Foot Anatomy
Sole/plantar aspect: the bottom of the foot
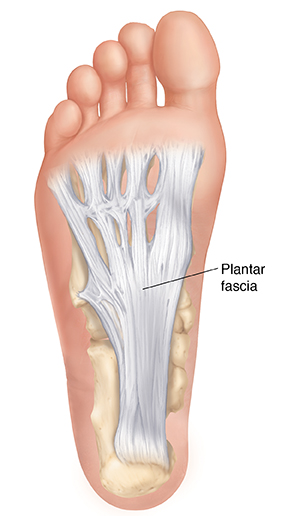
}}Plantar aponeurosis}}
a thick band of fibrous tissue which extends from heel to toes
@@Posteriorly@@: attached to medial tubercle of calcaneus
@@Anteriorly@@: divides into 5 slips that pass to all toes
@@Laterally@@: on each side, attached to metatarsal bones by %%medial and lateral plantar intermuscular septa%%
}}Sole muscles}}
2 groups of muscles:
- @@extrinsic muscles:@@ found in the lower leg, act to dorsiflex, plantarflex, invert and evert the foot
- @@intrinsic muscles:@@ found within the foot and primarily act to ==move the toes and support foot arches to maintain foot structure==
}}Intrinsic muscles}}
Divided into 4 layers:
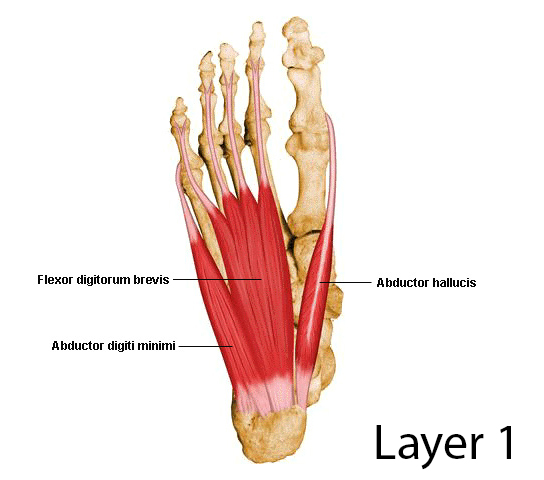
First layer
- most superficial
- immediately underneath plantar fascia
Contains 3 muscles:
- ^^Abductor hallucis^^
- ^^Flexor digitorum brevis^^
- %%Abductor digiti mini%%
All the muscles are supplied by ^^medial plantar nerve^^, except abductor digiti minimi (supplied by %%lateral plantar nerve%%)
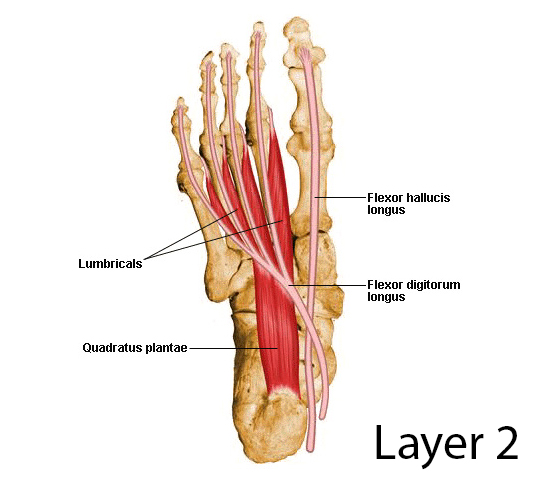
Second layer
- deep to 1st layer
Contains 2 muscles and 2 tendons:
- %%Quadratus plantae%% (flexor digitorum accessories)
- %%4 Lumbrical muscles%% (^^1st lumbrical muscle supplied by medial plantar nerve^^)
- Tendon of flexor digitorum longus (crosses superficial to FHL to reach insertion)
- Tendon of flexor hallucis longus
All the muscles are supplied by %%lateral plantar nerve,%% except 1st lumbrical muscle (supplied by ^^medial plantar nerve^^ )
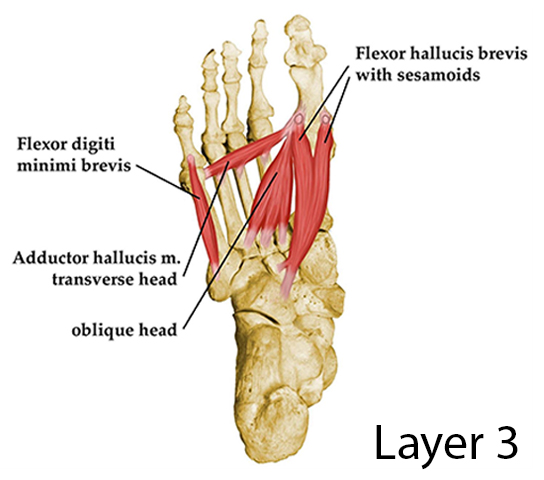
Third layer
- deep to 2nd layer
- 2 sesamoid bones develop in tendon of adductor hallucis
Contains 3 muscles:
- ^^Flexor hallucis brevis^^
- %%Adductor hallucis%% (originates by 2 heads: oblique and transverse)
- %%Flexor digiti minimi brevis%%
All the muscles are supplied by %%lateral plantar nerve,%% except flexor hallucis brevis (supplied by ^^medial plantar nerve^^ )
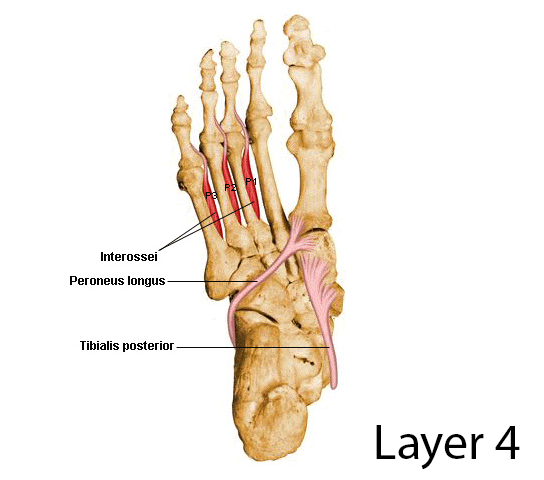
Fourth layer
- deepest layer
Contains 2 muscles and 2 tendons:
- %%Plantar interossei%%
- %%Dorsal interossei%%
- Tendon of fibularis longus
- Tendon of tibialis posterior
All muscles are supplied by %%lateral plantar nerve%%
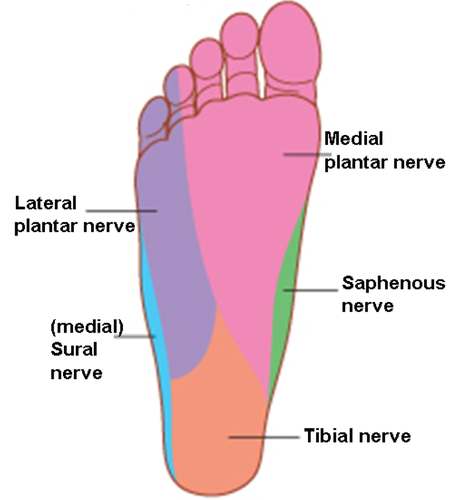
}}Sole Nerves and Vessels}}
{{Plantar nerves{{
The sole is innervated by ==2 terminal branches of tibial nerve:==
- @@medial plantar nerve@@: largest and accompanies medial plantar artery
- @@lateral plantar nerve@@: smallest and accompanies lateral plantar artery
Medial plantar nerve
- arises beneath the flexor retinaculum
- passes forward deep to the abductor hallucis muscle
Branches:
- Muscular:
- abductor hallucis
- flexor digitorum brevis
- 1st lumbrical muscle
- flexor hallucis brevis
- Cutaneous
- medial 2/3 of the sole
Lateral plantar nerve
- arises beneath the flexor retinaculum
- passes forward deep to the abductor hallucis muscle
- reachs base of 5th metatarsal bone, and divides into 2 branches:
- superficial
- deep
Branches:
- Muscular:
- abductor digiti minimi
- 2nd, 3rd, 4th lumbrical muscle
- adductor hallucis
- flexor digiti minimi brevis
- all interossei (4th layer)
- Cutaneous
- lateral 1/3 of the sole
<<Plantar vessels<<
Medial plantar artery
- smallest
- terminal branch of ==posterior tibial artery==
- arises beneath flexor retinaculum
- passes forward deep to abductor hallucis muscle
Lateral plantar artery
