Chapter 3: Evaluating Properties
key aspect of thermodynamics analysis is fixing states
the state principle for pure, simple compressible systems indicates that the intensive state is fixed by the values of any two independent, intensive properties
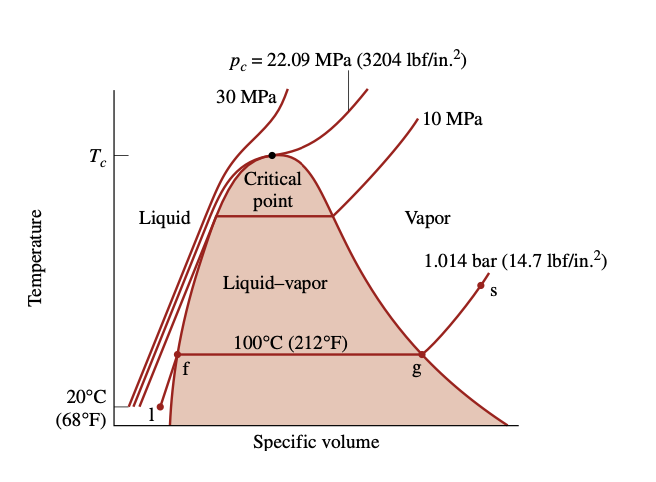
T-v diagram for water
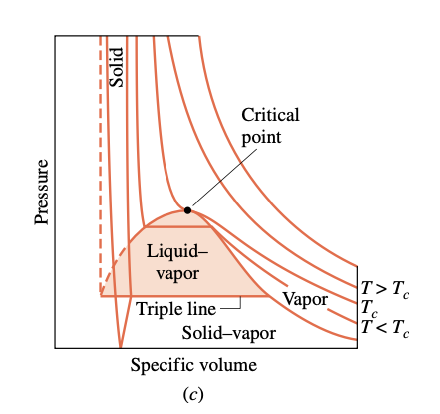
p-v diagram
Key Terms and Concepts
phase - refers to a quantity of matter that is homogeneous throughout in both chemical composition and physical structure (all solid, all liquid, or all vapor)
two-phase regions - two phases exist in equilibrium (liquid-vapor, solid-liquid, and solid-vapor)
triple line - three phases exist in equilibrium
saturation state - a state at which a phase change begins or ends
critical point - where the saturated liquid and saturated vapor lines meet
saturation temperature - the temperature at which a phase change takes place at a given pressure (the saturation pressure)
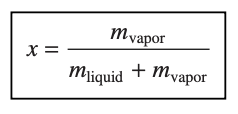
quality - the ratio of the mass of vapor present to the total mass of the mixture, ranging from 0 to 1 (for saturated liquid x = 0, for saturated vapor x = 1)
enthalpy - the sum of the internal energy and volume times pressure
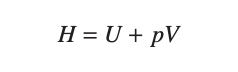
specific heat - defined for pure, simple compressible substances as partial derivatives of u(T,v) and h(T,p)
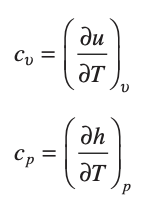
specific heat ratio = cp/cv
ideal gas model, universal gas constant, compressibility factor