Unit 3 Communication
Networks
Networks is a collection of computer devices connected together
Advantages
Hardware, software and datas can be shared
Easier for internal communication
Centrally backup
Easier to monitor the network activity
Can access data from any computer
Disadvantages
Network manager may be needed
Security issue - files sent between computer may cause spread of virus
If the server is down, all workstations on the network are affected
High initial cost
3 Types of Networks
LAN (Local Area Network)
A network where all computer system are all connected relatively close to each other, for example in the same building or schools
WAN (Wide Area Network)
A network where all computer system are all located relatively far from each other, for example in different buildings all over the country or different countries.
PAN (Personal Area Network)
A network where all computer system are all connected close to the user, for example in the same house
Network Toplogies
Topology of a network is the way in which the connection of the network are arranged
Bus Network
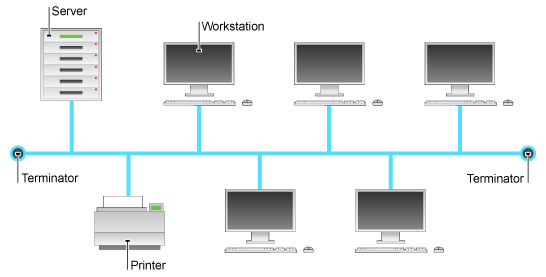
Advantages
Easy to setup and add more workstation
Quick to set up
Cost-effective
Disadvantages
Difficult to troubleshoot
Limited cable length and number of workstation
Problem with the cable, all workstation goes down
Low security
Data collisions
Ring Network
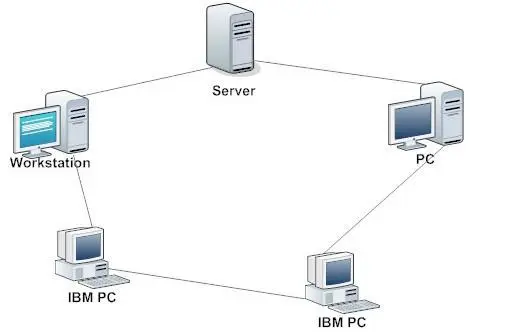
Advantages
Quick Data transfer
Simple data transmission
Little to no data collision
Can add additional workstation
Disadvantages
If one workstation fails, the whole network is broken
Problem with the main cable or connection, the whole network goes down
Difficult to troubleshoot
To add additional workstation need to shut down the entire network
Star Network
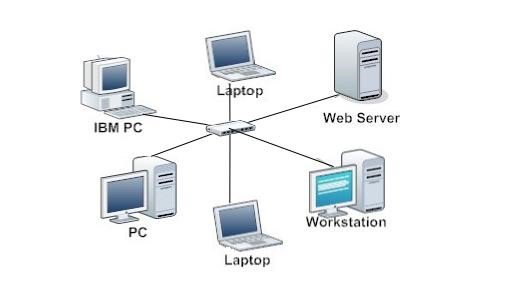
Advantages
Fast network speed
Easy to setup
Able to add more workstation without shutting down the entire network
Any non-centralised fail will have very little effect on the network
Minimal network collision
Better security
Disadvantages
Expensive to install
Switch/hub is needed
Switching
Data can travel around networks in two ways
circuit switching
packet switching
Circuit switching
Provides a dedicated link between two nodes.
No other data can be transmitted along the same route while the connection is open
A landline telephone system is an example of a circuit switched network
Advantages
Reliable
Once it is setup, it is fast and usually error free
Disadvantages
Take time to establish connection
If anywhere fails, the whole connection fails
Packet switching
Data is split up into small packets.
Each packet carries the address of its destination.
As the packet arrives at a switch or a router, the address is read and it is sent along the next free path.
Each packet contains information about how many packets there are in the message.
Each packet has information explaining where it fits into the message.
Packets may arrive at the destination in a different order to which they were sent, but can reassemble using the information contained in the packet once all packets have arrived.
Advantages
Do not need a dedicated line
Can take alternate route
Tends to error free
High efficiency as if one packet fails to send, you only need to resend that packet
Disadvantages
May arrive in wrong order
May cause a delay until all packets are sent
Large memory is needed to hold the packets
Mac Address (Media Access Control Address)
A hardware address
IP Address
Address of your network