RNA transcription
RNA transcription: the process of making and RNA copy from a gene’s DNA called the mRNA
The DNA code is transferred form a strand of DNA to mRNA in the nucleus and then the mRNA can take the code into the cytoplasm for protein synthesis.
Transcription only occurs in the nucleus and the mitochondria
Initiation
Unwind the double stranded DNA by locating the initiation point by a group of proteins called initiation factors
They move along the DNA strand until they reach the promoter region.
The promoter region is a special sequence of DNA nucleotides
it signals the RNA polymerase to begin the synthesis of DNA to join the protein complex
The most common DNA sequence in promoter region: consensus sequence
Elongation
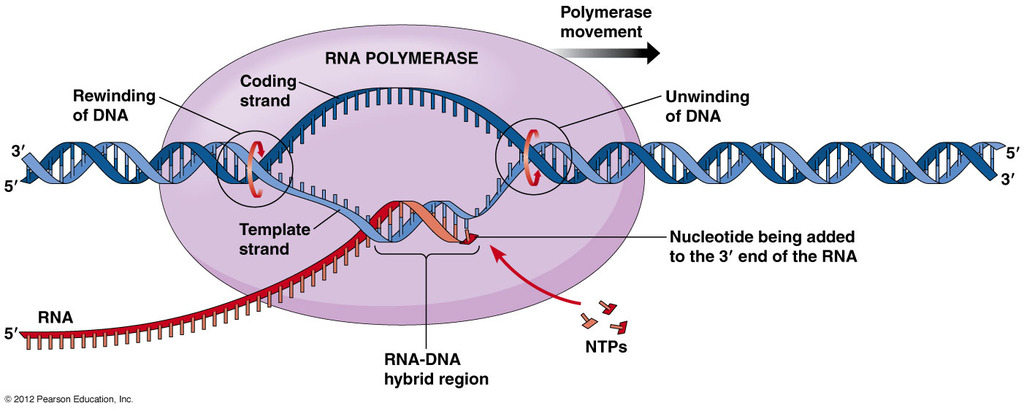
Once RNA polymerase combines with initiation factors to unwind DNA, it creates a transcription bubble.
Transcription bubble: region where two DNA strands are separated and exposed
only one DNA strand is used to synthesize the RNA molecule
RNA polymerase moves across the double strand that runs from the 3’ to 5’ direction
uses the anti sense strand to direct the synthesis of RNA molecule
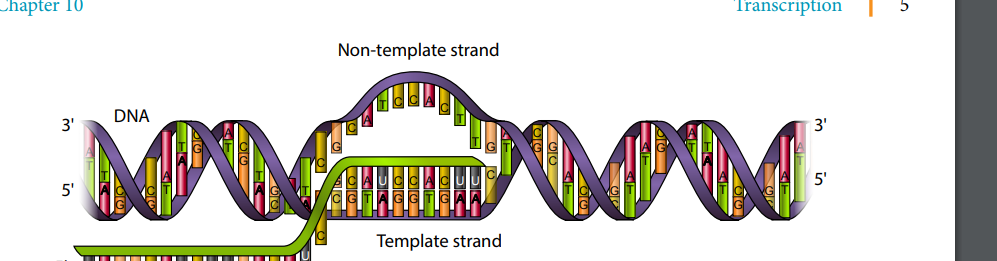
RNA is copied from the template strand, RNA polymerase can only read beginning at 3 end ending at 5 end.
RNA strand: template strand/antisense strand
DNA strand: coding strand/non template strand.
The nucleotides found on the sense strand is similar to the ones found in the RNA strand T is replaced with A.
RNA processing:
In eukaryotic cells they found that the mRNA code is significantly shorter than the DNA code.
the newly synthesized mRNA consists of non coding regions called introns/intervening sequences and coding regions called exons. (PREMRNA molecule)
Splicosome - essential for removing the introns while gluing and splicing together the exons
Processing of the mRNA:
adding a protective cap on the 5’ end and adding a tail of many adenine nucleotides called the polyadenosine tail tot he 3’ end of the mRNA.
connects the exon by forming proper phosphodiesther linkages
RNA polymerase
In prokaryotic organisms, there’s only 1 RNA polymerase
In eukaryotic organisms, there’s three different types of RNA polymerases.