Industrial Economics Final Notes
Types of Advertising
Informative: providing info how to use with new features Products and changes (launch of electric vehicles) range or charging time.
Persuasive: trying to persuade Customers to change their mind stimulating customers for buying process. (Nike Just do it)
Reminder: its used to reinforce(strengths) brand.
Presence and increasing customer's awarness. (holiday themed advertising) (solidarity)
Evolution of Advertising
conventional(traditional) marketing = newspapers, television, radio, magazines.
Digital Era: sm, sem, influencer's compaing anomaly addiction
Emerging trends: AI +big data (Personalised,customized)
Advertising Channel
•Traditional Media —> TV, Newspaper, Radio, magazine
•Digital Media —> Internet, SM, Stm inf. compaign
• Qutdoor Media → bill boards Posters
•Directing Marketing → emails, calls
•Sponsorship Product Placement → Nöronmarketing
→Branding (Brand Perception Reputation Status symbol)(History since...)
—>Additional Benefits →Private labels Products (increase loyalty),Events supporting,(Redbull) Sponsor for some events
-After sale service
-warranties (BMW) (otomobile company)
-Return Policies Strictors flexible
Types of Product Differentation
Horizontal:
—>Products differ in just some features, but they are still close each other in terms of quality.
—>Customer Choise is a function of Preferences.
—>flavours of ice cream —> serve as an example of horizontal differentiation, where consumers may prefer one flavor over another despite similar base ingredients and quality.(KAI suggestion)
—>car color
Vertical:
—>Products differ Substantially in terms of quality
Higher quality commands higher Prices
—>Budget vs Premium (Smart Phones)
PC(economy common) vs High and Professional luxury—> PC (economy common) typically offers basic functionality at a lower price point, while high-end and professional luxury products provide advanced features and superior performance, justifying their premium pricing. (KAI suggestion color)
—>The differentiation in quality not only influences consumer choices but also shapes market competition, as brands strive to establish their unique value propositions.
Benefits Product Differentation:
-Reduce Direct Price competition
-Create customer satisfaction and loyalty
-Provide competitive edge
-Enchances customer demand
increase perceived value—>firms can charge customers by Premium Prices
Sustainability in Product Pifferentation
(eco-labelling eco-friendly)+Sustainable features
Tesla
—>Electric vehicles reduce fossilefuel dependency
—>Energy Product (Promoting Reneivable energy uses)
—>Branding—>Positining itself high-Tech firms and environmentally responsible demand
Patagunia
—>Recyled materials
—>ecofriendly manufacturing
—>Programs for repair recycle to include USED CLOTHERS WASTE
—>Activist Support environmental Protection Compaions
Product Differentation and Advertising
—>conceptual framework
→identify distinguish
→ Explore to find out role of PD and AD
—>vertical vs horizontal
—>Real life applications case studies (in market structures firms, behaviours consumers prefences)
—>Evolute PD and A.D in building board loyalty and shaping consumer demand.
Product Differentation
—>Process that firms make Products distinct from Competitions they different from others.
Physical Differentation: color, size, design, texture,...
Quality improvement—>StandartsVS actual—>deviations
→ Supply chain management (scm)—>JIT
→ Reliability
→Durability
—>Performance
R&D (AR-GE)
—>innovation is triggired by RD Product innovation.
—>Higher RD spending correlates with increased Productivity and GDP grauth. (LONG RUN)
—>Teonotical foundations of RD
—>Solow's Growth model
Endogenous Growth Theory = investment in human capital, innovation and knowledge contributes directly to growth(ÇOK ÖNEMLİ)
>R&D and Productivity—
Global Trends in R&D:
→Global Statistics
→Top sectors
→visual
Advertising
→Can effect customer mind or preferences or influence of brand perspection.
Strong Strength→ Product demand→brand loyalty.
→Advertising can be used as tool for firms to apply premium charging for differentiated products.
→Premium Pricing has impact on market structure by enabling firms to Conduct higher pricing for different Product (shape benefits)
→Advertising can set Market barrier to entry for new competitions.