- largest
- terminal branch of ==posterior tibial artery==
- arises beneath flexor retinaculum
- passes forward deep to abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis muscles
- on reaching base of 5th metatarsal bone, it curves medially to form ==deep plantar arch==
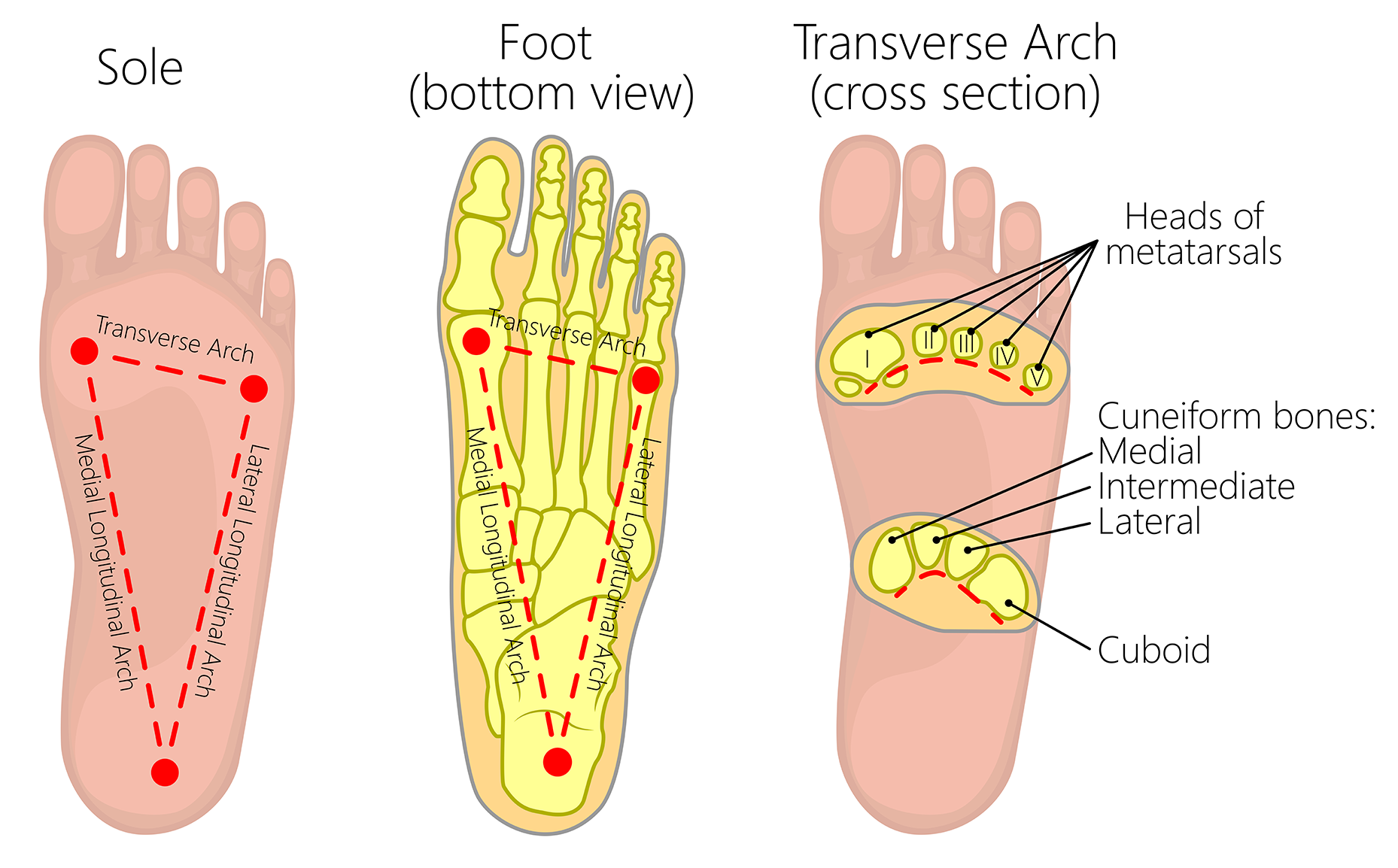
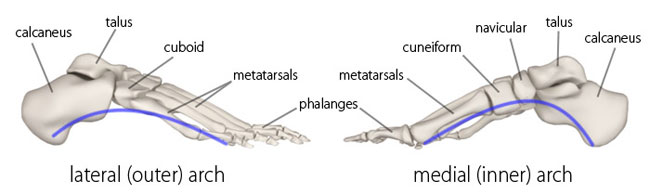
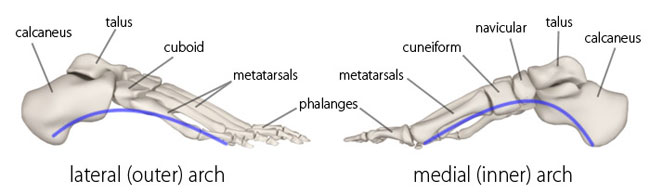
}}Arches of Foot}}
- 3 arches:
- 2 longitudinal (medial + lateral)
- 1 transverse
- main function: to support body weight and act as a lever to propel the body
Medial longitudinal arch
@@Formed by:@@
- calcaneus
- talus
- navicular
- 3 cuneiform bones
- medial 3 metatarsal bones
@@Keystone bone@@: ==talus==
@@Supporting structures:@@
plantar aponeurosis
muscles:
- tendons of tibialis anterior
- tibialis posterior
- flexor hallucis longus
- fibularis longus
- intrinsic muscles
ligaments:
- spring
- deltoid
- long and short
- plantar and interosseous
Lateral longitudinal arch
- flatter than medial arch
- lies on the ground during standing position
@@Formed by:@@
- calcaneus
- cuboid
- lateral 2 metatarsal bones
@@Keystone bone:@@ ==cuboid==
@@Supporting structures:@@
muscles:
- tendons of fibularis longus, brevis, and tertius
- intrinsic muscles
ligaments:
- long and short
- plantar and interosseous
Transverse arch
@@Formed by:@@
- cuboid
- 3 cuneiforms
- bases of metatarsal bones
@@Keystone bone:@@ ==intermediate cuneiform==
@@Supporting structures:@@
muscles:
- tendons fibularis longus (most important)
- slips of tibialis posterior tendon (pulling tarsal bone together)
- transverse head of adductor hallucis (drawing metatarsal bones)
ligaments:
- long and short
- plantar and interosseous