11: Tropical Forest Conservation
Compare and contrast global patterns of deforestation through time
Places that are far north have seen an upward trend in forest growth since the 1990's
The tropics have seen a strong negative trend
Southeast Asia, the perimeter of the amazon, around the equator have seen a loss of forest
In Brazil ppl were cutting down forests to make soy farms
2006: A consortium of soy customers agreed to stop purchasing soy from deforested land. Very effective in limiting deforestation
Explain the relationship between photosynthesis, respiration, combustion, and decomposition
Photosynthesis: plants use sunlight, CO2, and water to produce glucose and oxygen
Cellular Respiration: organisms break down glucose using oxygen to release energy, producing CO2 and water as byproducts
Combustion: burning carbon-based materials releases stores carbon as CO2, along with water and heat
Decomposition: microorganisms break down dead organic matter, releasing carbon back into the atmosphere or soil
Recognize the importance of covalent bonds
Carbon atoms form strong covalent bonds, especially with hydrogen, oxygen, and other carbon atoms.
In glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), carbon is stored in covalent bonds, which store chemical energy.
Breaking these bonds (via respiration, combustion, or decomposition) releases energy, which powers life or produces heat.
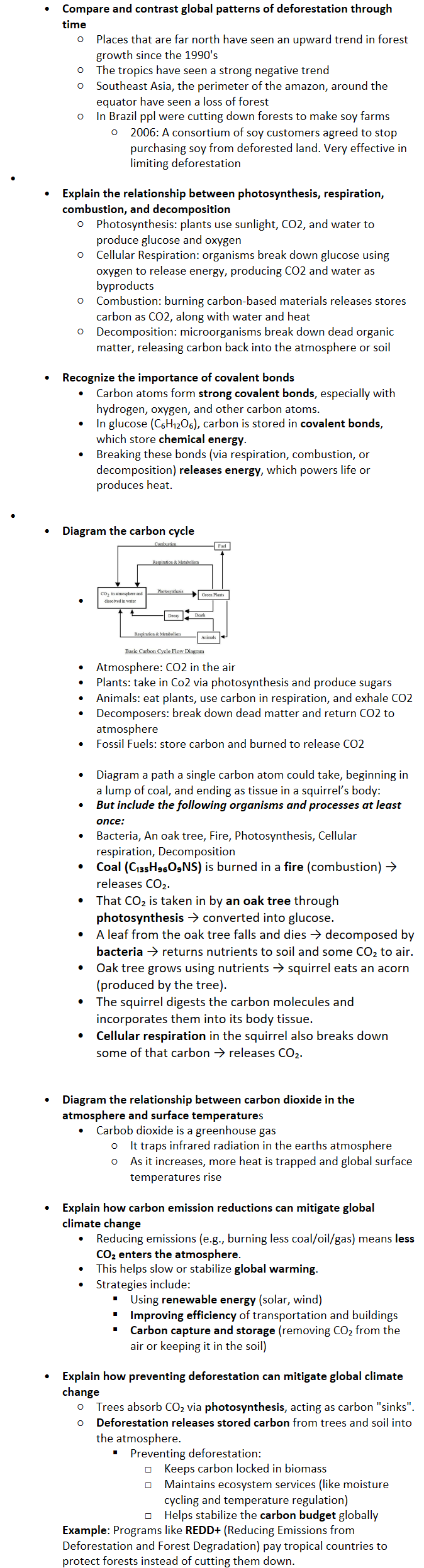
Diagram the carbon cycle
Atmosphere: CO2 in the air
Plants: take in Co2 via photosynthesis and produce sugars
Animals: eat plants, use carbon in respiration, and exhale CO2
Decomposers: break down dead matter and return CO2 to atmosphere
Fossil Fuels: store carbon and burned to release CO2
Diagram a path a single carbon atom could take, beginning in a lump of coal, and ending as tissue in a squirrel’s body:
But include the following organisms and processes at least once:
Bacteria, An oak tree, Fire, Photosynthesis, Cellular respiration, Decomposition
Coal (C₁₃₅H₉₆O₉NS) is burned in a fire (combustion) → releases CO₂.
That CO₂ is taken in by an oak tree through photosynthesis → converted into glucose.
A leaf from the oak tree falls and dies → decomposed by bacteria → returns nutrients to soil and some CO₂ to air.
Oak tree grows using nutrients → squirrel eats an acorn (produced by the tree).
The squirrel digests the carbon molecules and incorporates them into its body tissue.
Cellular respiration in the squirrel also breaks down some of that carbon → releases CO₂.
Diagram the relationship between carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and surface temperatures
Carbob dioxide is a greenhouse gas
It traps infrared radiation in the earths atmosphere
As it increases, more heat is trapped and global surface temperatures rise
Explain how carbon emission reductions can mitigate global climate change
Reducing emissions (e.g., burning less coal/oil/gas) means less CO₂ enters the atmosphere.
This helps slow or stabilize global warming.
Strategies include:
Using renewable energy (solar, wind)
Improving efficiency of transportation and buildings
Carbon capture and storage (removing CO₂ from the air or keeping it in the soil)
Explain how preventing deforestation can mitigate global climate change
Trees absorb CO₂ via photosynthesis, acting as carbon "sinks".
Deforestation releases stored carbon from trees and soil into the atmosphere.
Preventing deforestation:
Keeps carbon locked in biomass
Maintains ecosystem services (like moisture cycling and temperature regulation)
Helps stabilize the carbon budget globally
Example: Programs like REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) pay tropical countries to protect forests instead of cutting them down.