Nutrition/Metabolism Part 1
Nutrition and Health
- nutrition- composition and quality of food intake and the utilization of food by a living organism
- How does your body use nutrients from your diet?
- energy- biochemical reactions release the energy in carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
- building blocks for structures- this is how lots of proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids get used
- regulation of body processes- all chemical reactions in the body (metabolism) are regulated to create a stable environment that is said to be in homeostasis
- malnutrition- when the organism is not receiving the optimal amount of nutrients to be healthy
- undernutrition- inadequate supply of nutrient amount or type
- most organisms are thought to live in an undernourished state- on the edge of starvation
- overnutrition- plenty of nutrients in amount and type
- tends to be in humans in developed countries
- optimal nutrition- amount and type of nutrients in the diet designed to increase health and longevity
Cardiovascular Disease and Health Disparities
- heart disease is the leading cause of death for men & women as well as people of most racial & ethnic groups in the US
- 1 person dies every 37 seconds from cardiovascular disease in the US
- about 647,000 Americans die from heart disease each year- 1 in every 4 deaths
- heart disease costs the US about $219 billion each year from 2014 to 2015
- includes the cost of health care services, medicines, and lost productivity because of death
- 7 things that contribute to heart disease- smoking, BMI, physical activity, diet, total cholesterol, BP, diabetes
- children (ages 12-19) tend to be okay in all categories except diet, physical activity, and BMI
- children have increased consumption of energy-dense, nutrient-poor foods
- children also have lower physical activity now
- unhealthy diets + lack of physical activity = increased BMI and risk of obesity
- adults carry over these bad diet practices from childhood
- 10 dietary factors of cardiovascular disease
- low intake of fruit
- low intake of vegetables
- low intake of nuts/seeds
- low intake of whole grains
- low intake of seafood omega-3 fats
- low intake of polyunsaturated fats
- high intake of sodium
- high intake of unprocessed red meat
- high intake of processed meats
- high intake of sugar-sweetened beverages
- proportion of younger people (ages 25-54) dying because of cardiometabolic disease higher because younger people shouldn’t be dying of cardiovascular disease
- proportion of african-american people dying because of heart disease higher than proportion of white people
- mainly due to social determinants of health
- main comorbidities of COVID- heart disease & diabetes
Energy Density and Oxidative Metabolism
energy-dense/nutrient-poor foods- foods that have high caloric content with very other little nutrients
carbs and fats are broken down via metabolic processes and converted to adenosine triphosphate- the body’s energy currency
ATP has three phosphate groups with 2 high energy phosphoanhydride bonds and a lower energy phosphate ester bond linking the adenosine and the alpha phosphate
ATP is then used to fuel any mechanical work or process that requires energy input
calorie- the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1 g of water by 1 degree C
- different than the Calorie/kilocalorie- 1000 calories
amount of kcal/g in each macronutrient
- fats- 9 kcal/g
- alcohol- 7 kcal/g
- carbohydrates- 4 kcal/g
- protein- 4 kcal/g
compounds are broken down for energy by oxidative metabolism- which is why we need oxygen
- taking carbons in a compound from a reduced state where they have more electrons assigned to them to a compound where they are in an oxidized state with fewer electrons assigned to them
assign the central carbon 2 electrons per bond if bonded to a hydrogen, 1 electron per bond if bonded to another carbon, 0 per bond if bonded to oxygen
- this is because H < C << O in terms of electronegativity
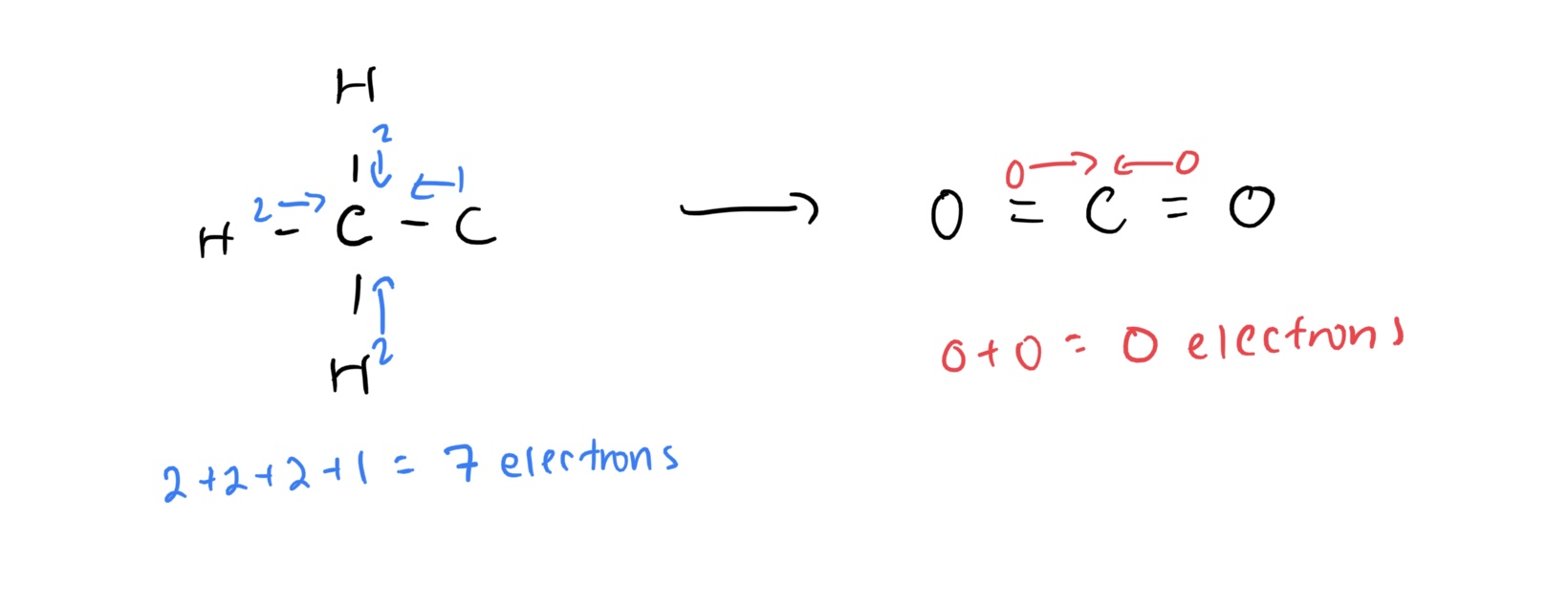
the above reactant compound is actually the first part of a fat
- so fats have more energy per g because they have high reduction potential
carbohydrates and proteins are already partially reduced because they have carbons bonded to oxygens
- alcohols are somewhat in between carbohydrates/proteins & fats because they have a hydrocarbon portion bonded to an OH group
Types of Fats
- different types of fats
- saturated fats- fats where all the carbons have as many hydrogens bonded to them as possible
- higher melting point, solid at room temperature, mostly animal fats
- unsaturated fats- fats that have at least one double bond within the carbon chain
- lower melting point, liquid at room temperature, mostly plant fats
- monounsaturated- only 1 double bond
- polyunsaturated- have many double bonds
- cis fats- have “kinks” in the carbon chain
- the parts of the carbon chain are on the same side of the double bond
- lower melting point because they can’t all line up
- trans fats- look like saturated fats
- the parts of the carbon chain are on opposite sides of the double bond
- formed by partial hydrogenation- reaction where polyunsaturated fatty acids get hydrogens attached to them to make them more saturated
- makes margarine
- saturated and trans fats are associated with increased blood cholesterol