Energy
Define energy?
Energy is a property of matter and radiation that is the capacity to do work. In physics, energy is defined as the ability to cause change through the application of force. Energy comes in many forms, including thermal (heat), mechanical, electrical, chemical, and nuclear, and it can be transformed from one form to another. The total amount of energy in a system is conserved, meaning that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. Energy plays a crucial role in many natural and technological processes and is a central concept in many areas of science, including physics, chemistry, and engineering.
Explain the term energy?
Energy is a property of matter and radiation that refers to the ability to do work. In physics, energy is defined as the capacity to cause change through the application of force. It can be thought of as a resource that can be transformed from one form to another, but cannot be created or destroyed.
Energy comes in many forms, including thermal (heat), mechanical, electrical, chemical, and nuclear energy. For example, chemical energy is stored in the bonds between atoms in a molecule, and can be released when these bonds are broken, such as in a reaction that releases heat or generates electricity. Mechanical energy is related to the movement of objects and can be either kinetic energy, which is energy associated with motion, or potential energy, which is stored energy due to an object's position or state.
In general, energy is a crucial aspect of many natural and technological processes, and a central concept in many areas of science, including physics, chemistry, and engineering.
What is potential energy?
Potential energy is a type of energy that an object possesses due to its position or state. It is energy that is stored and available for release, and it is related to the forces acting on an object.
For example, an object held at a height above the ground has potential energy due to its position relative to the ground. If the object is released, the force of gravity will cause it to fall, and its potential energy will be converted into kinetic energy, which is energy associated with motion. Similarly, an object stretched or compressed within a spring has potential energy due to its state, and when the spring is released, the potential energy will be converted into kinetic energy as the spring returns to its original shape.
Potential energy can be calculated using the formula:
%%PE = mgh%%
Where PE is the potential energy, m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object above the ground.
In general, the concept of potential energy is an important part of physics and engineering, and is used to describe a wide range of physical phenomena, including the behavior of objects under the influence of various forces, such as gravity, springs, and electric and magnetic fields.
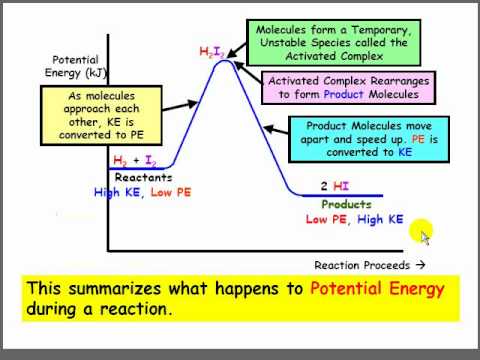
What do you mean by kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy associated with the motion of an object. It is the energy that an object possesses due to its velocity, and is proportional to the object's mass and speed.
Kinetic energy is given by the formula:
^^KE = 0.5 * m * v^2^^
where KE is the kinetic energy, m is the mass of the object, and v is its velocity.
In physics, kinetic energy is an important concept that is used to describe the behavior of objects in motion, and to calculate the energy changes that occur in a system. For example, when a ball is thrown or a car is in motion, it has kinetic energy. When the ball is caught or the car comes to a stop, its kinetic energy is converted into other forms of energy, such as thermal energy or sound energy.
In general, the study of kinetic energy is an important part of mechanics and is used to understand the behavior of objects under the influence of various forces, such as friction, air resistance, and the forces of collision.
Describe the conversion of energy?
conversion of energy:
Energy conversion refers to the process of changing energy from one form into another. Energy can be transformed from one form to another, but it cannot be created or destroyed. The total amount of energy in a system is conserved, meaning that the total energy before a conversion is equal to the total energy after the conversion.
Examples of energy conversions include:
^^Thermal to mechanical energy:^^ For example, when steam turns a turbine in a power plant, thermal energy is converted into mechanical energy.
^^Chemical to electrical energy:^^ For example, when a battery is used to power a device, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
^^Kinetic to potential energy:^^ For example, when an object is lifted to a higher height, its potential energy increases while its kinetic energy decreases.
^^Nuclear to thermal energy:^^ For example, in a nuclear power plant, nuclear energy is converted into thermal energy, which is used to generate steam to turn a turbine.
^^Electrical to light energy:^^ For example, when an electric current passes through a light bulb, electrical energy is converted into light energy.
Energy conversion is a fundamental concept in many areas of science and technology, including physics, engineering, and energy production. Understanding the processes of energy conversion is essential for the development of new technologies and the efficient use of energy resources.
Explain the conventional and non-conventional sources of energy?
