Peridoic Table - Chem - Quarter 3
7.1: Development of the Periodic Table
Mendeleev and Meyer recognized predictable patterns in elements as atomic weight increased
Moseley developed atomic numbers
7.2: Effective Nuclear Charge
Properties of the atom depend on electron configuration and how the attraction between electrons and the nucleus
Electron- electron repulsion-- same charge
- Cancel some of the electron nucleus attraction
- More electrons= more repulsion= less attraction between nucleus and electron
- Effective nuclear charge- net attraction
- Less than the actual nuclear charge
- increases right to left across a periodic table
- Number of core electrons stays the same; the number of protons increases
- increases slightly as we go down a column
7.3: Sizes of Atoms and Ions
bonding atomic radius: shortest distance between the two nuclei during an atomic collision divided by 2
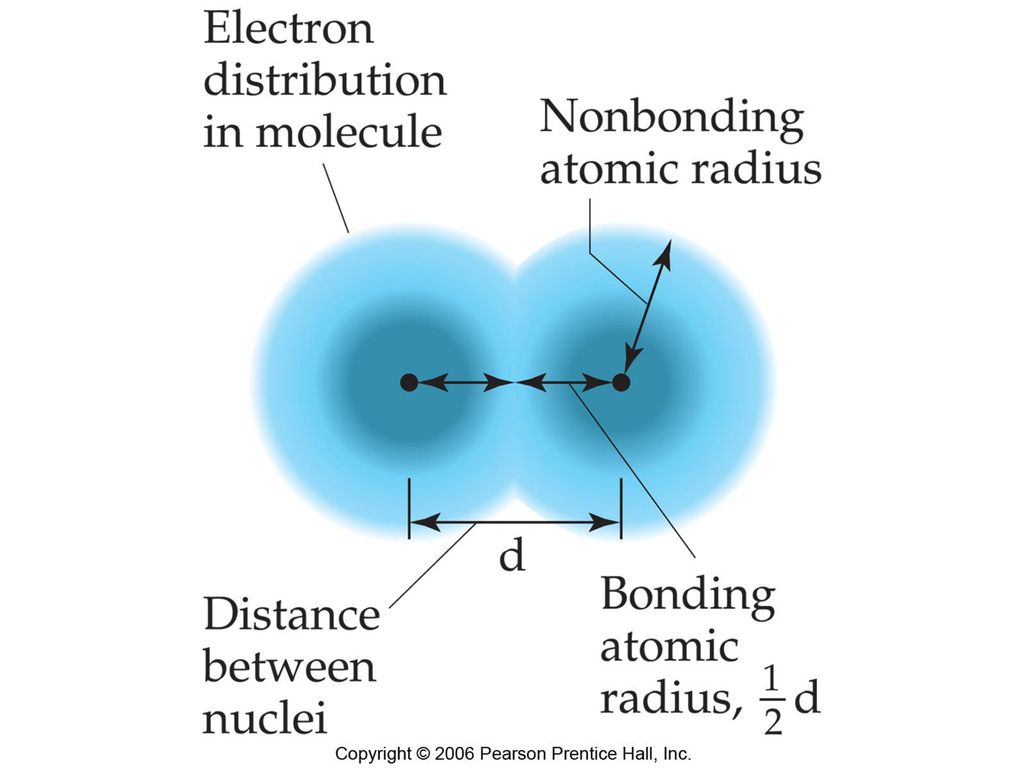
bonding radius< non bonding radius
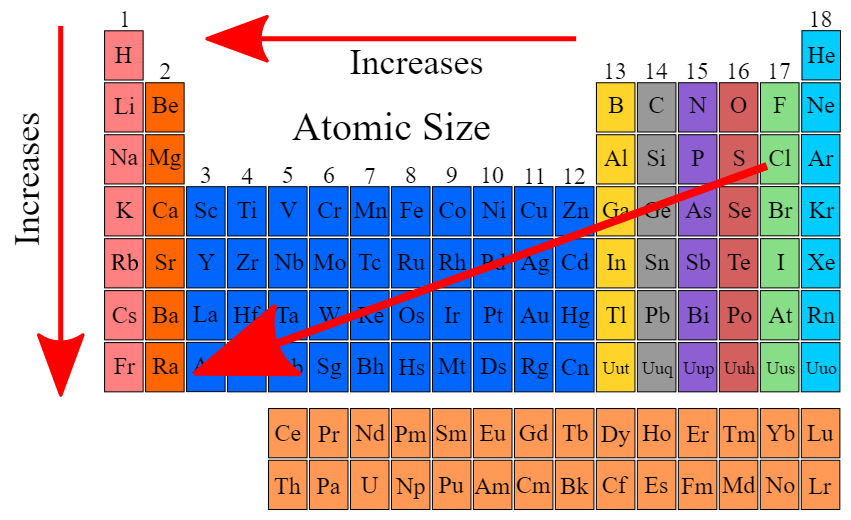
Atomic radius increases as you go down a column
- Increasing n (energy levels) therefore greater probability of electrons being farther from the nucleus
Atomic radius decreases left to right
- Effective nuclear charge decreases (less shielding ) and therefore increasing atomic radius
Cations are smaller than parent atoms
- electron - electron repulsion is reduced
Anions are greater than parent atoms
- electrons are added therefore electron- electron repulsion is increased, increasing radius
Isoelectronic series have the same number of electrons
