Improvement in food resources
Introduction
==Tissues== → Group of cells having common origin working together to perform a particular function.
Term Tissue was coined by “Xavier Bachat”.
Study of Tissue is known as “Histology”.
Plant Tissues
- Dead Tissues are abundant.
- They require less maintenance energy because they are autotrophic (makes its own food).
- Differentiation of tissues in meristematic tissues and permanent tissues which are located in different parts based on their dividing capacity.
- Dividing of meristematic tissues led to growth throughout the life.
- Organization of plant tissues are simple.
- Placement in based for their stationary position.
They were divided into two categories :-
- Meristematic tissues.
- Permanent tissues.
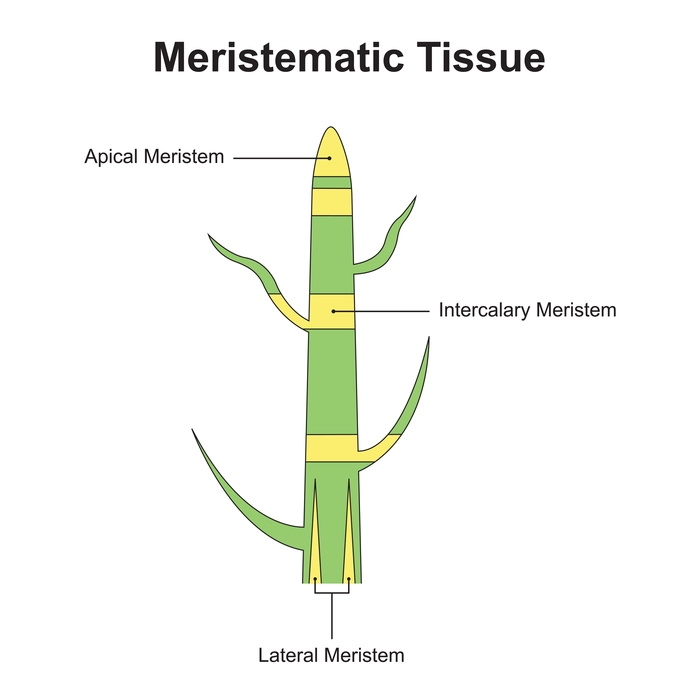
Meristematic Tissues
They are classified in 3 Groups.
Apical Meristem
Intercalary meristem
Lateral Meristem
@@Apical meristem@@
apex → tip
It is further divided into 2 categories.
- Shoot apical meristem.
- Root apical meristem.
%%Shoot apical meristem.%%
- Present at the tips of the shoot/stem.
- Help to increase the length or the shoots/stem.
- [Primary Growth]
%%Root apical meristem%%
- Present at the tips of the roots.
- Helps to increase the length / height of the roots.
- [Primary Growth]
@@Intercalary Meristem@@
- Present in only few plants, such as grasses.
- Present near the node / at the base of the internode.
- helps in the elongation of the internode in grasses thereby increases the length of the stem.
- Helps in the regeneration of leaves after the grazing of herbivores.
- [Primary Growth]
@@Lateral Meristem@@
- Helps to increase thickness / girth / width of the stem / root(rarely).
- [Secondary Growth]
- Also called [Secondary meristem]
- [Ring meristem]
- [Cylindrical meristem]
@@Characteristics of meristematic tissues@@
- they are made of living cells.
- the cells of meristematic tissues have dense protoplasm, and their cell wall is thin.
- the nuclei are large and clearly visible.
- vacuoles are almost absent.
- cells are tightly packed with almost no intercellular spaces.
- they do not store food and exhibits high metabolic activity.
- the cells actively divide to add new cells to the plant.
Permanent Tissues
Meristematic tissues are converted in permanent tissue by giving it a fixed & permanent shape, size, function and location.
- The cells are originating from pre-existing meristematic tissue.
- They do not divide.
- The cells are fully different from each other.
- The cells differ in shape and size.
- Visible intercellular spaces are present.
- Large vacuoles are present in mature cells.
- Metabolic activities occur at low rate.