Conventional sources of energy:
Conventional sources of energy are the traditional forms of energy that have been used for many years and are well established, such as coal, oil, natural gas, and nuclear power. These sources of energy are finite, meaning that they will eventually run out, and their extraction and use often have negative impacts on the environment, such as air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
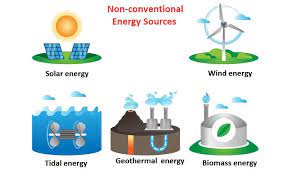
Non-Conventional sources of energy:
Non-conventional sources of energy, on the other hand, are relatively new sources of energy that are considered to be alternative or renewable. These sources of energy are considered to be non-conventional because they are not widely used or because they are not finite, meaning that they will not run out. Examples of non-conventional sources of energy include solar power, wind power, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass energy.
Non-conventional sources of energy are seen as a way to reduce dependence on finite and polluting sources of energy, and to reduce the impact of energy production on the environment. These sources of energy are often considered to be cleaner and more sustainable than conventional sources of energy, and they play a crucial role in the transition towards a low-carbon energy system.
In summary, conventional sources of energy are well established and widely used, but are finite and have negative impacts on the environment, while non-conventional sources of energy are relatively new and seen as a way to reduce dependence on finite and polluting sources of energy, and to promote a more sustainable energy system.
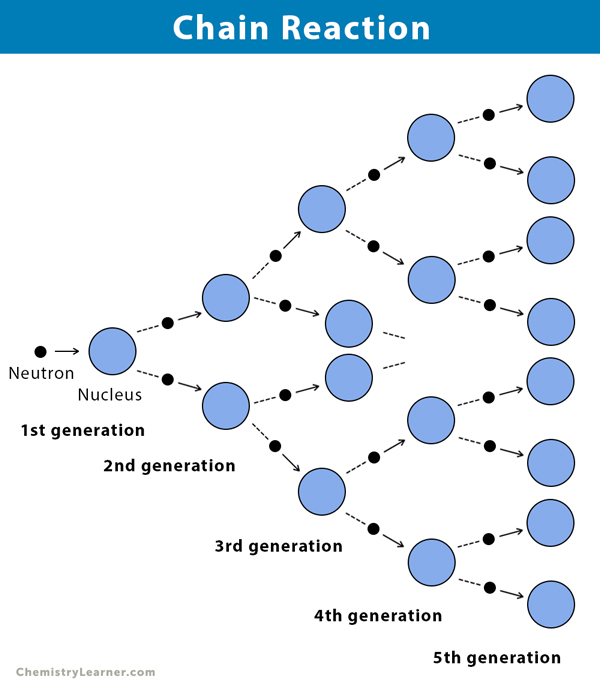
What do you understand by a chain reaction?
A chain reaction is a sequence of events in which a reactive substance or system triggers a similar reaction in adjacent or nearby substances or systems, leading to a chain of reactions that spreads rapidly. This process can result in a release of energy, as in a nuclear chain reaction, or a release of matter, as in a chemical chain reaction.
One of the most well-known examples of a chain reaction is a nuclear chain reaction, which occurs in a nuclear reactor or a nuclear bomb. In a nuclear chain reaction, the nucleus of an atom is split, releasing energy and additional particles that can collide with and split other nuclei, leading to a rapid release of energy in the form of heat and light.
Another example of a chain reaction is a chemical chain reaction, which occurs in a chemical system and involves a series of chemical reactions that release energy and lead to further chemical reactions. An example of a chemical chain reaction is the combustion of gasoline, which releases energy in the form of heat and light, and triggers further reactions in the surrounding air, leading to a rapid spread of the reaction.
In summary, a chain reaction is a rapid sequence of reactions that spreads rapidly and releases energy or matter, leading to a potentially explosive or hazardous situation.
Name any five different forms of energy in which you can convert the chemical energy of a dry cell.
A dry cell, also known as a zinc-carbon battery, converts chemical energy into several different forms of energy, including:
- @@Electrical energy -@@ This is the most common form of energy produced by a dry cell, and is used to power electrical devices such as flashlights, radios, and toys.
- @@Thermal energy -@@ As the dry cell produces electrical energy, it also generates heat as a byproduct, which is released into the environment as thermal energy.
- @@Kinetic energy -@@ If the electrical energy generated by the dry cell is used to power a motor, it can be converted into kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion.
- @@Light energy -@@ If the electrical energy generated by the dry cell is used to power a light bulb, it can be converted into light energy, which is the energy of light.
- @@Sound energy -@@ If the electrical energy generated by the dry cell is used to power a speaker, it can be converted into sound energy, which is the energy of sound.
In summary, the chemical energy stored in a dry cell can be converted into a range of different forms of energy, including electrical energy, thermal energy, kinetic energy, light energy, and sound energy, depending on the application and the device that the dry cell is powering.
\n