Organism Level Systems
I. Definitions and Concepts
1. ADH
A hormone secreted by the pituitary gland which increases water reabsorption in the kidney (making the kidney tubules more permeable to water)
2. Adrenaline
A hormone released by the adrenal gland which increases heart rate and breathing rate (involved in fight/flight).
It also raises blood sugar levels by increasing the conversion of glycogen into glucose
3. Auxin
A plant hormone that is responsible for cell elongation
4. Central Nervous System (CNS)
The brain and the spinal cord
5. Cerebellum
The region of the brain that controls unconscious functions such as posture, balance, and muscular movement
6. Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum
7. Cerebrum
The highly folded region of the brain that is responsible for controlling voluntary actions such as learning, personality, and memory.
It is divided into the right and left hemispheres
8. Ciliary Body
An extension of the iris
It contains the ciliary muscle which can contract or relax allowing the eye to focus
9. Colour Blindness
A condition where a person has a defect in the receptors or a lack of receptors in the retina
10. Contraception
Methods that are used to prevent pregnancy
11. Cornea
The part of the eye that refracts light as it enters, focusing it onto the retina
12. Dormancy
A period of time in which seeds hibernate
This stops when they germinate
13. Effector
A gland or muscle that produces a response to the stimulus to restore optimum conditions
14. Endocrine Glands
A group of cells that are specialized in secreting chemical (hormones) directly into the bloodstream
15. Endocrine System
A chemical messenger system that releases hormones directly into the bloodstream to control metabolism, development, growth, and reproduction
16. Ethene
A plant hormone that promotes fruit ripening
17. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
A female reproductive hormone that is released by the pituitary gland
It is responsible for the maturation of an egg in the ovary
18. Geotropism
The growth response of a plant to gravity
19. Germination
The process by which seeds develop into plants
20. Gibberellins
Plant hormones that initiate germination and flowering
21. Glucagon
A hormone produced by the pancreas which works with insulin to control blood sugar levels.
It increases blood glucose concentration by converting glycogen into glucose
22. Herbicide
A type of pesticide used to kill unwanted plants (weeds)
23. Homeostasis
The maintenance of a stable internal environment in the body despite fluctuations in internal and external conditions
24. Hormone
A chemical messenger secreted by the endocrine glands into the bloodstream and transported to receptors on target organs
25. Hypothalamus
The part of the brain that is the regulation center for temperature and water balance of the body
26. Infertility
The inability to reproduce after 12 months or more of unprotected sex
27. Insulin
A hormone produced by the pancreas which controls the body’s blood sugar levels
It works to decrease glucose levels
28. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
The fertilization of an egg using sperm outside of the body
IVF is used when a couple are having difficulty conceiving
29. Iris
The part of the eye that contracts or relaxes to control the amount of light entering the eye
30. Kidney
The organ in the body that maintains water balance and produces urine
31. Lens
A part of the eye that further refracts light to focus it onto the retina
32. Long-Sightedness (Hyperopia)
A defect of the eye where distant objects appear out of focus due to the convergence of light rays in front of the retina
33. Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
A female reproductive hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates the release of an egg
34. Medulla
The part of the brain responsible for non-voluntary movement such as breathing rate and heart rate
35. Menstrual Cycle
The monthly cycle in women that involves the development of the uterus lining, ovulation, maintenance of the uterus lining and it shedding
36. Motor Neuron
The neuron that transmits impulses from the relay neuron to the effector to produce a response
37. Negative Feedback System
A system which works to reverse the initial stimulus
38. Nephron
A kidney filtering unit
39. Estrogen
A female sex hormone produced in the ovaries that regulates the menstrual cycle and controls the development of secondary sexual characteristics
40. Optic Nerve
The nerve that carries impulses between the brain and the eye
41. Osmosis
The net movement of water molecules from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration across a partially permeable membrane
42. Osmotic Lysis
When water moves into an animal cell causing it to burst
43. Osmotic Shrinking
When water moves out of an animal cell causing the cell to shrink
44. Parthenocarpic Fruit Development
The development of seedless fruit
45. Phototropism
