AQA GCSE Product Design: 1.5 - Mechanical Devices
Mechanical Devices:
Types of Movement:
- Linear -
- Forward
- Reciprocating -
- Up and down movement
- Rotary -
- In a circle
- Oscillating -
- Side to side
Levers:
- Mechanism -
- A device that changes an input motion into a different output motion.
- Lever -
- A mechanism that moves around a fixed point (pivot)
- The oldest type of mechanism
- Changes an input movement and force (effort) into an output movement and force (load)
- Load -
- The object that needs to be moved
- Effort -
- Force applied to move the load
- Fulcrum -
- The point at which the load is pivoted
- 3 classes of levers -
- Class 1: L-F-E
- Class 2: F-L-E
- Class 3: L-E-F
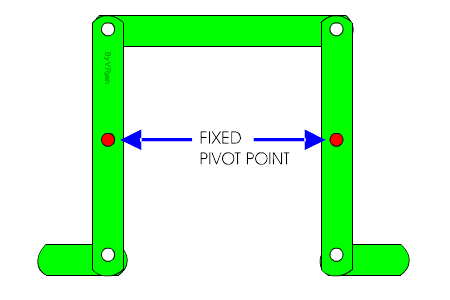
Linkages:
A linkage is used to transfer force and can change the direction and movement. They are an assembly of levers. 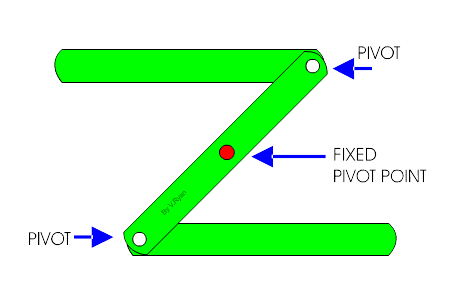
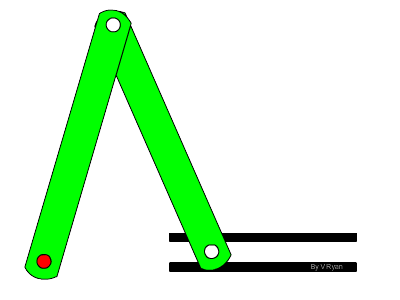
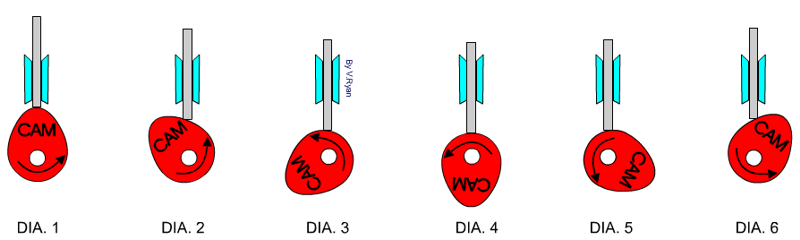
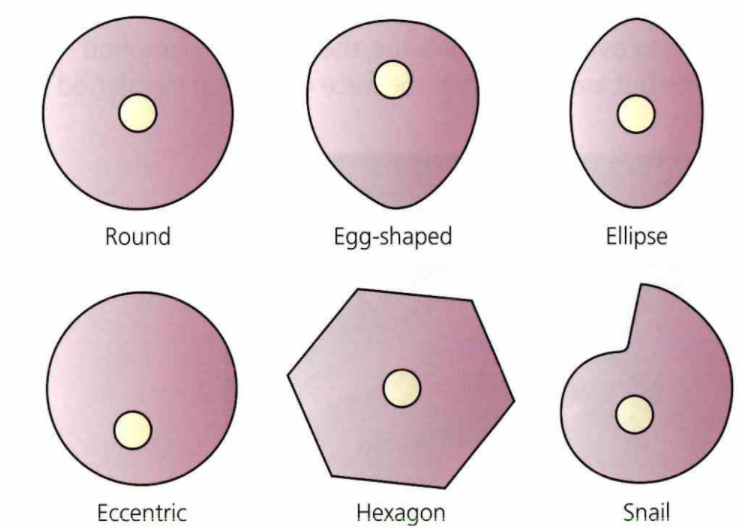
Cams:
A cam mechanism has 3 parts: a cam, a slide and a follower. A cam mechanism can either go up, go down or stay still.
