Overview
Exam: 9am Thursday, May 15
Ch 47 - Digestive Systems and Animal Nutrition
List four types of essential nutrients
Describe the four groups that animals fall into with respect to feeding methods and the physical state of the organic molecules they consume.
Compare intracellular and extracellular digestion
Describe the structure of the vertebrate digestive system and outline the steps of digestion in a vertebrate digestive tract.
Describe the major layers of the mammalian digestive tract
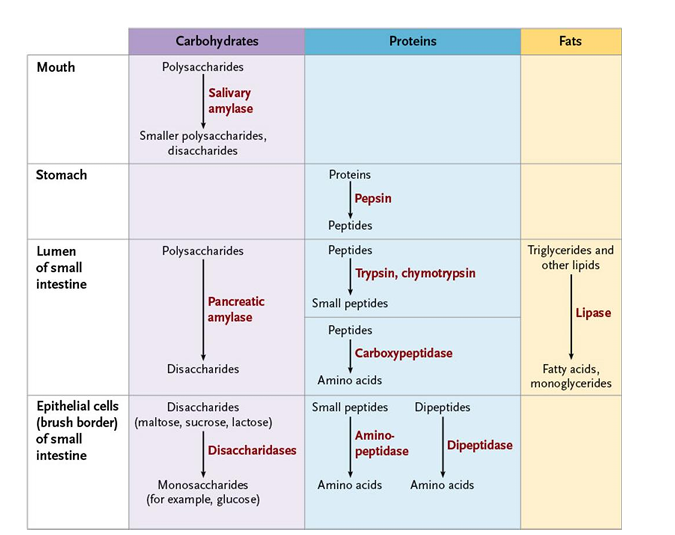
Explain the digestive processes that occur in the stomach
Explain the digestive processes that occur in the small intestine
Describe the role of the liver in the digestive process
Explain the digestive processes that occur in the large intestine.
Discuss how the digestive process is regulated
Describe the role of the gut microbiome in the digestive process.
Ch 45 - Defenses against Disease
Summarize how anatomical barriers help prevent infection by pathogens.
Describe how innate immunity combats cellular pathogens, and explain why it is a nonspecific defense
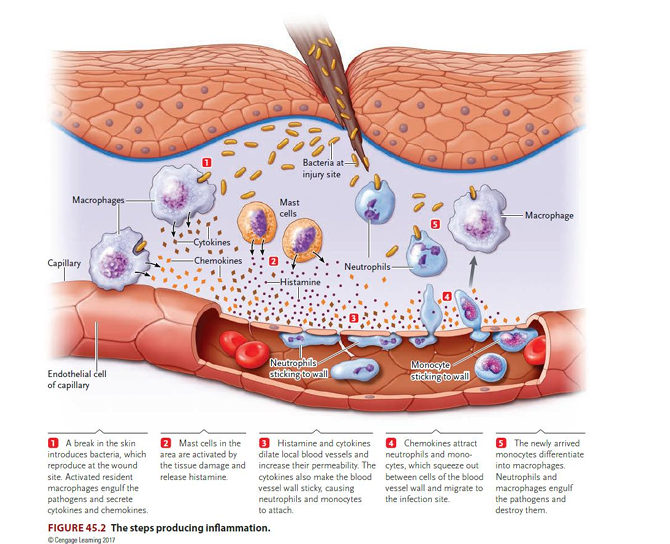
Discuss the steps producing inflammation
Describe how innate immunity combats viral pathogens
Describe the features of adaptive immunity
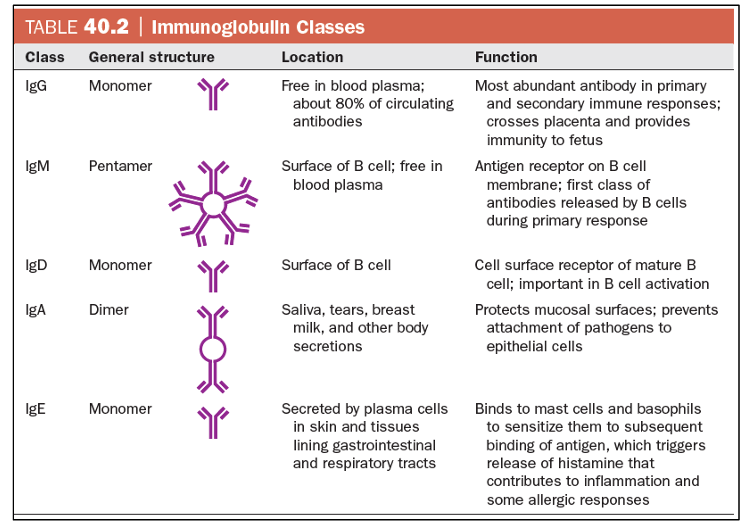
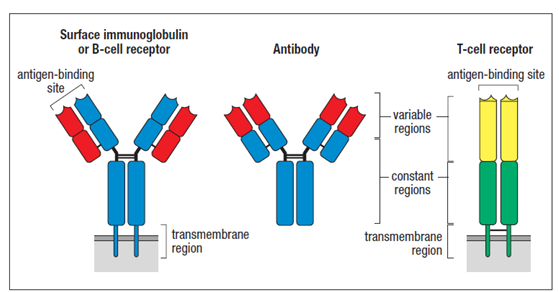
Explain the structure of antibodies and discuss how antibody diversity is generated
Compare and contrast the antibody-mediated immune response with the cell-mediated immune response
Explain how an autoimmune disease develops, and give examples of autoimmune diseases
Discuss how the immune system is involved in allergic reactions
Summarize the defenses against pathogens in non-mammalian animals
Ch 20 - Development of Evolutionary Thinking
Outline how ideas about order in the natural world changed from the natural world changed from the natural history studies of ancient Greek philosophers to the natural theology studies in eighteenth-century Europe
Describe how questions about biogeography, comparative morphology, fossils, and geology contributed to an understanding that living system change through time
Compare and contrast the evolutionary theories proposed by Lamarck and Darwin
Analyze how Darwin’s observations during the voyage of HMS Beagle led him to the conclusion that populations of organisms change through time.
Defend the proposition that Darwin’s theory of evolution profoundly changed out understanding of the living world.
Contrast the explanatory power of observing different species in their natural environments with the explanatory power of genomic studies that reveal the genetic basis of the differences between those species
Design an experiment to test whether or not a trait observed in a population is adaptive.
Ch 21 - Microevolution: Genetic Changes Within Populations
Describe the differences between quantitative and qualitative phenotypic variation
Design studies to distinguish between genetic and environmental causes of observed phenotypic variation
Analyze the genetics of a population using the Hardy-Weinberg model of genetic equilibrium to determine whether a gene locus appears to be undergoing evolutionary change.
Compare and contrast the mechanisms and effects of the five agents of evolutionary change in populations
Explain why small population size and genetic drift can undermine efforts to conserve endangered species.
Compare the effects of direction, stabilizing, disruptive, and sexual selection
Defend the proposition that the diploid condition protects harmful recessive alleles from the action of natural selection
Describe three circumstances under which natural selection can maintain a balanced polymorphism
Develop hypotheses and design an experiment to determine whether a phenotypic characteristic is adaptive under the environmental conditions in which an organism lives.
Generate hypotheses about how human impacts on the environment will alter patterns of microevolution in plant and animal populations