Prepositions - German II

About Prepositions:
prepositions are the words that say where or when something is, such as 'before, after, through, under, around, at' etc.
German prepositions affect a noun's companion-words, such as articles and adjectives
To determine the correct case for a noun's companion words, apply this two-step process:
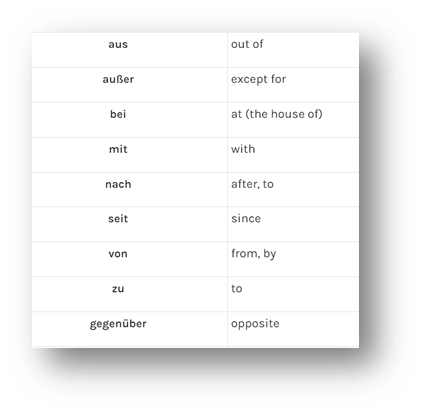
German prepositions are either on the Dative, Accusative, Genitive or 'Situational' list.
If the preposition is on the Dative, Accusative, or Genitive list, put the noun's companion words in the case the list indicates
If the preposition in NOT on the Dative, Accusative or Genitive list, chose the case for the noun's companion words according to the following rules:
for prepositions indication movement (change of location) use the Accusative case
for prepositions indication time or location, use the Dative case
for prepositions indication possession, use the Genitive case
level of fluency i need to achieve: 1. Er geht über die Wand.
2. Billy springt in den Baum. (acc – Motion)
3. Billy geht unter den Mann und in die Straße. (acc – Motion)
4. Billy springt auf das Sofa. (acc – Motion)
5. Billy ist auf dem Rasen. (dat – loc)
6. Billy ist mit der Katze. (dat. - Dat. List)
7. Das Sofa ist neben dem Billy. (dat. – Location)
8. Billy springt auf die Wand. (acc. – Motion)
9. Billy läuft die Straße entlang (acc. – Acc. List)
10. Billy kriecht unter den Briefträger (acc. – Acc. List)