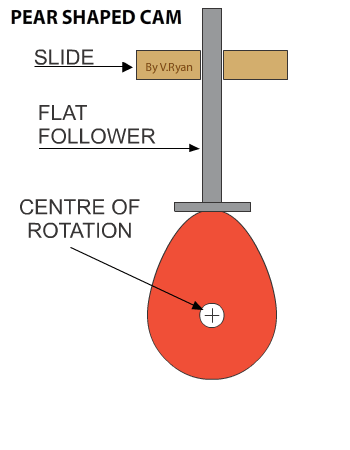
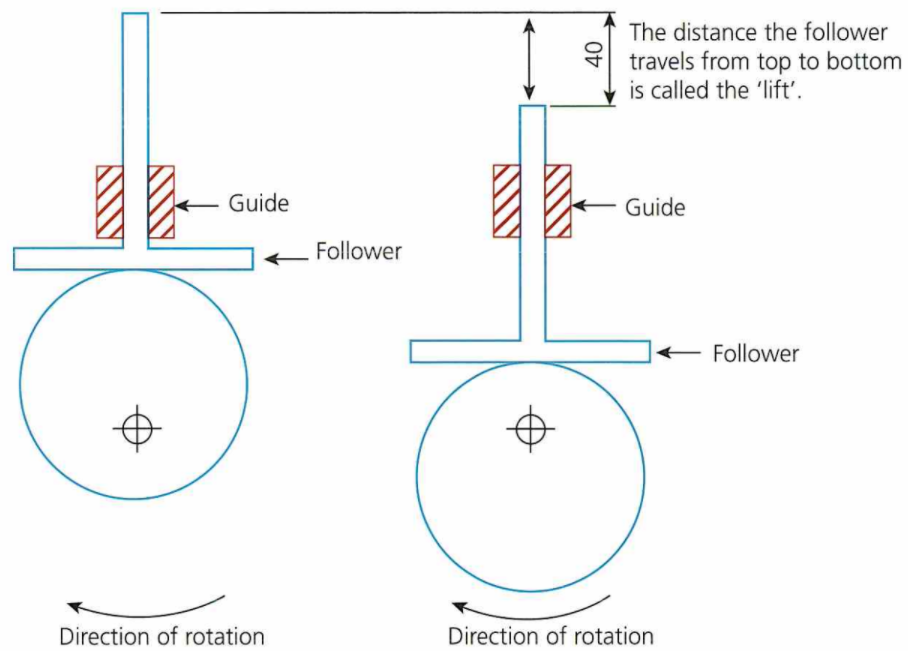
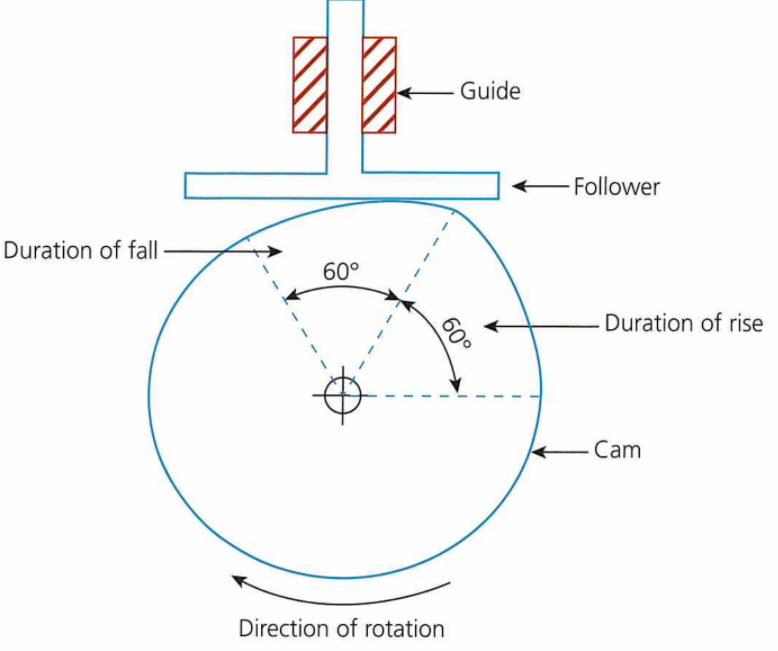
- Torque -
- The turning force that causes rotation
Gears:
Number of teeth on the driven gear
Velocity = -----------------------------------------------------------
Number of teeth on the driver gear
- Friction -
- Can cause thermal energy
- Usually a problem that needs to be resolved
- Breaking systems and pulley systems need high coefficients of friction
- Coefficiency
- How resistant a material is
Gear Trains:
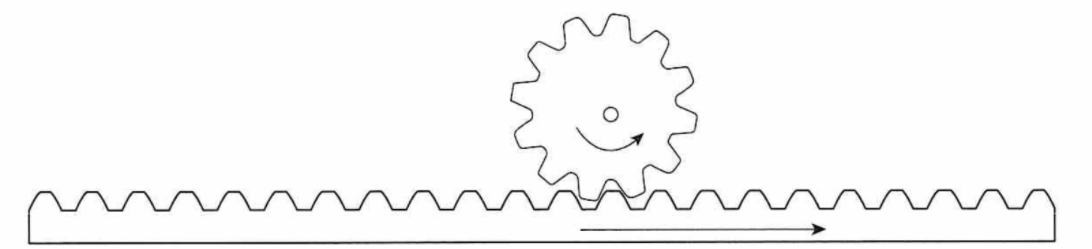
Rack and Pinion Mechanism:
Pinion = circular gear
