IBC Semester 1
Unit One - Introduction to Chemistry
Vocab
%%Science%% - A way of gaining knowledge about the natural world that depends on evidence, reasoning, and repeated testing
%%Scientific Law%% - Statement describing what happens under certain conditions
%%Scientific Theory%% - Broad explanation widely accepted due to lots of evidence
%%Chemistry%% - Study of matter and the changes it undergoes
%%Physical Chemistry%% - Physical properties of substances to chemical composition and their transformations
%%Organic Chemistry%% - Carbon-based materials and compounds (Living organic + synthetic materials)
%%Inorganic Chemistry%% - Non-carbon substances, properties and behaviors
%%Biochemistry%% - Study of chemical processes that occur in living things.
%%Analytical Chemistry%% - Separation, identification, qualification of chemical components in natural and artificial materials.
Inductive Reasoning - Process of drawing general conclusions based on evidence.
Scientific method - A process or investigation to produce evidence consisting of many steps.
Observation - Anything detected by the senses
Hypothesis - Tentative explanation that can be tested and is falsifiable
Experiment - A process made under controlled conditions to test a hypothesis
Manipulated variable - Variable changed by the researcher
Dependent Variable - Variable dependent and changes depending on the Independent/Manipulated variable.
Matter - Anything with mass that occupies space
Classifying Matter
Vocab
%%Mass%% - Measure of amount of matter in an object
%%Volume%% - Measure of how much space an object takes up
%%Physical Property%% - A property of matter that can be observed without changing it to another substance.
%%Chemical Property%% - A property of matter that can only be observed through a chemical change
%%Extensive Property%% - A property that depends on how much matter there is an a substance
%%Intensive Property%% - A property that only depends on the type of matter
%%Physical Change%% - A change in matter that does not change the substance to another substance
%%Chemical Change%% - A change in matter that changes the substance to another substance, usually in a chemical reaction
%%Solid%% - Matter with definite volume and definite shape
%%Liquid%% - Matter with definite volume and indefinite shape
%%Gas%% - Matter with indefinite volume and shape
%%Vapor%% - Water in gaseous form
%%States of Matter%% - Different phases that matter can exist in
%%Substance%% - Pure material with uniform and definite composition
%%Viscosity%% - A liquid’s resistance to flowing
%%Mixture%% - Two or more elements that are not chemically combined
%%Compound%% - Two or more elements that are chemically combined
%%Precipitate%% - A solid that forms during a chemical reaction
%%Chromatography%% - A process during which substances (usually liquid) are separated based on polarity
%%Decanting%% - Separating a liquid from a solid through pouring
%%Solution%% - A homogeneous mixture where particles are too small to reflect light or separate
%%Homogeneous Mixture%% - A mixture with uniform properties and composition throughout
%%Heterogeneous Mixture%% - A mixture that does not have uniform properties and composition throughout
%%Phase%% - Part of a sample that has uniform properties and composition
%%Distillation%% - A process to separate liquids through boiling points
%%Filtration%% - A separation method through particle size
%%Element%% - A pure substance that cannot be broken down
%%Compound%% - Two or more elements that are chemically combined
%%Molecule%% - Smallest part of a compound that still retains its properties, made of atoms.
%%Chemical Reaction%% - Two or more substances/reactants are changed into two or more new substances/products
%%Flammability%% - Ability of matter to burn
%%Reactant%% - The substances that start a chemical reaction
%%Product%% - The substance that is the result of the chemical reaction
%%Reactivity%% - Ability of matter to combine chemically with other substances
Scientific Measurement
Vocab
%%Accuracy%% - How close an experimental value is to the accepted value
%%Precision%% - How close measurements are to each other
%%Error%% - Experimental Value - Accepted Value
%%Percent Error%% - Error as a percentage
%%Significant Figures%% - Rules for measurements to make sure the end result is not more precise than the starting measurements
%%Base Units%% - Can be measured directly
%%Derived Units%% - Cannot be measured directly
%%Conversion Factor%% - Fraction made from equivalency
%%Equivalency%% - Two different units that equal the same amount
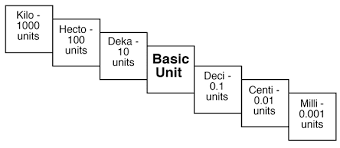
Measurement Units
%%Kilo%% - 1000
%%Hecto%% - 100
%%Deca%% - 10
%%Deci%% -0.1
%%Centi%% - 0.01
%%Milli%% - 0.001
%%Micro%% - 0.000001
%%Nano%% - 0.000000001
%%Pico%% - 0.000000000001
Dimensional Analysis
- Dimensional Analysis is a logical process for converting from one unit to another
- There are three steps for Dimensional Analysis:
- Identify given and needed units
- Write given unit as the numerator
- Write equivalencies and conversion factors (Make sure to write them so they cancel out)
- Multiply
Atomic Structure
Atom - Smallest Unit of Matter
Proton - Subatomic particle with a positive charge
Electron - Subatomic particle with a negative charge
Neutron - Subatomic particle with neutral
Quarks - A particle that makes up protons and neutrons
Mass Number - #Protons + #Neutrons in an element
Atomic Number - #Protons in an element
Nucleus - The center of an atom that has a positive charge
Isotope - An atom of an element with a different number of neutrons (All variations of an element are isotopes)
Percent Abundance - How naturally abundant an isotope is
Atomic Mass - The average mass of an atom
Atomic Mass Unit - Mass of 1 proton/neutron