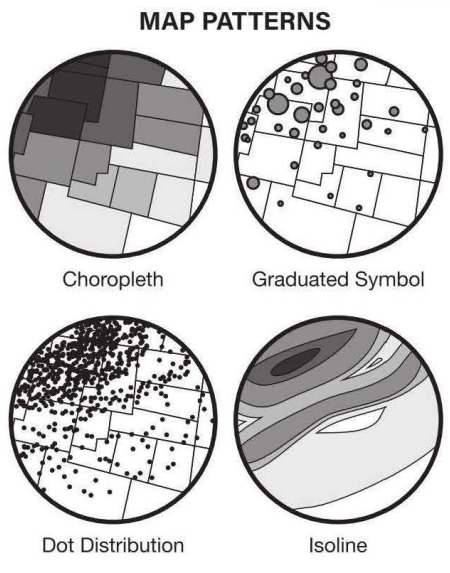
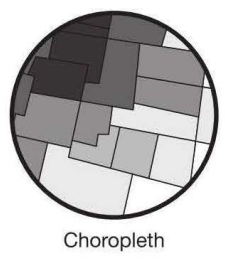 percentage of people that speak English
percentage of people that speak English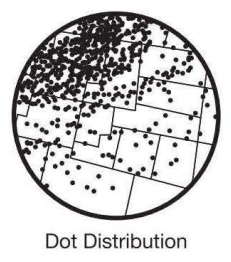 the number of cities on a map
the number of cities on a map population density in a state
population density in a state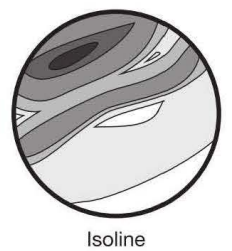 elevation of the United States map; LA and NY are connected
elevation of the United States map; LA and NY are connected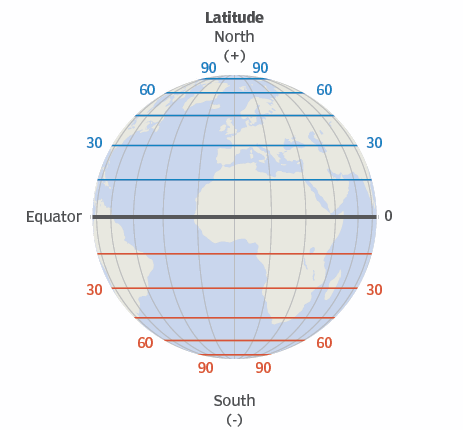


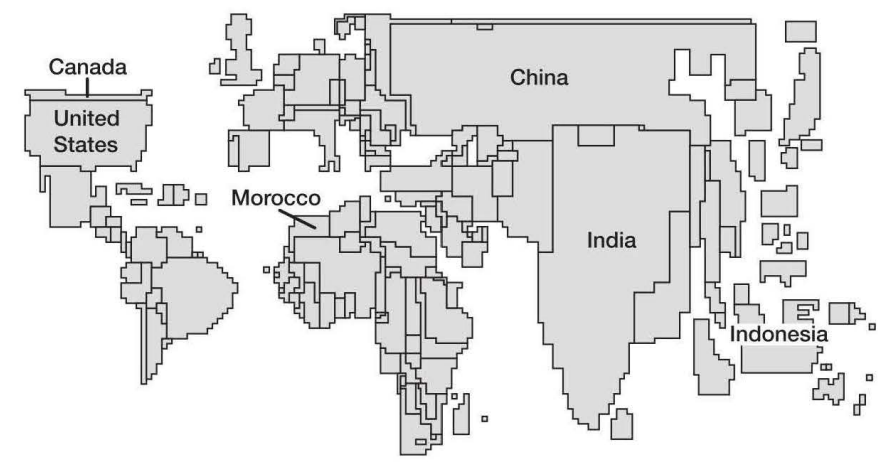 the size of Morocco and Canada are roughly the same size, given their similar population
the size of Morocco and Canada are roughly the same size, given their similar population