Geography
Biome |
Tundra |
Chaparral |
Tropical Rainforest |
Desert |
Boreal Forest |
Temperate Deciduous Forest |
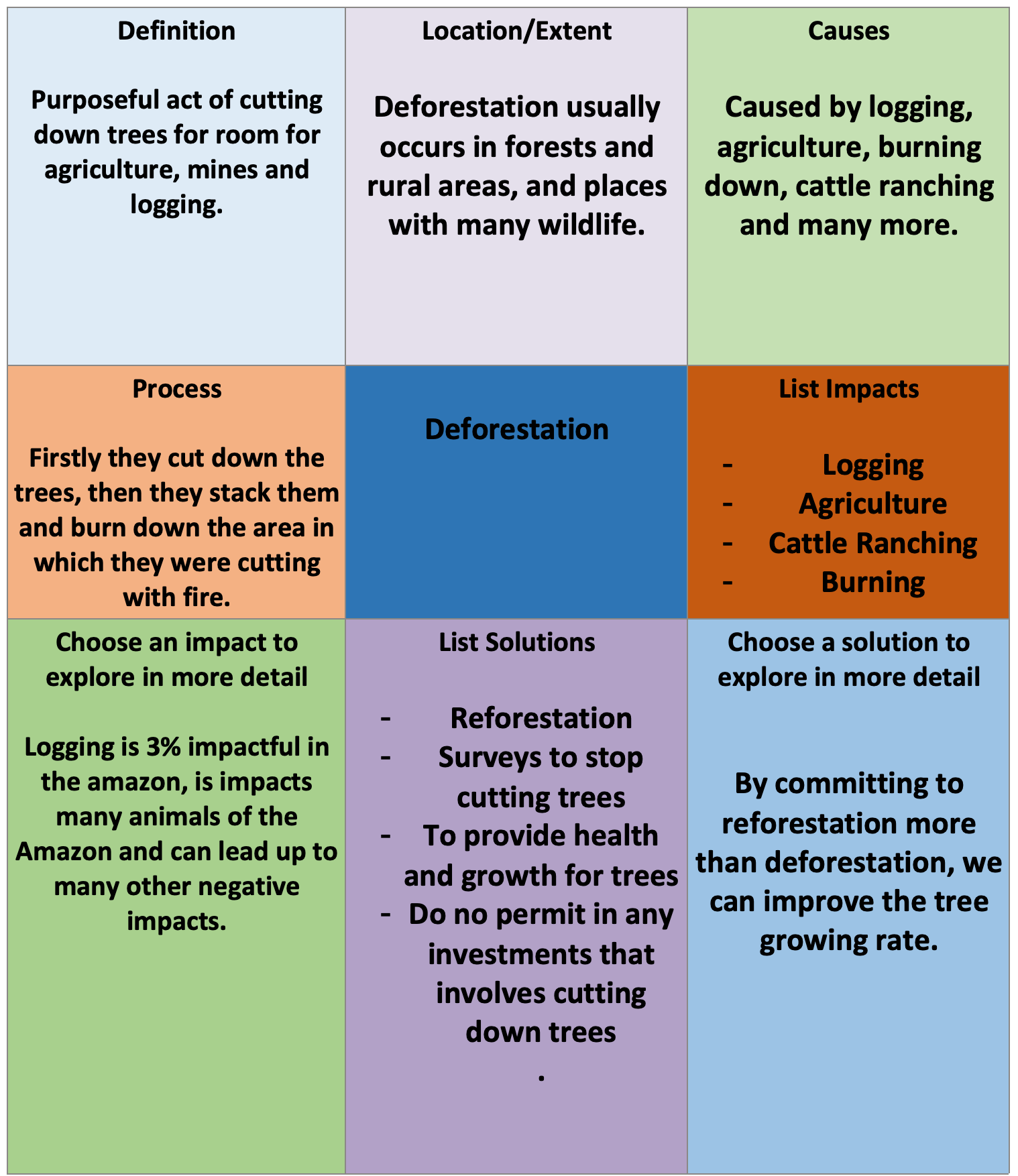
Impact on Deforestation in the Amazon
Economic development | Development of land for mining, The number of tourist attracted by farming and energy will lead to jobs rainforests could decrease both directly (construction and Pollution of some water sources and farming) and indirectly (supply and an increasing dry climate may result support industries). in wate
| Minerals such as gold are very plants that could bring huge medical valuable benefits and high profits may become improved transport infrastructure extinct opens up new areas for industrial development and tourism.
|
farming land), could cause harmful hydro electric power will provide pollution. They can burn out of cheap and plentiful energy control, destroying cast areas of valuable rainforests. |
Loss of biodiversity | Biodiversity is a measure of the variety of plants and animals that in a particular ecosystem. Rainforests are the most biodiversity ecosystems in the world. | Deforestation destroys the ecosystem and the many habitats that exists on the ground and in the trees. This reduces biodiversity.
