3.5f - CPU Features: Professor Messer
Virtualization support
Allows other operating systems to be run within a single hardware platform.
Virtualization capacity is typically added to hardware components - like the CPU, as this is faster and easier to manage.
Intel Virtualization Technology (VT) supports virtualization, along with AMD Virtualization (AMD-V) for AMD CPUs.
CPU architecture
x86/x64
Refer to a 32-bit (x86) or 64-bit (x64) architecture of the CPU working on a system.
A 32-bit processor can access up to 2³² bits of information (4,294,967,296) values.
A 64-bit processor can access up to 2^64 bits of information (18,446,774,073,709,551,616) values.
64-bit can access max. 17 billion Gb vs 32-bit’s 4 Gb
Hardware drivers are specific to the OS version (x86/x64).
A 64-bit OS can support both 32-bit and 64-bit applications.
A 32-bit OS can only support 32-bit applications.
Advanced RSIC [Reduced Instruction Set Computer Machine (ARM)]
CPU architecture/design specifications manufactured by Arm Ltd.
Arm Ltd. creates the design, other companies license it to build CPUs
Simplified instruction set that offers benefits:
Efficient/fast processing
Less power use
Less heat production
Traditionally used for mobile/IoT devices, but this is expanding - blur between ARM and x86/x64 systems.
Core configurations
Motherboards can have multiple CPU cores that distribute processing demands.
Architecture is referred to as dual-core, multi-core, or quad-core.
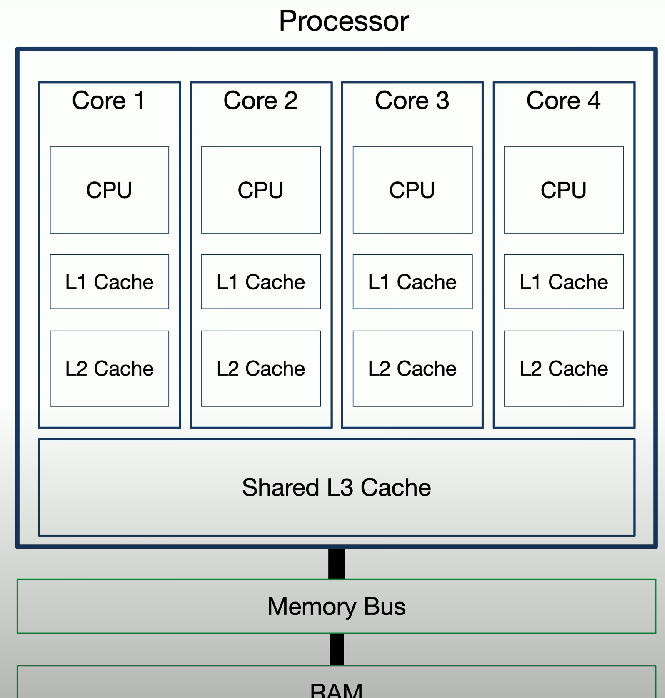
Not uncommon for multiple cores to have their own separate caches or to shared caches.
Caches are designed to speed information processing from to and from the CPU.