1c. Production Possibility Frontiers
What is the PPF
- The Production Possibility Frontier represents the maximum combinations of goods or services that can be produced in a given period with available resources.
- It therefore represents the maximum output an economy can achieve when all resources (the factors of production) are used efficiently (the most that can be made using the available resources)
- It is also known as the production possibility curve
Capital goods vs Consumer goods
Capital goods are goods that are used to make consumer goods and services. These are more likely to support economic growth than consumer goods
Consumer goods and services are products which satisfy our needs and wants directly. These are more like to increase living standards than capital goods
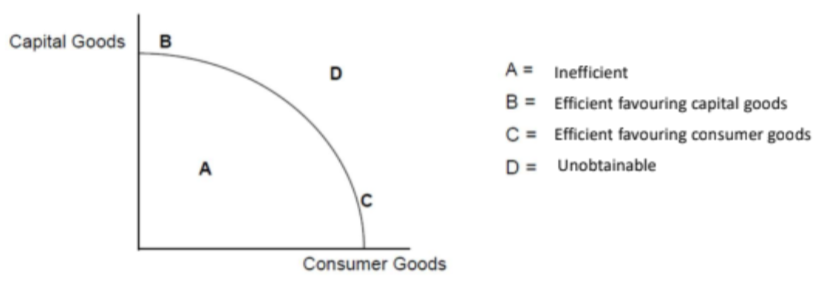
A) An inefficient allocation of resources means that the factors of production are not being used fully.
B) All factors of production are being used to their potential, however are being used more in the production of capital goods rather than consumer goods. This allocation of resources is more likely to increase future economic growth.
C) All factors of production are being used to their potential, however they are being used more in the production of consumer goods rather than capital goods. This allocation of resources is more likely to improve living standards
D)This represents a point beyond the available factors of production and is therefore unobtainable. It is possible to get there in the long run by increasing or improving the factors of production
Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative forgone. Decision making is key to economics and decisions we don’t make are as important as the ones we do.
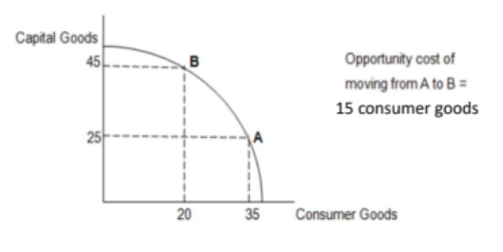
It is important to remember that the opportunity cost is what is given up and not what is gained. As this economy increases its production of capital goods by moving from A to B, it gains 20 capital goods, however the opportunity cost is 15 consumer goods.
Why is the PPF curved?
- Factors of production are not necessarily as good at doing one thing as they are another. For example, someone might be trained to produce capital goods and, if required, could not produce the same amount of consumer goods.
- This means that the opportunity cost will change along the curve and hence the PPF is not a straight line
- The further the resources move away from doing what they do best, the more the line curves and the higher the opportunity cost.
- PPFs that do have a straight line have constant returns to scale, meaning that the opportunity cost is equivalent to the gain when there is movement along the curve. It also suggests that factors of production are as exactly good at doing one thing, as they are the other.
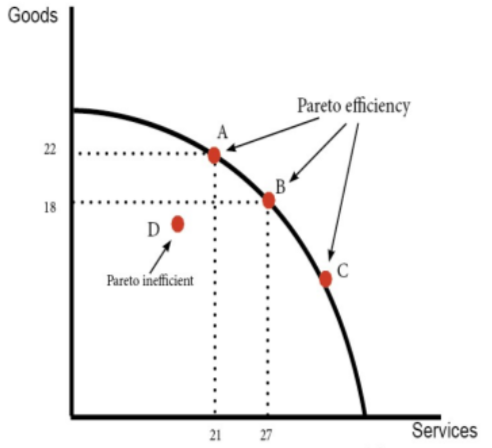
Pareto efficiency
Pareto efficiency is said to occur when it is impossible to make one party better off without making someone worse off.
A Pareto improvement is said to occur when at least one individual becomes better off without anyone becoming worse off.
Pareto efficiency will occur on a production possibility frontier. When an economy is operating on the curve, (e.g. at point A, B or C) it is not possible to increase output of goods without reducing output of services
However, at Point D (16 goods and 17 services) It is possible to increase either without leading to a decline in the output of the other. Thus to be at point D would be classed as Pareto inefficient, and this is generally considered to be bad for the economy.