The growth response of a plant to unilateral light
46. Pituitary Gland
The gland that stores and releases hormones which regulate many bodily functions
47. Progesterone
The hormone that maintains the uterus lining during the later stages of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy
48. Pupil
A hole in the center of the iris
49. Receptor
A cell or organ that recognizes the stimulus
50. Reflex Arc
The pathway of neurons involved in a reflex action

51. Relay Neuron
The neuron that transmits electrical impulses from the sensory neuron to the motor neuron
52. Renal Artery
The blood vessel that provides the kidney with blood
53. Renal Vein
The blood vessel that takes blood away from the kidney
54. Retina
The layer at the back of the eye that contains light receptors and is sensitive to light
55. Root Cuttings
A method of cloning plants in which a root is cut from a parent plant and replanted in compost
56. Rooting Powder
A powder that contains auxins
The cut root is dipped into this before being replanted (during root cuttings)
57. Sensory Neuron
The neuron that detects the stimulus and transmits the electrical impulse to the relay neuron located in the spinal cord
58. Short-Sightedness (Myopia)
A defect of the eye where distant objects appear out of focus due to the convergence of light rays in front of the retina
59. Suspensory Ligaments
Attach the lens to the ciliary muscle
60. Synapse
The junction between two neurons (nerve cells)
61. Testosterone
The male reproductive hormone that controls sperm production and the development of the secondary sexual characteristics
62. Thyrozine
A hormone released by an endocrine gland (thyroid gland) that controls the metabolic rate and the rate of glucose uptake during respiration
It also promotes growth
63. Tissue Culture
A method of cloning plants where plants are grown in a growth medium containing many nutrients
64. Type 1 Diabetes
A condition in which the pancreas fails to produce insulin resulting in high blood sugar levels
65. Type 2 Diabetes
A condition in which a person develops insulin resistance or doesn’t produce enough insulin
66. Urine
A liquid produced by the kidneys to help maintain water balance
It contains mineral ions, water, and urea
67. Vasoconstriction
The constriction of blood vessels
68. Vasodilation
The dilation of blood vessels
69. Water Potential
A measure for the tendency of water to move from one area to another are
It is represented by the Ψ (Psi)
II. Coordination and Control: The Nervous System
1. How the Nervous System Coordinates Responses
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord
It allows us to make sense of our surroundings and respond to it in order to survive
Receptor cells convert a stimulus (such as a bright light) into an electrical impulse
This electrical impulse travels along cells called sensory neurons to the central nervous system (CNS)
Here, the information is processed and the appropriate response is coordinated, resulting in an electrical impulse being sent along motor neurons to effectors
The effectors carry out the response (this may be muscles contracting or glands secreting hormones)
2. Reflex Arc
The reflex arc is a subconscious response to a dangerous stimuli, such as a hot surface
Sometimes an extremely quick response is needed and there is not enough time for it to go through the conscious portion of brain so the CNS is involved instead
A stimulus is detected by receptors, such as thermoreceptors in fingertips detecting heat
Impulses are sent along a sensory neuron
In the CNS the impulse passes to a relay neuron
Impulses are sent along a motor neuron
The impulse reaches an effector resulting in the appropriate response, such as a contraction of the biceps to move the arm away from the heat source
3. The Eye
a. Structures of the Eye:
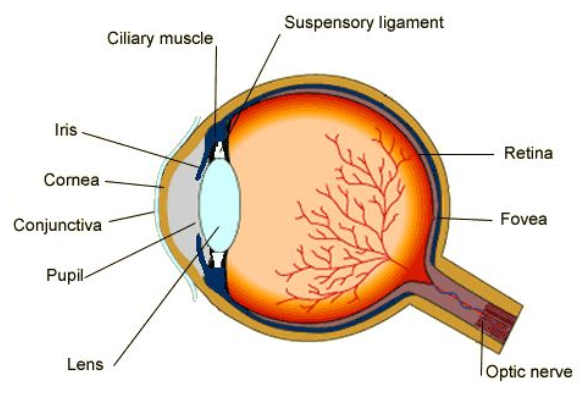
Cornea
The transparent outer part of the eye
It refracts light to reach the retina
Iris
The colored part of the eye that does not allow light to go through
Controls how much light enters the eye
In bright light, the circular muscles contract and radial muscles relax to make the pupil smaller, avoiding damage to the retina
In dim light, the circular muscles relax and the radial muscles contract to make the pupil larger, so more light can enter to create a better image
Lens
Transparent, biconvex disc that attaches to ciliary muscles by the suspensory ligaments
Focuses light onto the retina
Retina
Contains light receptors
Contains rods (respond to dim light) and cones (respond to color)
Optic Nerve
Carries impulses between the eye and the brain
b. Common Defects
Color Blindness
The inability to tell the difference between different colors due to the lack of or defects in the receptors in the retina
It is an inherited condition and the most common form is red-green color blindness
Myopia (Short-Sightedness)
The ability to see near objects but not distant objects, due to the lens focusing the image in front of the retina.
