Unit 6 - Managing water supplies
6.1 Global water distribution
Salt water in oceans
Surface fresh water: glaciers, lakes, rivers, permafrost
Inflows: precipitation, overland runoff, groundwater seepage, & glacial/snow melt
Outflows: evaporation, infiltration into ground stores, & abstraction by humans
Sub-surface fresh water: groundwater, soil moisture, permafrost
Aquifer = zone of rock saturated with water
Top of this zone = water table (rises & falls based on input + output)
Confined aquifers lay below + above impermeable material (aquitard)
Unconfined aquifers are more susceptible to drought
Atmospheric water (e.g. rain)
Water security: the ability to access sufficient quantities of clean water to maintain adequate standards of food and manufacturing of goods, adequate sanitation and sustainable health care
Causes of water insecurity
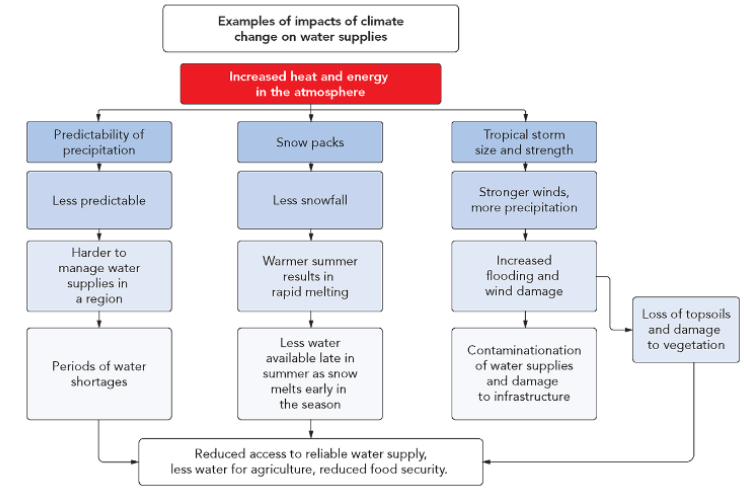
Climate change → changes in rainfall because warmer air holds more moisture
Can cause increased drought, flooding, & decline in snow fall
Natural disasters:
Flooding → erosion of topsoil, pollutes water supply (e.g fertilizer), damages sanitation infrastructure
Pollution events:
Water pollution: can occur after a point-source event or misuse of a water resource for dumping of waste
Run off of: domestic waste (e.g. sewage), industrial waste (e.g. heavy metals), agricultural chemical & fertilizer run off (eutrophication)
Groundwater can be contaminated by metals like iron & fluoride
From: leachate, septic tanks, storm water drains, saltwater intrusion (saltwater moves into freshwater aquifers)
Salt-water intrusion: over abstraction of freshwater reduce pressure & salt water can enter the aquifer
Population growth: population increases → demand for water increases
Leads to more waste & over abstraction of water from aquifers (drops water table + makes them harder & more expensive to access)
Impacts flora & fauna: springs + streams that wildlife rely on may dry out & trees that access the water table with deep roots will dehydrate + die
Changes in land usage → deforestation & urbanisation
Forest + wetlands can act as natural water reservoirs → water can’t infiltrate & recharge groundwater supplies
Competing demands from agricultural, industrial, and domestic sectors
Industrial: power plants, metal/plastic manufacturing
Municipal: households (toilet, shower, drinking water)
Agriculture: water for livestock, irrigation water for crops
Most human water use
International competition over water sources: conflict b/t regions/countries over water access
Waterways being damned can deprive users of water source
Some rivers cross int’l borders (e.g. Jordan River b/t Syria/Israel)
Inequality of water availability: people in LICs are less likely to have access to clean drinking water than HICs (can pay for infrastructure for a safe water supply)
Differing access to safe drinking water in urban and rural areas: urban areas have better access to clean water (have financial resources) than rural ones
Urban areas may face significant water supply problems + impoverished urban areas may not have access to clean water + sanitation
Mismanagement of irrigation (e.g. salinisation): water supplies can run out & create human-drought conditions
Overuse of water → soil salinization → salt on top layer & reduces productivity
Eutrophication, increased turbidity, toxic water pollution, harm to ecosystems + groundwater
Inadequate sanitation: sewage systems + water management plants
Sanitation mismanagement: changes in supply/demand + aging infrastructure
Septic waste contamination → cholera, diarrhea, etc.
Impacts of water insecurity
Reduced crop yield, crop failure, livestock death → food shortages, malnutrition and famine
Illness caused by contaminated drinking water: polluted water can cause insecurity + illness
Exposure to bacteria in septic waste → cholera & diarrhea
Poverty: unable to grow food & stay healthy
“Poverty trap” = sick person is unable to work & struggles to afford healthcare
Strategies for managing water insecurity
Sustainable water extraction and improved supply:
piped supply: transports water
Improves access & reduces water insecurity, BUT can be expensive & leaks add to water stress
aquifers and artesian wells: body of rock/sediment that holds groundwater; well drilled into an aquifer where pressure pushes water out
Steady supply (none lost to evaporation) & cheap to extract, BUT can get depleted if over-pumped, saltwater intrusion in coastal areas, & difficult to de-contaminate
boreholes: narrow hole to locate water
Affordable, safe water that can be used for non-potable actions, BUT can lead to contamination + be over-extracted
gravity-fed schemes
Cheap & effective for a smaller sized crop area, BUT not applicable in flat terrain + needs management
reservoirs and dams
Cheap electricity, year-round water supply, BUT flooded land destroys land + displaces people, migration and spawning of fish may be disrupted
Increasing holding supply can protect water supply during stress
Reduction in water usage
Domestic: rainwater tanks, low flow shower heads, low flush toilets, overall awareness
Agricultural: improved irrigation techniques (e.g. drip irrigation/soil moisture), growing crops less dependent on high water supply
Industrial: reusing/recycling clean water, upgrading technology to more efficient solutions, routine maintenance (checking for leaky pipes)
Education on sustainable water use: gives people knowledge about their responsibility for their own water consumption
Poverty reduction: population will be healthier, agricultural development/cultivation, & produce manufactured goods (job opportunities)
International agreement and water-related aid
Water Convention of 1996: established 3 main pillars to promote cooperation b/t nations & ensure fair + secure water usage
Water aid: aims to ensure a safe water supply → reduce infant mortality + food insecurity
Rationing
Existing resources last longer, BUT doesn’t find an alternative & difficult to manage
Distillation of saltwater: heating saltwater until it evaporates
Improves access to clean water & cheap, BUT leaves behind waste (brine) and requires an energy sources