When listed in increasing atomic number, nuclear charge increases ; electron number stays the same, but protons increase; stronger attraction of electrons to the nucleus; ionic radius decreases.
7.4: Ionization Energy
Ionization energy is the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from the ground state of an atom
- Greater ionization energy = more difficulty removing electrons
- first ionization energy is the smallest and increases with each successive ionization
- Sharp increase in the ionization energy occurs when inner shell is removed
- Always positive- energy must be absorbed to remove electrons
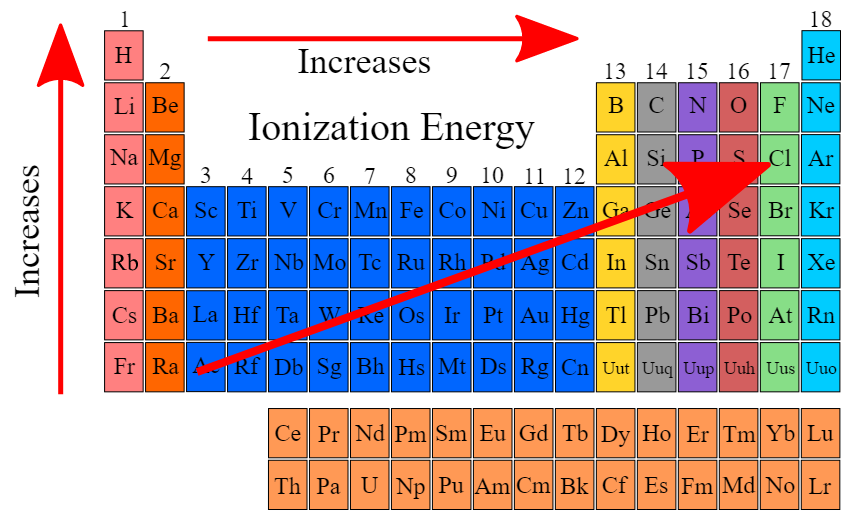
%%Ionization energy increases as we move across a period%%
- Increase in effective nuclear charge and decrease in atomic radius
%%Ionization energy decreases are we move down a period%%
atomic radius increases
7.5: Electron Affinity
Electron affinity is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom
- Energy is released--- answer is in negatives
- Greater attraction between atom and added electron the more negative the answer
- Energy change when atom gains and electron
7.6: Metals, Non-metals and Metalloids
Metals:
- Low ionization energy
- Loose electrons
Non Metals:
- Gain electrons
Metalloids: in between the two
7.7: Trends for Group 1A and Group 2A Metal
Group 1A-- alkali metals
- Low densities and melting points
- Increasing atomic radius, decreasing ionization energy
- Very reactive
Group 2A -- alkaline earth metals
- Denser, higher melting points
- Less reactive
7.8: Trends for Selected Nonmetals
Hydrogen is the most reactive
Oxygen is polar
7A is halogens
8A is noble gases-- not reactive
- High first ioniization energy