Economics
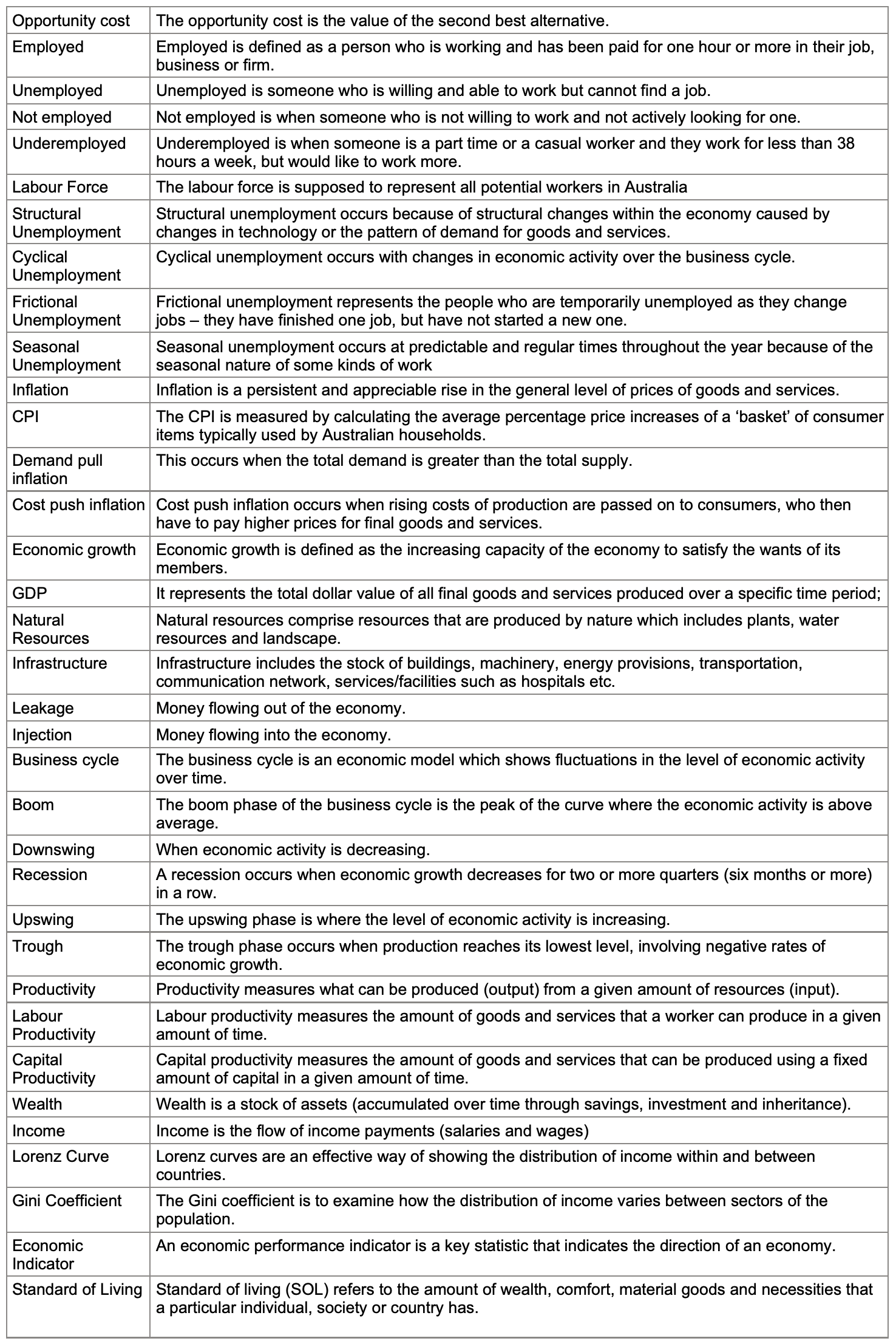
Opportunity cost | The opportunity cost is the value of the second best alternative. |
Employed | Employed is defined as a person who is working and has been paid for one hour or more in their job, business or firm. |
Unemployed | Unemployed is someone who is willing and able to work but cannot find a job. |
Not employed | Not employed is when someone who is not willing to work and not actively looking for one. |
Underemployed | Underemployed is when someone is a part time or a casual worker and they work for less than 38 hours a week, but would like to work more. |
Labour Force | The labour force is supposed to represent all potential workers in Australia |
Structural Unemployment | Structural unemployment occurs because of structural changes within the economy caused by changes in technology or the pattern of demand for goods and services. |
Cyclical Unemployment | Cyclical unemployment occurs with changes in economic activity over the business cycle. |
Frictional Unemployment | Frictional unemployment represents the people who are temporarily unemployed as they change jobs – they have finished one job, but have not started a new one. |
Seasonal Unemployment | Seasonal unemployment occurs at predictable and regular times throughout the year because of the seasonal nature of some kinds of work |
Inflation | Inflation is a persistent and appreciable rise in the general level of prices of goods and services. |
CPI | The CPI is measured by calculating the average percentage price increases of a ‘basket’ of consumer items typically used by Australian households. |
Demand pull inflation | This occurs when the total demand is greater than the total supply. |
Cost push inflation | Cost push inflation occurs when rising costs of production are passed on to consumers, who then have to pay higher prices for final goods and services. |
Economic growth | Economic growth is defined as the increasing capacity of the economy to satisfy the wants of its members. |
GDP | It represents the total dollar value of all final goods and services produced over a specific time period; |
Natural Resources | Natural resources comprise resources that are produced by nature which includes plants, water resources and landscape. |
Infrastructure | Infrastructure includes the stock of buildings, machinery, energy provisions, transportation, communication network, services/facilities such as hospitals etc. |
Leakage | Money flowing out of the economy. |
Injection | Money flowing into the economy. |
Business cycle | The business cycle is an economic model which shows fluctuations in the level of economic activity over time. |
Boom | The boom phase of the business cycle is the peak of the curve where the economic activity is above average. |
Downswing | When economic activity is decreasing. |
Recession | A recession occurs when economic growth decreases for two or more quarters (six months or more) in a row. |
Upswing | The upswing phase is where the level of economic activity is increasing. |
Trough | The trough phase occurs when production reaches its lowest level, involving negative rates of economic growth. |
Productivity | Productivity measures what can be produced (output) from a given amount of resources (input). |
Labour Productivity | Labour productivity measures the amount of goods and services that a worker can produce in a given amount of time. |
Capital Productivity | Capital productivity measures the amount of goods and services that can be produced using a fixed amount of capital in a given amount of time. |
Wealth | Wealth is a stock of assets (accumulated over time through savings, investment and inheritance). |
Income | Income is the flow of income payments (salaries and wages) |
Lorenz Curve | Lorenz curves are an effective way of showing the distribution of income within and between countries. |
Gini Coefficient | The Gini coefficient is to examine how the distribution of income varies between sectors of the population. |
Economic Indicator | An economic performance indicator is a key statistic that indicates the direction of an economy. |
Standard of Living | Standard of living (SOL) refers to the amount of wealth, comfort, material goods and necessities that a particular individual, society or country has.
 |