CEN 304 Exam II Review (copy)
Define the following term
Porous Media-particles of solids (sand, soil) with spaces (pores) in between
Saturated Zone- where pores are filled with water
Vadose Zone- pores have a mix of air and films of water
Porosity- percentage of empty space that exists within a particular porous media
What are in situ methods for groundwater remediation?
Bioremediation
Chemical Reaction
TRUE OR FALSE: The 1980 Comprehensive Environmental response, Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA) established the National Priorities List (NPL), a ranked list of sites needing hazardous waste cleanup-TRUE
Globally, which sector uses the most water?
Agricultural
TRUE OR FALSE: The Maximum contaminant Level Goals (MCLGs) are enforceable standards set by the EPA.-FALSE
The TMDL for Belleville Pond was developed to address which pollutant
Phosphorus
BOD is mostly measured over how many days?
5 day
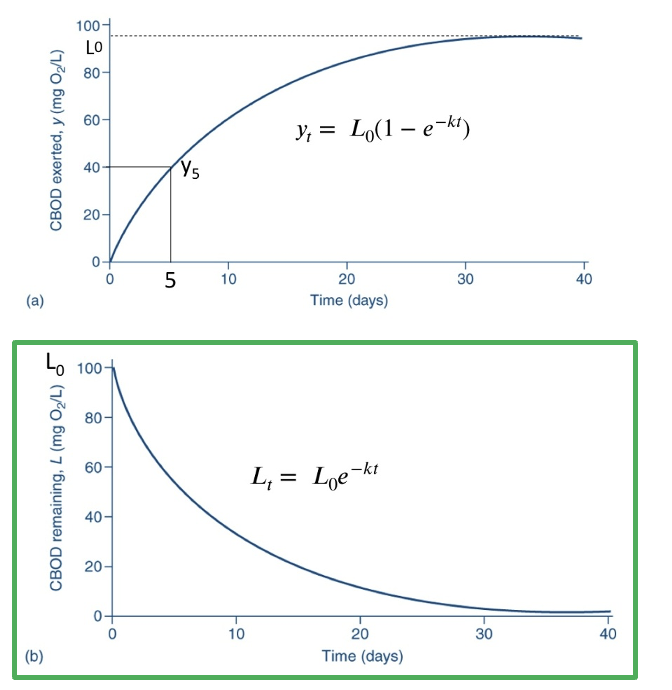
Which of the plots represents L which is the BOD remaining?
Determine the method of oxygen demand determination with the disadvantage
Theoretical oxygen demand- require knowing the structure and concentration of every molecule
Chemical oxygen demand- overstates impact on natural waters
Biochemical oxygen demand- takes a long time to measure
For a proper BOD measurement, one must make sure the final DO is at least how many mg/L?
1 mg/L
TRUE OR FALSE: In most water bodies, P is the element that algae run out of first as they grow; this is therefore limiting.
Define the Terms
Oligotrophic- Nutrient rich
Eutrophic- Nutrient rich
Hypoxia- a severe oxygen deficiency
Mesotrophic- moderate amount of dissolved nutrients
Water Treatment Steps in Order:
Pre-screen
coagulation
flocculation
sedimentation
filtration
final disinfection
Define the following terms:
Coagulation- the process of causing suspended partuicles to merge to form larger particles, which are easier to remove.
Flocculation- aggregation of destabilized particles to form flocs
Van der Waals forces- attractive forces that are weak at long distances
What is used as a disinfectant used to kill pathogens?
UV light
Chlorine
ozone
TRUE OR FALSE: During sedimentation , particle whose vs >vc will be collected. TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE: Non carbonated hardness is when cations are associated with on alkalinity anions (e.g. SO4-2)- TRUE
Define the wastewater treatment steps
Pretreatment- large solids, oily scum
Primary treatment- TSS (Total Suspended Solids), BOD, and phosphorus (in particulate phase)
Secondary treatment- Dissolved BOD
Tertiary treatment-Nitrogen and Phosphorus
Disinfection-pathogenic organisms
Define the following terms:
Yield Coefficient- Quantity of organisms produced per unit food utilized
Mixed Liquor- mix of activated sludge and wastewater
Solids retention time or mean cell residence time- average amount of time microorganisms are kept in the system
Nitrification- the conversion of ammonia to nitrate
Anoxic Zone-a region lacking oxygen
Microbes that uptake large amounts of P- phosphate accumulating organisms
TRUE OR FALSE: A low F/M means organisms are saturated with food, so poor treatment efficiency- FALSE
Explain how nitrogen and phosphorous are removed
Nitrogen and phosphorus are removed from wastewater to prevent environmental harm like algal blooms. Nitrogen is typically removed biologically through a two-step process: nitrification, where ammonia is converted to nitrate under aerobic conditions, and denitrification, where nitrate is converted to nitrogen gas under anoxic conditions. Phosphorus can be removed either chemically, by adding metal salts that precipitate it out, or biologically, using specialized bacteria that absorb excess phosphorus under alternating anaerobic and aerobic conditions.
Explain what a TMDL is and how and why states go about preparing one (e.g. the Belleville Pond TMDL).
A TMDL (Total Maximum Daily Load) is a pollution limit set for an impaired waterbody that defines the maximum amount of a specific pollutant it can receive while still meeting water quality standards. States develop TMDLs for waterbodies that fail to meet these standards, identifying pollution sources, calculating safe pollutant levels, and outlining steps to reduce them. For example, the Belleville Pond TMDL in Rhode Island was created to address phosphorus pollution, which was causing water quality issues like algae blooms. The plan includes strategies to reduce runoff and improve land management to restore the pond’s health.
Explain the difference between in situ and ex situ groundwater remediation techniques and give examples
In situ methods treat contamination directly in the ground, using techniques like injecting microbes (bioremediation) or chemicals (oxidation), or installing permeable reactive barriers. These methods are less disruptive and often cheaper. Ex situ methods involve pumping groundwater to the surface for treatment using systems like pump-and-treat, air stripping, or carbon filtration. These are more controllable and effective for heavily contaminated sites but can be more expensive and time-consuming