Rack= long gear
Linear motion
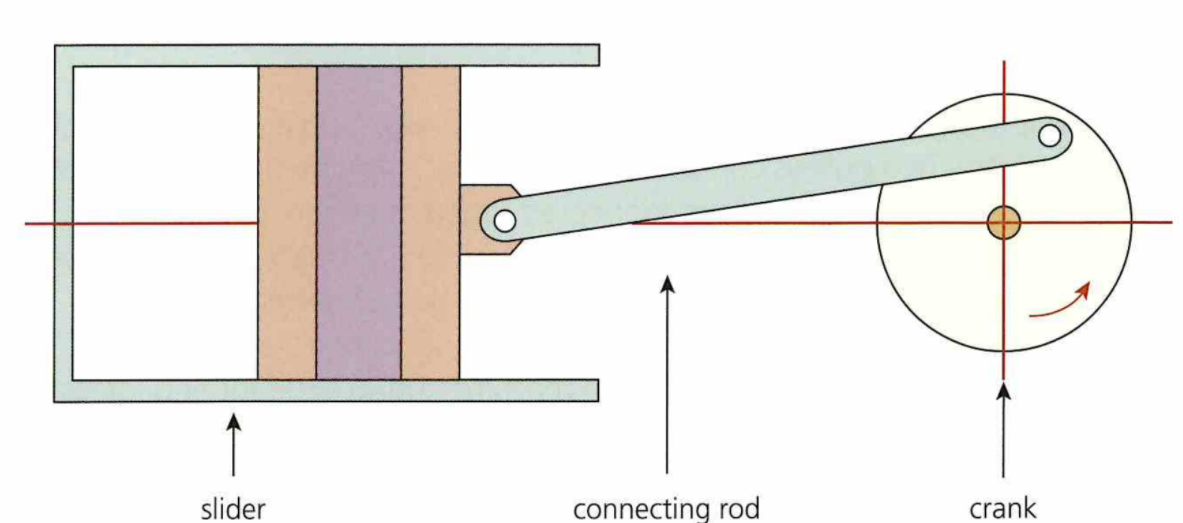
Crank and Slider Mechanism:
Rotary motion to linear motion
Used in pistons in car engines.
Chain and Sprocket Mechanism:
Rotary motion to rotary motion
Used in bike chains
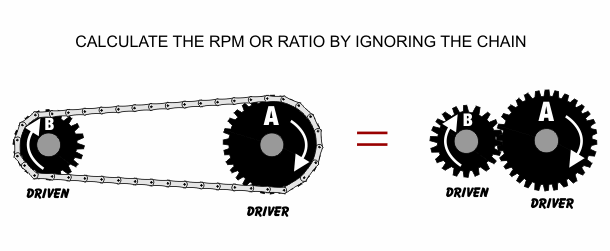
Number of teeth on the driven sprocket
Velocity = ------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of teeth on the driver sprocket
Pulleys and Belts:
- Pulley Systems -
- Rotary to rotary motion
Number of teeth on the driven pulley
Velocity = -------------------------------------------------------------
Number of teeth on the driver pulley