Photosynthesis
Photosynthetic reaction
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose. This process occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells where a green pigment (chlorophyll) absorbs the light energy needed for this reaction to occur.
Carbon dioxide + water → oxygen + glucose
CO2 + H2O → O2 + C6H12O6
Balanced : 6CO2 + 6H2O → 6O2 + C6H12O6
It is an endothermic reaction
Carbon dioxide - Taken in from the air via the stomata in the leaf
Water - Absorbed via the roots and transported via the xylem
Oxygen - Released back to the air via the stomata
Glucose - Used for respiration or stored as an insoluble starch
The glucose produced in photosynthesis may be:
Used in respiration
Converted into insoluble starch
Used to produce fat or oil for storage
Used to produce cellulose which strengthens the cell wall
Used to produce amino acids for protein synthesis
Rate of photosynthesis
Key factors for photosynthesis to occur: Carbon dioxide, light intensity, colour, amount of chlorophyll, temperature
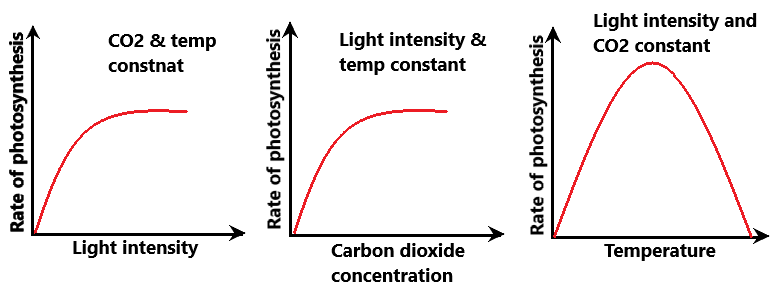
- Light intensity - as the amount of light intensity increases so does the rate of photosynthesis at this point the limiting factor is light. When the graph stops going up the light intensity is no longer having an effect on the rate of photosynthesis now the limiting factor is carbon dioxide or temperature
- Carbon dioxide - as the amount of carbon dioxide increases so does the rate of photosynthesis the limiting factor is carbon dioxide, when the curve stops the amount of carbon dioxide has no effect on the rate the limiting factors are now light intensity and temperature
- Temperature - Photosynthesis is controlled by enzymes, if the temperature is too low the rate of photosynthesis is slow. If the temperature is too hot the enzymes will denature. At the top of the curve it has reached the optimum temperature for photosynthesis
Required practical
We measure the rate of photosynthesis by using pondweed. It gives off oxygen when it photosynthesises so we can either collect the gas or count the bubbles released in a certain time
A LED lamp should be used because it reduces the effect of temperature on the experiment the LED produces less heat.
Independent variable: Light intensity
Dependant variable: Number of bubbles
Control variable: Same piece/ type of pondweed, amount of water, lightbulb, length of time you measure the bubbles for
Hazards/Risks:
Water near electricity so keep water as far away as possible
Wear goggles ( sodium hydrogen carbonate )
Use equipment to put pondweed into solution because sodium hydrogen carbonate is an irritant
Method:
- Fill a beaker with water and sodium hydrogen carbonate solution
- Place freshly cut pondweed into the beaker
- Set up LED lamp at a distance of 10cm to the beaker, turn on and leave to acclimate for a few minutes
- Start the stopwatch and count the number of bubbles released in your chosen time
- Repeat 2 more times and find the mean average
- Repeat steps 2-6 altering the distance of the lamp increasing in 10cm intervals
Uses of glucose
Glucose is used by a plant as a store of energy and some of it is used for respiration. The energy released from respiration can be used to make amino acids or build up fats and oils as a food store in a seed
Testing a leaf for starch:
- Fill a kettle with water
- Boil the water
- Use forceps to place the leaf in the beaker of boiling water. Leave it for two minutes
- Add ethanol to a boiling tube. The ethanol needs to fill about a third of the boiling tube
- Remove the leaf from the water using forceps and place in the boiling tube
- Put the boiling tube into the beaker of hot water
- Leave for about 20 mins (or until most of the green chlorophyll has been removed)
- Remove the leaf from the ethanol using forceps and dip into the beaker of water for 30 seconds
- Gently spread the leaf onto a white tile using the forceps
- Add a couple drops of iodine over the leaf using a pipette