Newton's Laws
Force
Force - The cause of motion (what causes objects to move)
- Two types of force
- pushes
- pulls
- Forces are measured in Newtons
- SI unit of force
- Symbol N
- Measured by using a spring scale
- Forces may be unbalanced or balanced
Balanced Forces - all forces acting on an object are equal
- there sis no change in motion
Unbalanced Forces - one or more forces acting on an object are stronger than others
- There is change in motion
- A net force
u7 
Newton’s Laws
- First Law - Inertia
- Second Law - Acceleration, Force & Mass
- Third Law - Action-Reaction
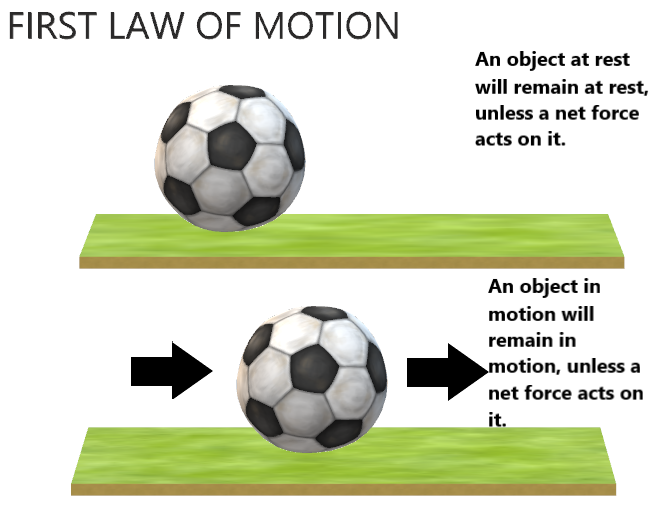
First Law
Inertia
- An object at rest (not moving) remains at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force (push or pull)
- An object in motion remains in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force (push or pull)
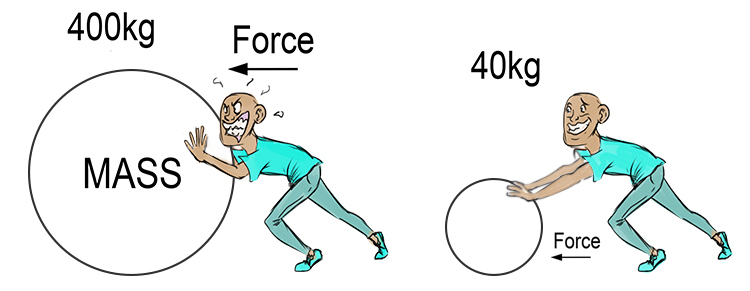
Inertia & Mass
Mass is the amount of matter in an object
The more mass an object has, the more inertia the object has
Bigger objects are harder to start and stop
Second Law
Acceleration & Mass definitions
- Acceleration is a change in velocity (speed or direction)
- Mass is the amount of matter in an object
Acceleration & Force
- The more force placed on an object, the more it will accelerate (change its motion)
Acceleration & Mass
The more mass (or inertia) an object has, the more force it takes to accelerate the Object
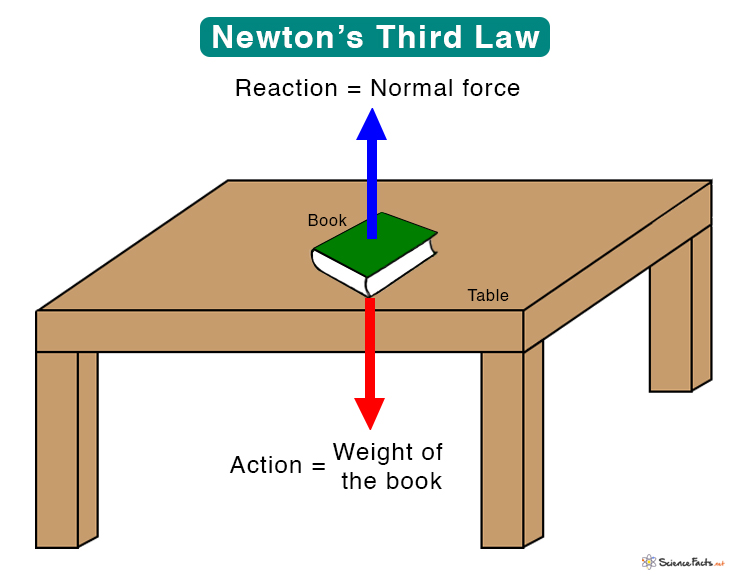
Third Law
Action - Reaction
Forces are always produced in pairs with opposite directions & equal strengths
For every force there is an equal and opposite force
Newtons cradle is an example of this law in practice