Unit 2: Cognition
Cognitive Dissonance → the way the brain processes information
Cognitive → our cognitions: thoughts, beliefs, attitudes, values
Dissonance → inconsistency, clash, not in harmony
reason that you find ways to justify your actions
Ex:
Beleif: I dont eat donuts. Action: I just slammed three donuts
clash = dissonance = bad = reduce
change your thought → “I don’t eat donuts past noon”
What can you do about it?
Change a thought
Change a behavior
Add a thought
Trivialize the inconsistency
Leon Festinger
classic experiment demonstrating cognitive dissonance
had people preform a really boring task
asked them to report to the next subject that the task was enjoyable
½ the people paid $1
½ the people paid $20
Metacognition → thinking about the way that you think
Clive Wearing → man in England got sick with Herpesviral Encephalitis
attacked Hypocamus
transfers short-term memory to long-term
only remebers 10 seconds at a time
one doctor recemmended journaling to try and remember
would forget he wrote stuff and would cross it our and re-write it
suggested making a video to watch every day
didn’t work as he would forget it everyday
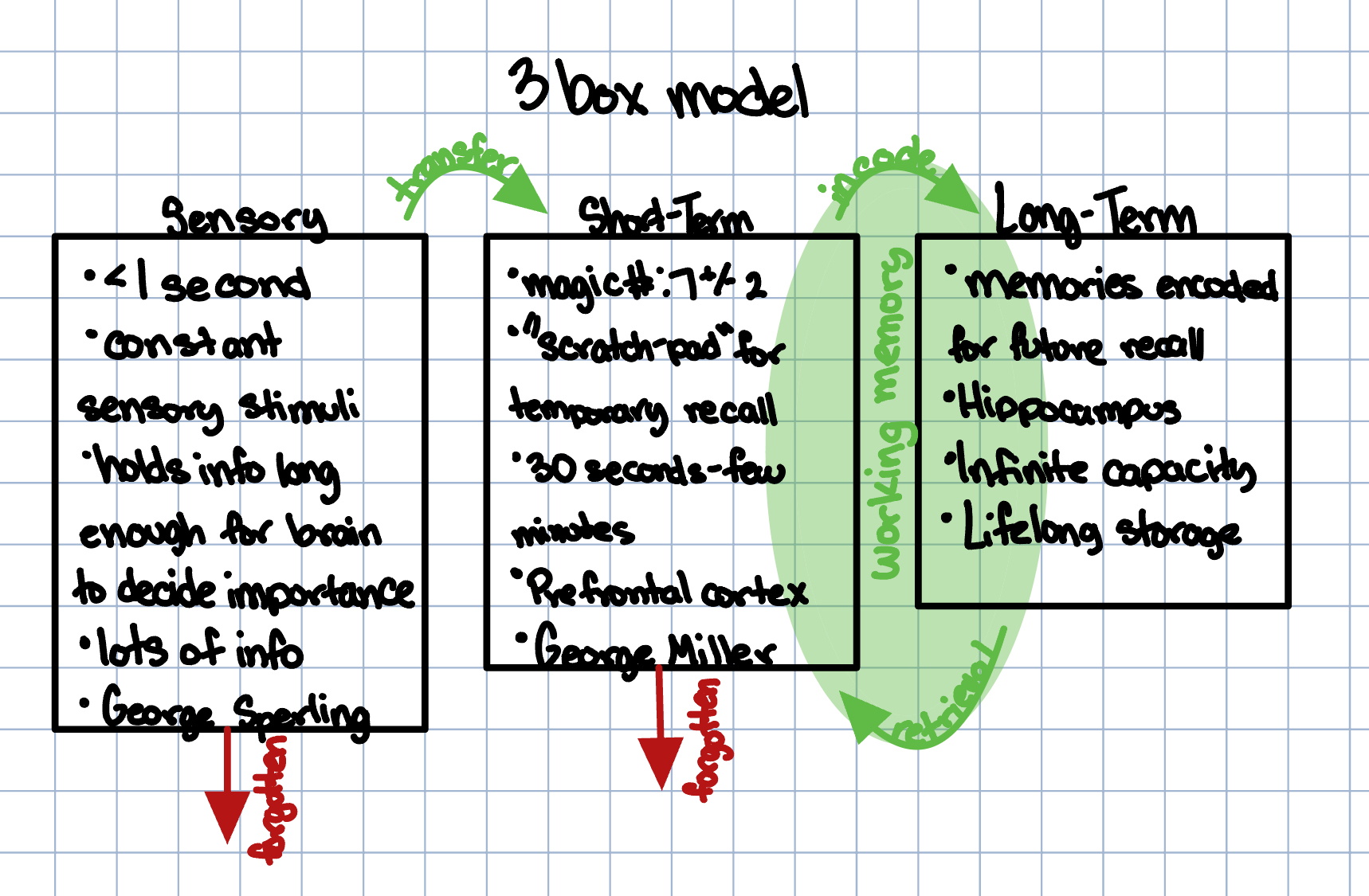
Sensory Memory
George Sperling
flashed 3×3 grid for twentieth of a second to participants
had to reall one of the rows immediatley after
indicaated which to remember with tone
participants could recall
Primacy Effect → ability to remember things at the beginning but forget things at the end
Recency Effect → ability to remember things at the end more than at the top
Serial Position Effect → remember things at the beginning and the end but foget things in the middle
Short Term Memory is stored in acoustic formation →ex: rhyming words
Long Term Memory is stored in semantic format → ex:similar words but acoustically dissimilar
Semantic Network Theroy → storage in our LTM based largley in semantics
similar to word webs in another class
folders in your bag or you HD computer
sleep, slumber, tired, night, day, dream, comfort, morning, awake (9)
Sleep wasnt on the list but because of semantic network we thought it was
Types of Memory:
Episodic → memories of specific events,”flashbulb”
Semantic → general knowledge of the world
Procedural → memory of skills and how to perform them, “Muscle memory”
Explicit Memories → conscious memories of facts or events we try to remember
Implicit Memories → Unintentional memories that may not know we have
Retrival errors
Proactive Interference → can‘t remember new information because old information is interfering
forgetting new infromation
Retroactive Interference → can’t remember the old information because of the new information
Levels of Processing → Long-term Potentiation
focus on the depth of processing involves memory, and predicts the deeper information is processed, the longer a memory trace will last
Shallow Processing
Structural processing → when we encode only the physical qualitites of something
Phenomic processing → which is when we encode its sound
shallow processing only involves mainting rehearsal and leads to fairly short-term retention of information
Deep Processing
Semantic processing → happens when we encode the meaning of a word and relate it to similar words with similar meaning
Deep processing → elaboration rehearsal which involves a more meaningful analysis
giving words meaning or linking them with previous knowledge
Constructive Memory → Elizabeth Loftus
memories are not always what they seem
Constructed memory = created memory
aka “false recollection”
aka “misinformation effect”
your memory of what happened, what others said happened,and what you wished had happened
used 6 different groups
verbs and mean speed estimates:
smashed - 40.5
collided - 39.3
bumped - 38.1
hit - 34.0
contacted -31.8