They are treated by concave lenses in glasses
Hyperopia (Long-Sightedness)
Ability to see distant objects but not near objects, due to the lens focusing the image behind the retina
They are treated by convex lenses in glasses
4. The Brain
a. Structure of the Brain
Cerebrum
a. Functions
Intelligence
Vocabulary
Personality
Conscious Thought
b. Features
The largest part of the brain and divides into 2 cerebral hemispheres
Each half processes the information it receives from the opposite side of the body
The outside is made from grey matter (containing myelinated nerves) and the inside is made of white matter
Cerebellum
Coordinate voluntary body movements and help with balance
Medulla
Control center for heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate
Hypothalamus
Control temperature and water balance in the body through the hormonal system
Pituitary gland
An important gland releasing hormones, such as growth hormone into the blood
b. Limitations in Investigating and Treating Brain Damage
There are ethical issues with investigating brain damage, as it is unethical to ask patients who may not be in the state to make and informed decision about whether they want to take part in a study
The investigative study would require surgery, which has many risk in itself
There is also a considerable amount that we have yet to learn about the brain and its functions so it may be hard to interpret findings of case studies
There are limitations in treating brain damage because the central nervous system cells do not have the ability to regenerate and repair and there may be areas that are very difficult or dangerous to access during surgery
Drugs may also have difficulty penetrating the different membranes surrounding the brain
III. Coordination and Control: The Endocrine System
1. Endocrine System
Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted by endocrine glands into the bloodstream, where they are transported around the body to receptors on the target organ
The pituitary gland, mentioned before, it one of the most important glands
Endocrine System | Nervous System | |
|---|---|---|
Type of Signal | Chemical | Electrical |
Transmitter | Hormones in Bloodstream | Nerve Cells |
Speed of Response | Slower | Very Fast |
Duration of Response | Long | Short |
a. Examples of Hormones
Adrenaline
Produced by the adrenal glands that sit on top of kidneys
Targets many different organs, such as the heart and lungs
Responsible for the ‘fight or flight’ response for survival
Increases heart rate, dilates pupils, makes hairs stand erect, increasing breathing rate
Thyroxine
Produced by thyroid gland in the neck
Responsible for controlling metabolic rate, meaning it controls how quickly oxygen and food react to release energy. It is therefore responsible for growth.
Example of negative feedback
If thyroxine levels are too low it stimulates the hypothalamus to produce a hormone called TRH and the pituitary then releases TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) which causes the thyroid to produce more thyroxine.
When the levels are returned to normal these hormones are inhibited to stop further increases.
2. Human Reproduction
Hormones are responsible for controlling puberty and also the menstrual cycle
a. Puberty
Hormones are responsible for the changes to the body that occur during puberty.
Testosterone
Produced by the testes, are responsible for the development of sperm and also secondary sexual characteristics in males, such as deepening voices and increased hair.
