World History Review
1) Common goals at Congress of Vienna
Restore balance of power by redrawing map of Europe so no one has too much power
Maintain absolute rule and suppress liberal ideas - keep everything conservative and do things like they always have been
Resulted in Concert of Europe - system where European powers cooperated to maintain stability
2) Causes of 19th century revolutions
liberal origins:
Civil Rights - people demanded constitutions, suffrage, and political representation
Ethnic nationalism - several groups like Greeks, Belgians, and Poles sought independence from empires
Economic Reasons - Industrialization led to worker exploitation and economic instability which sparked revolts. the poor wanted more
3) Greek and Belgian Revolutions
Greek
Fought for independence from the ottoman empire (turks)
gained international support due to admiration for classical Greece and Christian solidarity
Belgium
Revolted against Dutch by citing cultural and religious differences
Became a neutral state after securing independence
4) Junkers
German elite who run the country and want to unify German states
Own a lot of land in Prussia
5) German Unification
Northern unification happened first, before Southern.
Northern
Schleswig & Holstein - Prussia wanted these states but Denmark and Austria are in the way
Southern
Catholic & more liberal
Franco-Prussian War - start war w/ France in hope of southern states joining which they later did
War proved Germany was the strongest country
Later capture Napoleon and Spain, Alsace & Lorraine, becoming bigger with new territory
King Wilhelm gives Bismarck his blessing and gets crowned at Versailles to piss off the French
6) Industrial Revolution
When
late 1700s (late 18th century)
Where
Britain
First Industry
Textiles
Why
increasing population
natural resources in Britain
colonies (imperialism) - provided raw materials and markets
Stable political system that encouraged investment
economic strength
7) Results of Industrialization
Mass production - factories replaced handcrafting
innovation and applied science
urbanization - growing cities leading to slums and diseases
New Social classes - middle class gained influence and working class suffered from poor conditions
Social mobility increased- education and wealth creation
Foreign Policy (Imperialism) - more nations that start industrializations become imperialism nations
8) Adam Smith
advocated laissez-faire (self-interest) - govt should keep hands off economy but not 100% laissez-faire
Government’s roles: provide schools, provide and build roads, and provide army for nation
9) Karl Marx/Marxism
father of socialism, thought laissez-faire was garbage, advocated for poor.
communism vs. socialism
communist manifesto - predicted class struggle and revolution
10) Classical vs. Contemporary Liberalism
Classical
Contemporary
want gov. to be involved, environmental improvements, taxation and who benefits form it
11) Social Darwinism
“survival of the fittest”
used to conquest other countries, justify racist actions and beliefs, just extreme nationality, used to build stronger and a more powerful military to conquer other countries
12) Otto von Bismarck
Realpolitik - policies based on pragmatism, not ideology
advocated “Blood & iron” - if there’s war needed to accomplish a goal, they go to war
13) William/Wilhelm of Prussia
Kaiser (Emperor)
gave blessing to Bismarck, crowned at Versailles to piss off French
14) Charles Darwin
was very controversial
said we share a common ancestor (monkey)
Herbert Spencer took Darwin’s ideas of evolution and applied it to society
Social Darwinism vs. Enlightenment ideas: we’re not equal/we’re better than others vs. we’re all equal
15) Urban Problems
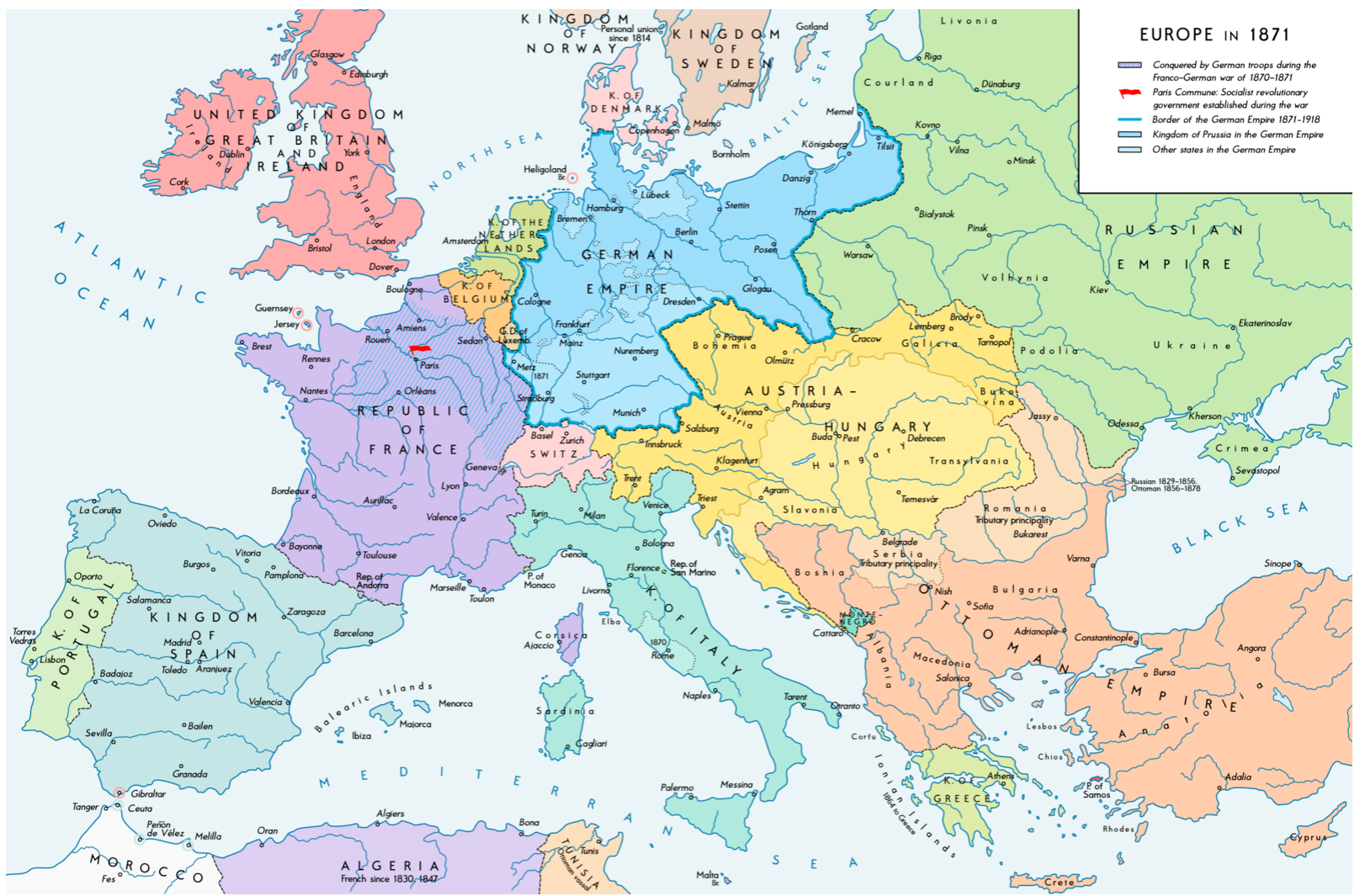
16) Map of Europe c. 1870 (5 nations)