| White-cheeked spider monkeys, which feed on fruits high in the forest canopy, are endangered because of the expansion of farmland and road building. The population of Brazilian bare-faced Tamarins (type of monkey) has halved in 18 years, as cities, agriculture and cattle ranching have pushed into the rainforest. The endangered giant otter, found in the slow-moving rivers and swamps of the Amazon, faces water pollution from agricultural runoff and mining operations in the area 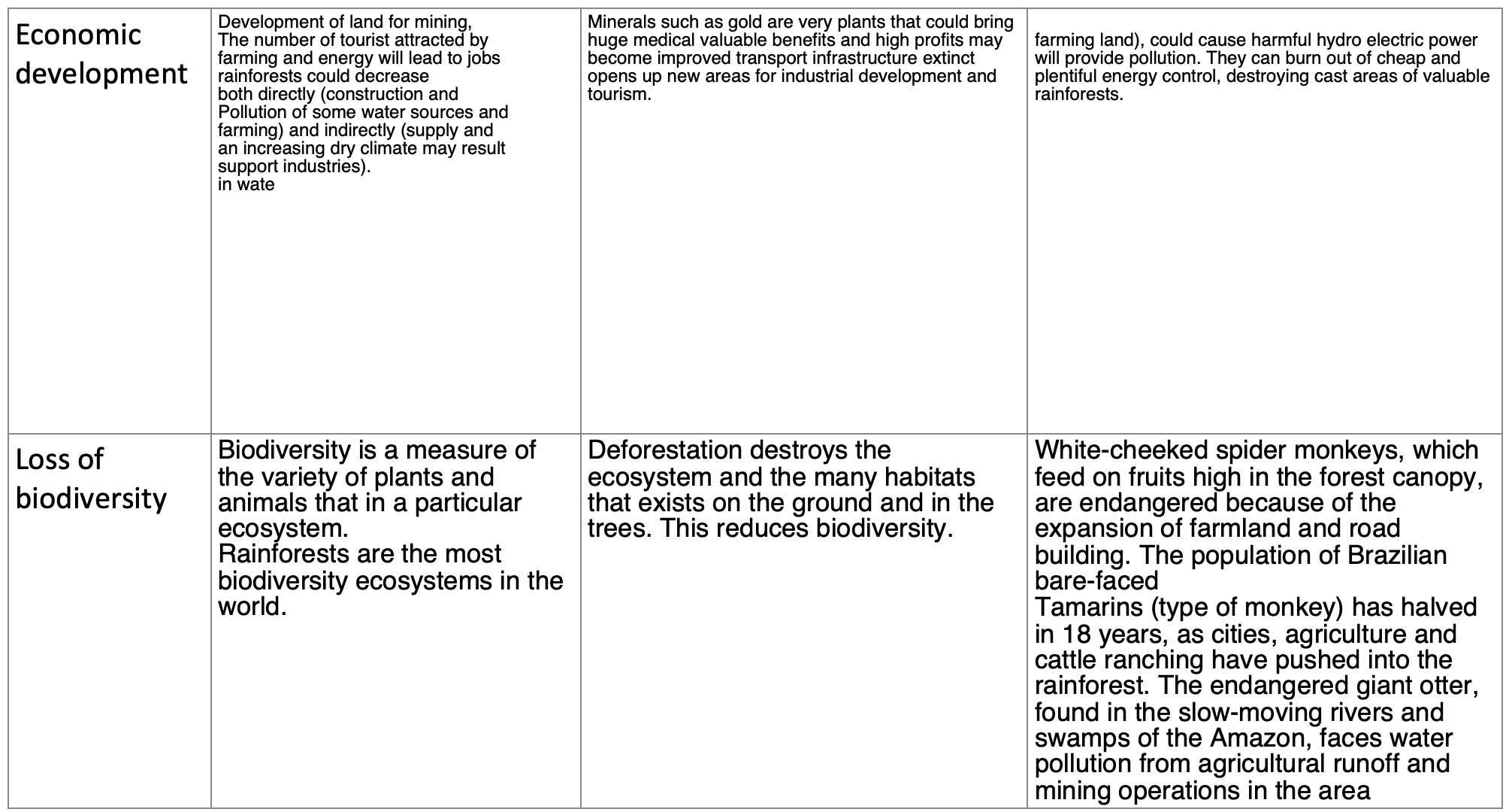 |

Big Challenge | Notes |
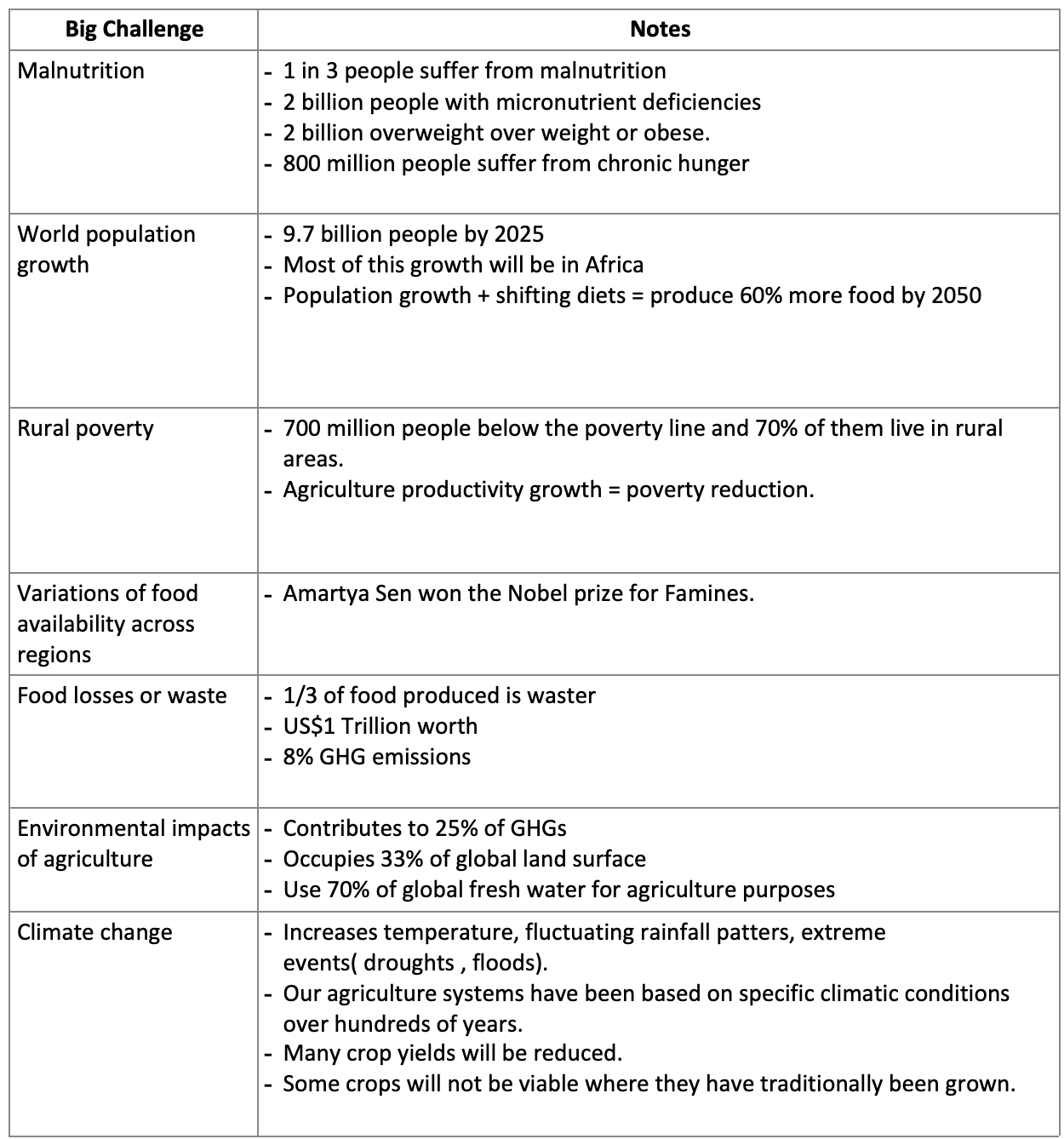
Malnutrition |
|
World population growth |
|
Rural poverty |
|
Variations of food availability across regions |
|
Food losses or waste |
|
Environmental impacts of agriculture |
|
Climate change |
|
Factors include labour, capital or money available also is an impact. Technology is used more natural and human resources. Market sells the produce made. Government has a lard affect on farming, some have to pay less or more financial money to the government.

|
BASIS FOR COMPARISON | INTENSIVE FARMING | EXTENSIVE FARMING |
Meaning | Intensive Farming refers to an agricultural system, wherein there is high level use of labor and capital, in comparison to the land area.
| Extensive Farming is a farming technique, in which large farms are being cultivated, with relatively lower inputs, i.e. capital and labor. |
Population | It is practiced in densely populated region.
| It is practiced in moderately populated region. |
Land holding | Small and expensive
| Large and inexpensive |
Farmland | Near to the market
| Remotely located |
Per hectare output
| Large | Small |