6th group - “Was the car going faster or slower than 60mph?” How fast was the car going?
Called all participants back and asked if they had seen any broken glass
Smashed → yes - 16 no-34 Hit → yes- 7 no - 43
Trial-and-Error → trying and failing, over and over again
Thomas Edison tried thousands of light bulb filaments before he stumbled upon one that worked
Algorithms → step-by-step procedure that guarantees you arrive at the correct answer
Heuristics → a mental shortcut that allows people to solve problems and make judgments quickly and efficiently
Why do we use them?
reduce mental efforts needed to make decisions
simplify complex and difficlt questions
they’re generally a fast and accurate way to make conclusions
helps with problem solving
Downsides?
make out lives easier
allows us to use a rule-of-thumb to make decisions
leads to Cognitive Biases
Anchoring Heurisitcs→ influences the way people intuitvely assess probabilities
Availability Heurisitics → mental shortcut that relies on immediate, easily recalled examples that come to mind
Representativeness Heuristics →decisions made based on whether or not they match our prototype
Prototype matching
Language → the combination of gestured,spoke, and/or written words to communicate meaning
phonemes
morphemes
grammer
syntax
semantics
Phoemes → smallest distinctive sounds in a language
not the same as letters
english uses about 40
Bat “b-a-t”
That “th-a-t”
Morphemes → smallest meaningful units of language
most morphemes combine two or more phonemes
some are words, others are parts of words
“Readers” = 3 morphemes
Grammar → Language’s set of rules that enable people to communicate
Guide us in deriving meaning from sounds(semantics) and ordering words in a sentence(syntax)
Language development → babbling stage
3-4 months after birth
a stage of speech development where the infact utters sounds unlike the family language
consonant-vowel pairs
10 months or so - recognize native language
Language Development → one-word stage
around first birthday
learned that sounds cary meaning
can begin to say small words
meant to convey a sentence
18 months = 1 word per day
Language Development → Two-word Stage
telegraphic speech
around the 2nd Birthday
Mostly nouns and verbs
Language Acquisition and Development
Behavioritste beleive that languge develops as a result of certain behaviors
Nativisits beleive that we’re born with a specific language-learning area in our brain
Behaviorists → langage like all behaviors is learned through operant conditioning and shaping
Nativisits
Noam Chomsky
Language Acquisition Device
theorized that humans are born with langiage acquisition devices(ability to learn language rapidly as children)
critical period for learning language may exist
nativist theory of language acquisition
Linguistic Relativity Hypothesis
Language and Cognition
Physcologist Benjamin Whorf
the language we use might control, and in some ways limit our thinking
Broca’s Area
area of the brain that is chiefly responsible for structuring speech
Temporal Lobe of the dominant hemisphere (usually left)
Patients know what they are trying to say, and know that they get it wrong. Just can’t help it
Aphasia → speech problem
Wernicke’s Area
area of the brain that is chiefly responsible for the understanding of written and spoken language
In the parietal lobe of the dominant side of the brain
patients know in their head what to day, are unaware that they are not speaking correctly
Fluency Aphasia
Insight Learning → when one suddenly realizes how to solve a problem
Wolfgang Kohler → Gestalt Psychologist
explors insight learning with chimpanzees
suspended a bannana from the ceiling out of reach of a group of chimpanzees
room had many boxes with tools
chimps spent most time running around in frustration
suddenly, they piled up the boxes, climbed up, and grabbed the bannana