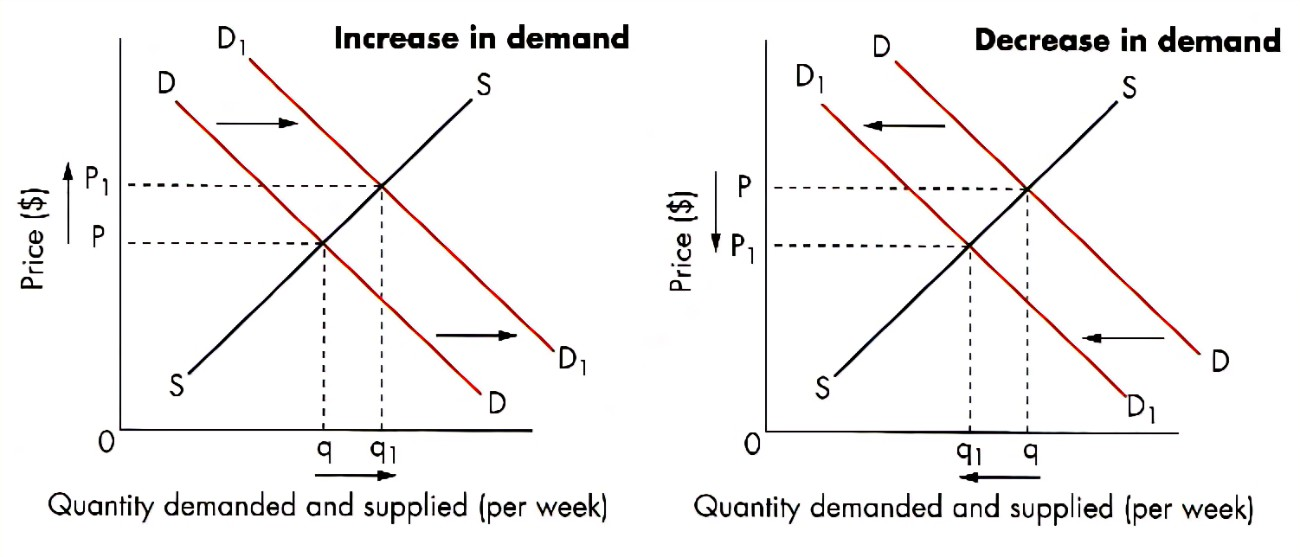
Demand and supply
demand:
the amount that buyers are willing and able to buy (effective demand)
the law of demand:
the law of demand says price and quantity demanded are inversely related (e.g., the cheaper something is, the more we will buy)
- if the price of a good gets higher, we might:
- buy less of it
- do without it
- buy something else (a substitute)
- if the prices of a good gets cheaper, we mightL
- buy more of it
- stop buying a substitute and buy this instead
factors that affect demand
fashion/taste
income
price of substitutes (good in competitive demand)
price of complements (good in joint demand)
population
advertising
price of products
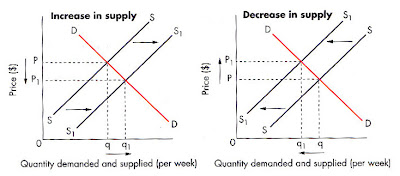
supply:
the amount of a product a firm is willing and able to supply a market at a given price
law of supply:
the price and quantity sold have a positive relationship (e.g., as the price increases, the firm looks to supply more)
factors that affect supply:
cost of raw materials
price selling at
taxes
cost of labour
new technology
weather
changes in the size of the industry