business internal → ← externals (rivals)
4P’s:
→Place (logistic)(delivering)
→Promotion
→Product
→Price
Aşşağıdaki sayfa sınavda sorulacak
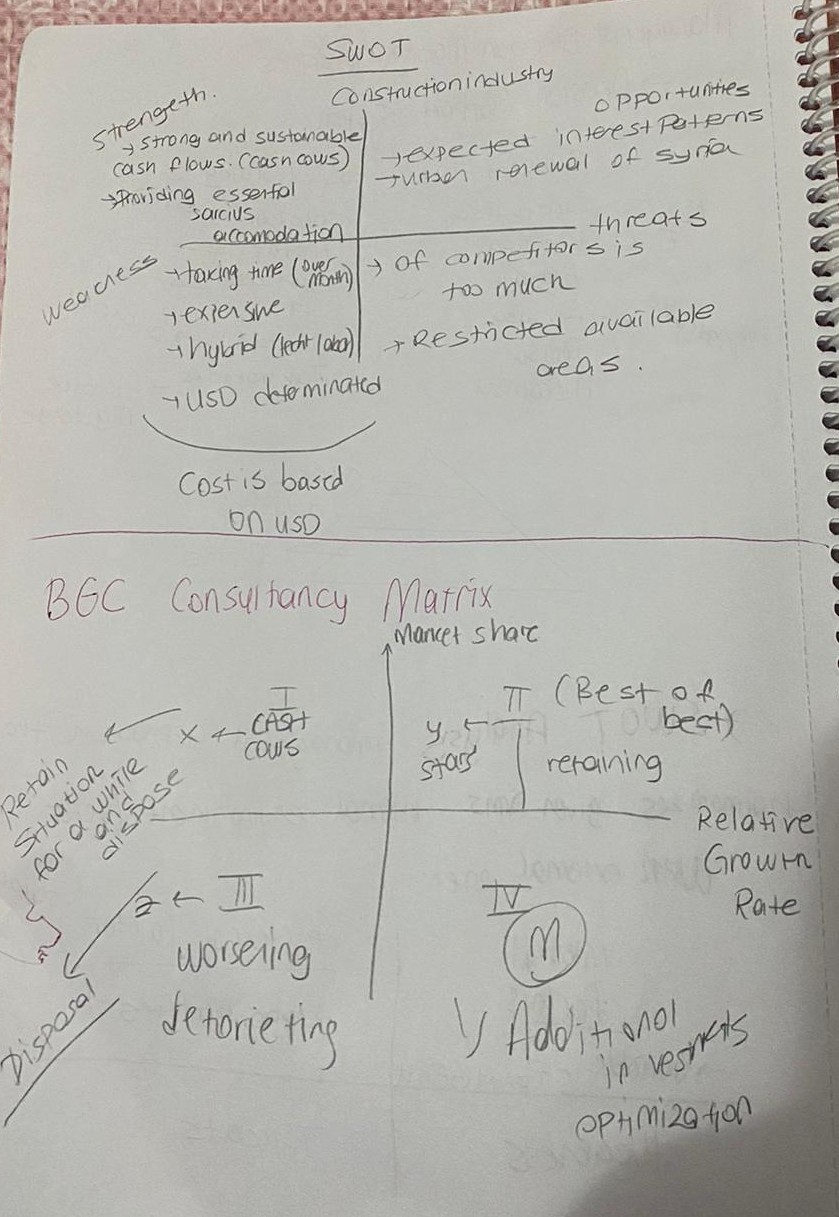
Sınavda IT sorarım demişti swot analysis için
IT İÇİN SWOT ANALYSIS:
Overall IT Sector:
Strengths: High demand for technology solutions, continuous innovation, skilled workforce.
Weaknesses: Rapid technological changes leading to skill gaps, cybersecurity threats, dependency on global supply chains.
Opportunities: Emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain, increasing digitization across industries, expansion into new markets.
Threats: Intense competition, regulatory challenges, data privacy concerns, economic downturns affecting IT spending.
Market Structure
↳ how the market organized based on number of players (sellers) product's nature, some market dynamics.
1-Perfect Competration / Competitive Market
↳ many firms-Small
No, one is winners / No one can set the price/ Abnormal profilt cannot observes.
Identical Products
↳ There is significant mobility
↳ No barrier to entry
2-Monopoly
+ A single entity (firm) dominates market.
→Unique product
→High market barrier.
3-Oligopoly
↳ few large firm exist
↳ inter depency is strong = prices are stich (Mid) -> katı
→significant barrier
→capital Intensive
4-Monopolistic Competition
↳ There 're many firms.
↳ Product's are differentiated → unique product (restuarant/Mall)
=> Market Barrier = obstacle(engel) for new competitions, it discoverage prevent from entering market.
→Nautral
→Artifical (yapay)
Economic Barrier=
A)High Economics Scale
→Reducing UFC
→Cost leadership
→mass producting
→standards
B-) Capital Intensity
C-) Network Effects
Market Entry
1)Fixed Cost
2)Revolutionary Cost.
→Financial Cost + non- Financial Cost
→Licensing and compliance(uyumluluk) cost
↳ Medical ↳ in line with regulatory nuentory.
↳Law
↳ Qualitity
↳Banking
↳ Aviation (Havacılık)
A-) Establishment
B-) Operation
3) Marketing Distribution Cost
↳ build in your firm's awarness (Farkındalık)