Estrogen
Produced by the ovaries, are responsible for secondary sexual characteristics in females, such as breast development and widening hips.
b. Menstrual Cycle
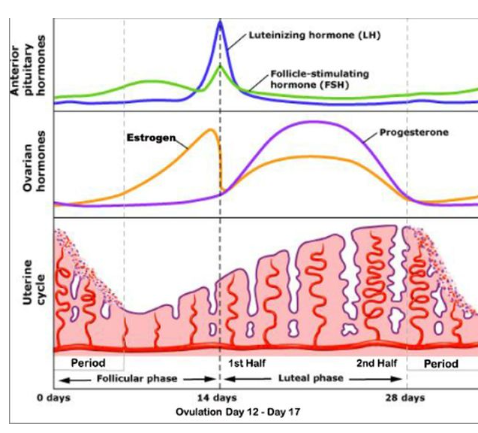
The menstrual cycle last 28 days and the egg is usually released on day 14 (ovulation).
Estrogen
Estrogen causes thickening of the uterus in preparation for implantation of an egg
Levels peak on day 10 and then begin to fall
FSH and LH
Follicle Stimulating Hormone causes maturation of the egg within the ovary
Luteinizing Hormone stimulates the release of the egg during ovulation
A decrease in estrogen causes LH and FSH to start increasing
Ovulation (the release of an egg cell from one of the ovaries) occurs when LH and FSH levels peak
Progesterone
Progesterone maintains the thick lining of uterus
Inhibits the release of LH and FSH
The egg matures on day 14 and progesterone starts increasing after this until it reaches its peak 3 days later
If the egg is not fertilized progesterone levels fall and the uterus lining breaks down in a period that lasts for around 5 days
💡 Menopause occurs when a woman no longer has a menstrual cycle, usually around 50-55 years of age
c. Contraception
Hormonal Methods
a. Oral Contraceptives (The Pill)
Contains progesterone and estrogen, which inhibit the production of FSH so that eggs do not mature
More than 99% effective if taken properly
Side effects such as mood swings, weight gain
b. Contraceptive Implants
More than 99% effective
Cause slow release of progesterone to prevent ovaries from releasing the egg, thickens mucus in cervix so sperm cannot swim through
Will not need to remember to take everyday
Non-Hormonal Methods
a. Physical Barrier Methods such as condoms
Easy to use and obtain and also protects from STIs
However, condoms can rip
Over 99% effective
Can be made more effective with spermicidal agents, but some people can be allergic to it
b. Vasectomy/Tubal Ligation
Sperm tubes/oviducts are cut to prevent gametes becoming fertilised
Almost 100% reliable
However, can be irreversible
c. Copper Intrauterine Device (IUD/The Coil)
T-shaped device implanted into uterus
Stops fertilized embryos implanting, copper kills sperm
Can last for up to 10 years, over 99% effective
Must be fitted by a doctor, small chance of ectopic pregnancy
d. Abstinence
Not taking part in any sexual activity (vaginal, anal, or oral)
d. Fertility Treatments
Allow infertile couples the opportunity to have children
Infertility can be caused by many issues, such as sperm quality or quantity problems or a lack of FSH to mature eggs
However, fertility treatments are not guaranteed to work and if they do they can increase the likelihood of twins, triplets, etc.
Fertility Drugs
FSH and LH mainly used because they stimulate the maturation and release of the egg.
The woman can then become pregnant normally.
IVF
Mother is given FSH and LH to stimulate eggs to mature
Eggs are collected and fertilized by the father’s sperm in a laboratory
The fertilized eggs develop into embryos
These embryos are then implanted into the mother’s uterus
However, can be extremely expensive if it needs to be repeated
3. Plant Hormones
Plants need hormones to coordinate and control growth.
They are needed for tropisms.
Examples of these include phototropism, the response to light, and gravitropism or geotropism, the response to gravity.
Hormones move from the place they are made to where they are needed in order to produce the appropriate response.
a. Auxins
Most plants show positive phototropism because they grow towards the light source.
