chapter one notes
%%chapter 1.1%%
what is science?
the nature of science
- Uses evidence to construct testable explanations and predictions of natural phenomena
scientific methodology:
- scientific methodology is a general style of investigation
observing and asking questions
inferring and hypothesizing
- inference: a logical interpretation based on what scientists already know
- hypothesis: a tentative scientific explanation that can be tested further
designing controlled experiments
- testing hypotheses often involves designing experiment that measure factors that can or, or variables.
- a control group is necessary!
collecting data
- quantitative data are numbers. qualitative data are descriptive.
analyzing conclusions
- data analysis in science often relies on the use of statistics
- graphs!!!!!
Scientific Theory: scientific explanation of events in the natural world that has been tested and is highly reliable.
%%chapter 1.2%%
why is science? || science in context
the process of science
- science is not linear!
- testing ideas // experiments
- exploration and discovery
How do you decide what to test?
- Making observations
- Asking questions
- finding inspiration
- Exploring the literature
- Sharing data and ideas
- community analysis and feedback
- Feedback and peer review
- Discussion with colleagues
- Replication
- Publications
- Coming up with new questions and ideas
- Theory building
benefits and outcomes
- Develop tobacco
- Address societal issues
- Build knowledge
- Inform policy
- Satisfy curiosity
- Solve everyday problems
%%chapter 1.3%%
patterns of life
characteristics of living things:
- living things share basic characteristics
- they are made up of cells
- they reproduce
- they are based on a universal genetic code - (A,T,C,G!)
- they grow and develop
- they respond to the environment
- they maintain an internal balance
- HOMEOSTASIS
- they change over time (evolution)
cross cutting concepts in biology
- cause and effect: mechanism and explanation
- systems and system models
- stability and change
- patterns
- scale, proportion, and quantity
- energy and matter: flows, cycles, and conservation
fields of biology:
- GLOBAL ECOLOGY
- MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
- ZOOLOGY
- MICROBIOLOGY
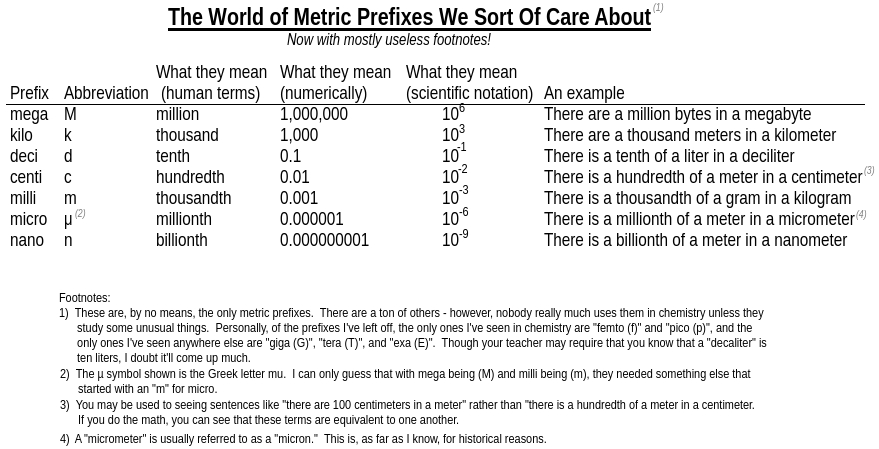
scientific measurement is metric!