Chemical Effects Of Electric Current 🧪⚡
Conductor: A material which allow current to flow through them
Good Conductor = High conductivity 👍
Bad conductor = Low Conductivity 👎
Insulators: Do not allow current to flow through ‘em
Electrical Conductivity: Ability of a material to conduct electricity
Tester: A patrial circuit made such that it can indicate the presence of a conductor by lighting up a bulb
Testing elements - Bulb, Magnetic compass, Buzzer
Electrical Conductivity of Liquids 💧
Liquids need Ions & solids need free electrons
A solution can be made more conductive by adding ions aka adding acids or salts
Pure water = insulator
Lekin, Tap water = conductor Bcoz it has impurities & salts dissolved in it
Sugar solution = insulator
Sugar just dissolves, doesn’t give ions
To make distilled water a conductor -
Acid
Base
Salt
Chemical Effects Of Electric Current ⚡
To identify chemical effect:
Change in colour of solution
Evolution of gases
Deposition of metals
(Collection of metals near electrodes [from where current comes/goes])
Effect of electric current on a potato 🥔
When 2 terminals of a cell r connected to the potato, the part where the positive terminal is connected turns green
Electroplating : Plating of a metal over another metal using electricity
Plate connected to positive terminal = Anode - Copper
Plate connected to negative terminal = Cathode - Alluminium
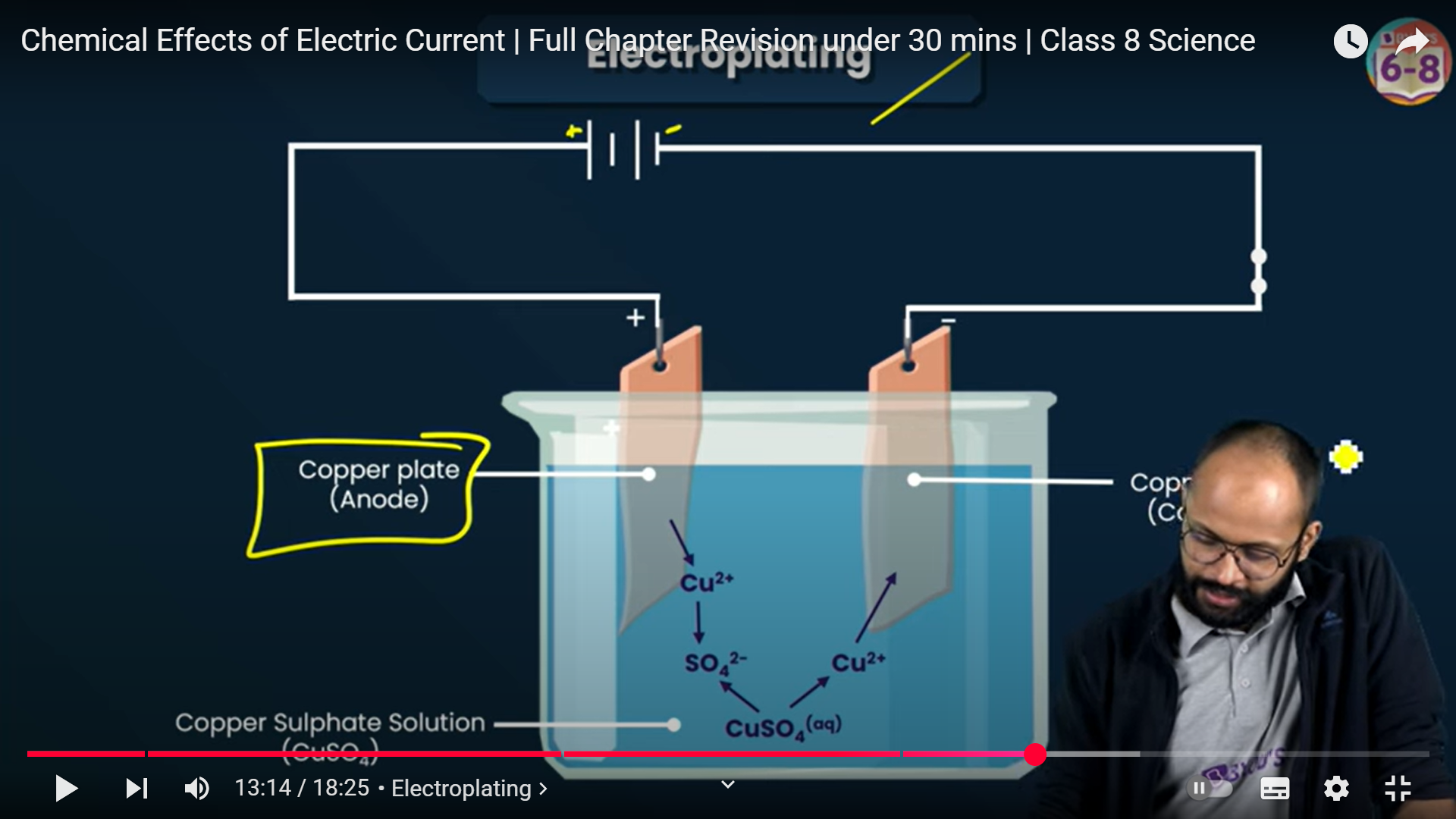
Current will flow from +ve to -ve
So, copper from Anode will start depositing on Cathode
In Electroplating, the ions of the Anode will start depositing on the Cathode
Electrolyte - the aqueous solution containing metal ions essential for the deposition of the metal plate
The type of electrolyte influences the efficiency, quality & characteristics of the electroplated layer
So, if the Anode is of copper, the electrolyte will have CuSo4 (copper sulphate) ions
If Zinc is to be plated, the electrolyte will have Zinc sulphate
Uses of electroplating
To prevent scratches
To prevent corrosion
To make things shiny [ Gold plating can happen by electroplating ]