The plant is exposed to light on one side.
Auxin, a growth hormone, moves to the shaded side of the shoot.
Auxin stimulates cells to grow more here.
This means the shoot bends towards the light.
The plant receives more light, meaning photosynthesis can occur at a faster rate.
Most shoots show negative gravitropism as they grow away from gravity. If a shoot is horizontal:
Auxin moves to the lower side.
The cells of the shoot grow more on the side with most auxin, so it stimulates cells to grow more here.
This makes the shoot bend and grow away from the ground.
This is beneficial as light levels are likely to be higher further away from the ground.
Most roots show positive gravitropism as they grow towards gravity. If a root is horizontal:
Auxin moves to the lower side.
The cells of the root grow more on the side with less auxin, so it stimulates cells to grow on the upper side.
This makes the root bend and grow downwards.
This is beneficial as there are more likely to be increased levels of water and nutrients lower down, and it provides stability for the plant.
When the auxin distribution becomes equal on both sides it grows straight in that directions.
You can investigate the effect of light or gravity on newly germinated seedlings by varying conditions.
Placing in cardboard box and shining light from one side
Attaching a petri dish containing the seedlings to a wall (effects of gravity)
Uses of Auxins
a. As Weed Killers
Many weeds are broad-leaved
Weed killers, containing auxin, have been synthesized so they only affect broad-leaved plants
The increased amount of auxin causes the cells to grow too rapidly
This results in the weed dying
b. As Rooting Powders
Plants with desirable features are cloned to make more plants with the same feature
One way to clone a plant is to take a cutting from the original plant
Rooting powder containing auxin is applied to it and it is placed in the ground
Roots grow and the new plant begins to grow very quickly
c. To Promote Growth in Tissue Culture
Another way to clone a plant is to use tissue culture
Cells from the plant are taken are placed in a growth medium containing lots of nutrients
Hormones such as auxins are added
The cells begin to form roots and shoots
b. Gibberellins
Gibberellins are another plant hormone important to stimulate seed germination, flowering and shedding of leaves
Uses of Gibberellins
a. Ending seed dormancy
In the brewing industry, the germination rate of barley seeds is increased to make malt.
b. Promoting flowering
Instead of requiring certain conditions such as longer days and low temperatures to flower, applying this hormone allows it to flower in any conditions and with bigger flowers.
c. Increasing fruit size
The seeds in fruit produce gibberellins to increase fruit size.
This means that seedless fruit is generally smaller.
Seedless fruit can be sprayed with gibberellins to increase their size.
c. Ethene
Ethene is involved in cell division and the ripening of fruits.
Uses of Ethene
Used in the food industry.
Fruit is picked when it is not ripe
It is firm which means that during transport it gets less bruised and damaged
When it is needed to be sold, it is exposed to ethene and warmer temperatures
Ethene is involved in controlling cell division and stimulates enzymes that result in fruit ripening.
This reduces wastage as more fruit is suitable to be sold and it does not ripen too early
IV. Maintaining Internal Environments
1. Controlling Temperature
a. Homeostasis
The maintenance of a constant internal environment.
Mechanisms are in place to keep optimum conditions despite internal and external changes.
This is needed for enzyme action and all cell functions
b. Thermoregulatory Center
Monitors and controls body temperature is found in the brain.
Has receptors that monitor the temperature of the blood
Has receptors in the skin that send impulses to the thermoregulatory center
c. Human Body Temperature
37.5 degrees celsius
If it becomes too high:
Sweat (evaporates from skin surface resulting in increased energy transfer away from body) is produced from sweat glands
Vasodilation means more blood flows closer to the surface of the skin, resulting in increased energy transfer from the body
If it decreases too much
Sweating stops
Skeletal muscles contract rapidly (shivering) to generate heat from respiration
Hairs stand on end to create an insulating layer, trapping warm air
Vasoconstriction means blood does not flow so close to the surface, resulting in less heat lost
2. Controlling Blood Sugar Levels
The concentration of glucose in your blood needs to be kept within a certain limit because glucose is needed by cells for respiration.