- Cell wall may be thin or thick.
They are divided into 3 categories.
@@Parenchyma@@
- It is a living tissue.
- Most abundant tissue.
- Cells of this tissue have a thin cell wall made up of cellulose.
- Cells of this tissue have dense cytoplasm with small nucleus and large vauoles.
- Intercellular spaces are present between cells.
- It is present in all organs of plant.
- Idioblast ( parenchyma ) stores resin, tannin, gums and oil.
%%Modification/types of parenchyma%%
Chlorenchyma
Parenchyma that contains chloroplast that contains chlorophyll that helps in photosynthesis.
In short, Chlorenchyma → Chloroplast → Chlorophyll → Photosynthesis
Aerenchyma
A type of parenchyma made of rounded cells with large air cavities.
It is found in aquatic plants
Function is to provide tendency to float to plants
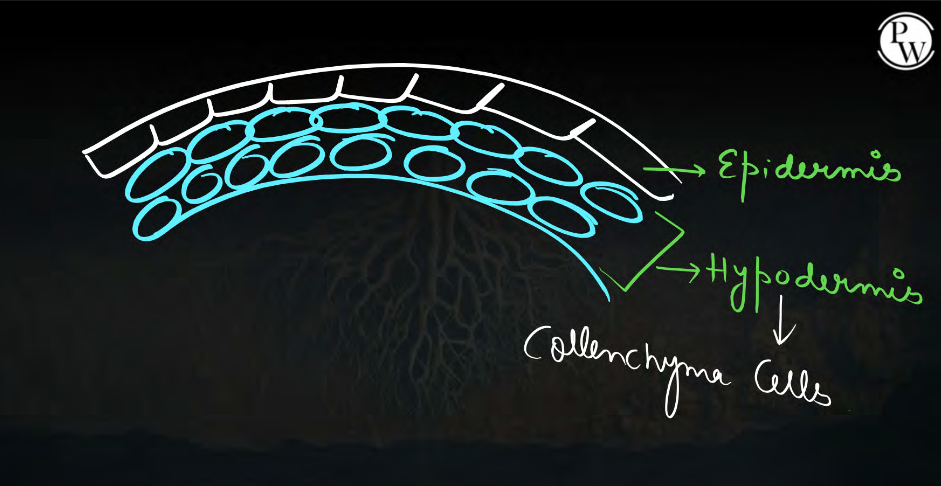
@@Collenchyma@@
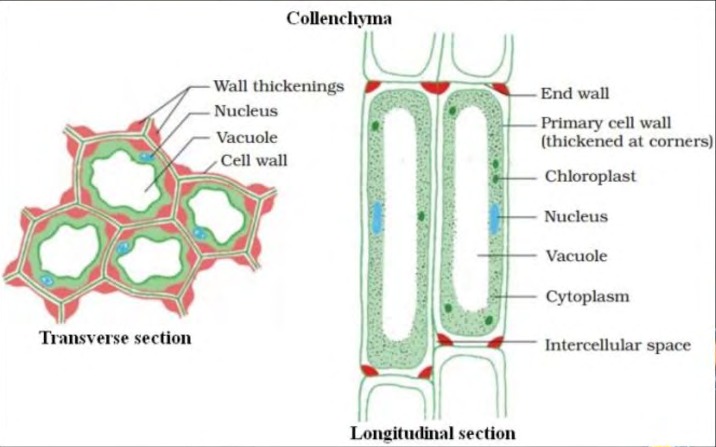
- Cells of this tissue are living, elongated or vary in structure.
- Cells of this tissue are irregularly thickened to the deposition of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin.
- Intercellular spaces are very little or absent between cells of this tissue.
- sometime, chloroplast is also present.
@@Sclerenchyma@@
Animal Tissues
- Living Tissues are abundant.
- They require more maintenance energy because they are heterotrophic (have to move for food).
- Differentiation of tissues is absent in animal as their growth is uniform.
- Animal does not show growth after reaching maturity. Reparative growth is present.
- Organization of plant tissues are complex.
- Tissue organization is targeted towards high mobility of animals.