Chapter 2: Cells-The building block of life
Structure of a cell:
- Cell is a basic unit of life. It consists of a mass of living matter called ^^Protoplasm.^^
- %%Protoplasm%% is the ^^living essence of a cell^^. It includes the ^^cell surface membrane, the nucleus and the cytoplasm^^, where numerous biochemical reactions take place.
- Mainly has water; and some proportion of mineral salts and organic compounds.
- %%Cell Surface membrane%% ^^surrounds cytoplasm^^ externally.
- Also called plasma membrane.
- It is partially permeable and ^^allows some substance to pass through in and out of the cell.^^
- %%Nucleus%% is responsible for ^^cell division and and cell reproduction^^.
- Also needed for the ^^continued life of the cell, as well as for the repair of worn-out parts.^^
- Cell without a nucleus, for example, the red blood cells, have a short life span and are unable to reproduce.
- %%Cytoplasm%% is the part of protoplasm ^^surrounding the nucleus.^^
- Usually ^^forms the larger part of the cell^^ and is the ^^place where most of life processes occur.^^
- %%Mitochondria%% are small elongated organelles with folded inner membranes.
- Aerobic respiration takes place here.
- %%Cell Wall%% is ^^non-living and fully permeable.^^
- It ^^protects the cell from injury^^ and ^^gives the cell its shape^^.
- It is ^^made up of cellulose.^^
- %%Cell Vacuoles%% are ^^small fluid-filled spaces^^ bound by a membrane.
- In animal cells they ^^store water and food substances.^^
- %%Chloroplast%% are ^^sites where plants make their own food^^, combining together CO2 and water, using energy from sunlight to make sugar (Photosynthesis).
- %%Vacuoles%% are ^^large vesicles^^ that take up a large part of the interior of plant cells.
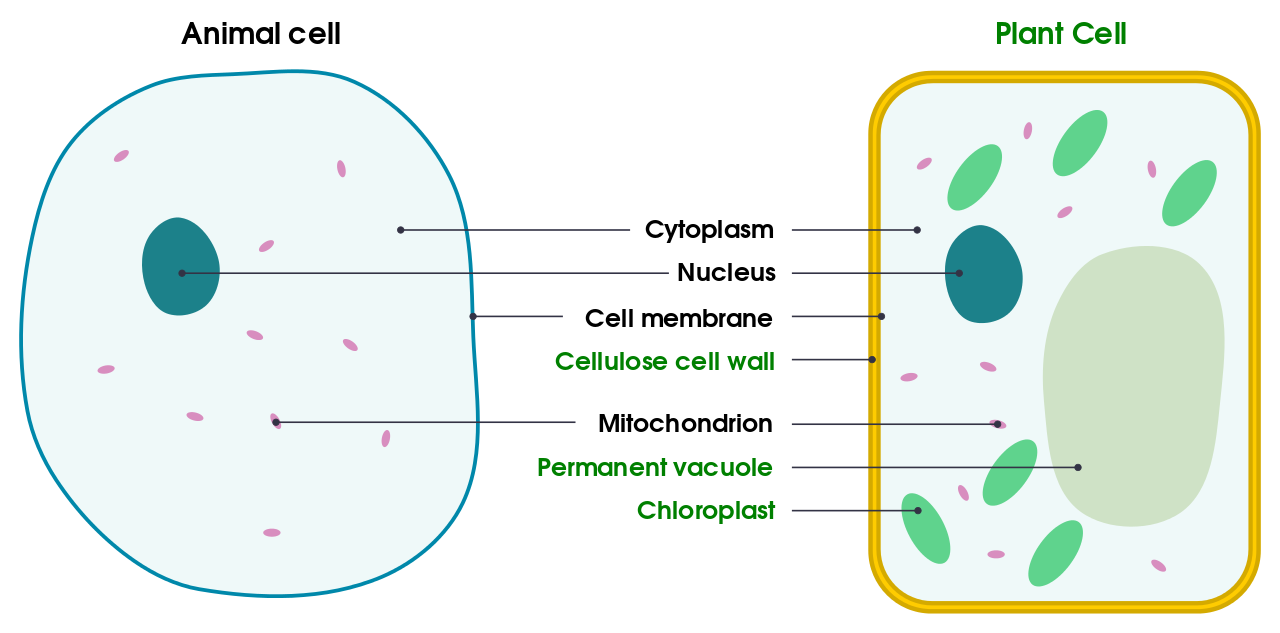
Difference in Plant and Animal Cell:
- Animal Cell:
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- Vacuole
- Plant Cell:
- Cell membrane
- Cell Wall
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Large/ Permanent Vacuole
- Nucleus
Cell Specification:
| CELL STRUCTURE: | ADAPTATION TO FUNCTION: |
|---|---|
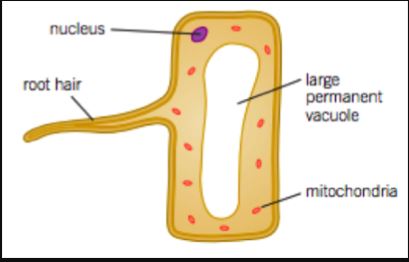 | ROOT HAIR CELL - Being ^^long and narrow, roots surface area to volume ratio increases^^; which helps in efficient absorption of water and mineral salts from the soil. |
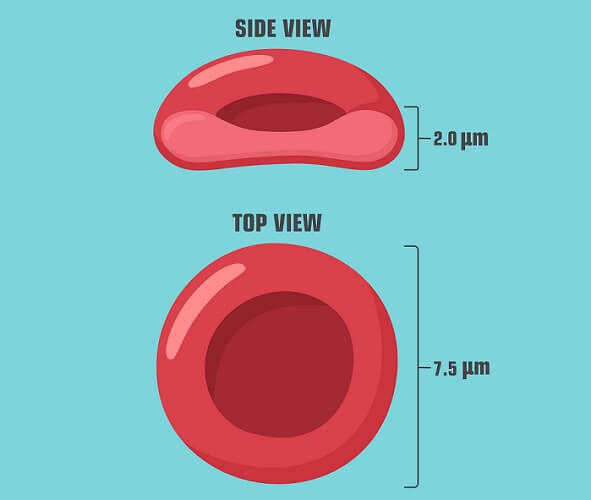 | The RED BLOOD CELL - Contains a ^^red pigment called haemoglobin^^, enabling the cell to transport oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body. Its ^^circular, biconcave shape increases surface area to volume ratio^^. As a result, oxygen can diffuse into and out of the whole cell at a faster rate. |
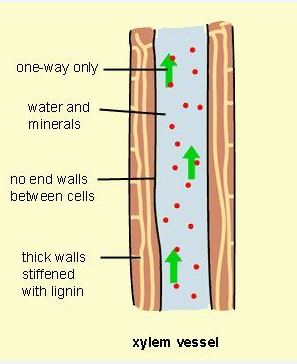 | XYLEM VESSELS - ^^Transports water and mineral salts^^ from roots to the stem and leaves. ^^Absence of cross walls and protoplasm enables water to move easily through the lumen^^ (space inside). It also ^^provides mechanical support to the plant.^^ |
Levels of Organization:
Tissue:
Is the ^^group of similar cells^^ working together to carry out a particular process of a movement.
Organ:
Is the ^^group of tissues^^ working together to carry out a specific function.
Organ System:
Is the ^^group related organs^^ working together to carry out functions in the body.