It is controlled by the pancreas
a. Insulin
Eating foods that contain carbohydrates increases the glucose levels in the blood.
If the glucose levels are too high, the pancreas produces the hormone insulin
Insulin binds to cell in target organs (muscles and liver) causing:
Glucose to move from the blood into muscle cells for respiration
Excess glucose to be converted into glycogen which is stored in the liver
The blood glucose concentration is reduced
b. Glucagon
Rigorous activity, e.g. exercise, uses glucose for respiration and therefore there is less in the blood.
If glucose levels decrease, the pancreas produces the hormone glucagon
Glucagon binds to to the liver cells causing glycogen to be broken down into glucose
Glucose is released into the blood, increasing the blood glucose concentration
Your blood glucose concentration is kept constant through using these two hormones. They work in a negative feedback loop.
When blood glucose levels increase/decrease, a hormone is secreted to oppose the change.
The action of this hormone cannot occur continually because when the blood arrives at a certain glucose concentration the other hormone is produced, resulting in the opposite effect.
c. Diabetes
Diabetes is a disease where the body cannot control blood sugar levels properly.
Type 1 Diabetes
The pancreas cannot produce enough insulin
Blood glucose level can rise to a fatal amount
Glucose is excreted with urine and lots of urine is produced leaving the individual very thirsty
It is treated with insulin injections at meal times, which results in glucose being taken up from the bloodstream
It is also advised to limit the intake of simple carbohydrates which contain lots of glucose
Doctors are attempting to cure diabetes with pancreas and pancreatic cell transplants, and genetically engineering pancreatic cells from mice to make insulin
Type 2 Diabetes
The body cells no longer respond to insulin
Blood glucose levels can rise to a fatal amount
Obesity is a risk factor for this disease
Treatments include reducing the number of simple carbohydrates in diet, losing weight and increasing exercise
There are also drugs to make insulin more effective on body cells, help the pancreas make more insulin or reduce the amount of glucose absorbed from the gut
3. Kidneys
a. Effects of Osmotic Changes to Body Fluids
If water concentration of the blood increases, i.e. has higher water potential than the cells, water will move into the cells causing them to expand. Eventually this can lead to bursting (lysis)
If the water concentration of the blood decreases, i.e. has lower water potential than the cells, excess water will leave the cell causing shrinking.
b. Function of the Kidneys
The kidneys are very important in maintaining the balance of water and other substances in the body.
As blood moves through the body, it makes urine by:
Filtering out the waste products, such as water, ions and urea (from amino acids), at high pressures
Selectively reabsorbing useful substances such as glucose, ions and water
c. Structure of the Kidney
The inner part of the kidney is called the medulla and the outer part is called the cortex.
The ureter carries from kidneys to the bladder to be excreted out the body.
The kidney is supplied by the renal artery and a renal vein takes blood away.
Each kidney contains millions of kidney tubules or nephrons and these are made up of a glomerulus (ball of capillaries), a region for selective reabsorption of substances to occur and a kidney tubule where water and salt is regulated.
d. ADH
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) is a hormone involved in the control of the loss of water as urine.
It is released into the pancreas by the pituitary gland when a receptor in the brain detects that the blood is too concentrated.
It travels in the bloodstream to the kidney tubules
An increased amount of ADH reaching the tubules increases their permeability to water, so more moves out of the tubule and back into the bloodstream
This results in a smaller volume of more concentrated (yellow) urine and the blood becoming less concentrated as more water moves into it.
This is an example of a negative feedback loop, because if the concentration of the blood increases/decreases, more/less ADH is secreted to reverse this change.
In high temperatures, increased sweating can lead to dehydration. This can lead to salt loss in sweat, meaning that the kidneys may try to compensate for the change by increasing salt retention. The brain detects this and makes us feel that we are thirsty so that we drink more water to dilute the salts in our blood.